Combining best of both worlds for cancer modeling
Tiny devices use samples taken directly from patients to combine in vivo and in vitro testing.
2021-01-21
(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON, January 21, 2021 -- Despite cancer being a leading cause of death worldwide, treatment options for many types of cancers remain limited. This is partly due to the in vitro tools used to model cancers, which cannot adequately predict the behavior of a cancer or its sensitivity to drugs.
Further, animal models, like mice, biologically differ from humans in ways that play a critical role in immunotherapy, and results from animal studies do not always translate well to human disease.
These shortcomings point to a clear need for a better, patient-specific model to improve the understanding of cancer cells and their impacts.
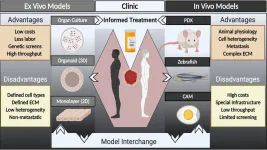
Researchers from the University of Wisconsin and the University of California, San Francisco suggest bioengineered microscale organotypic models (BMOMs) can address this need. They discuss the advantages and capabilities of this technique, as well as its challenges, in the journal APL Bioengineering, from AIP Publishing.
Due to their very small size, BMOMs require only a tiny patient-derived biopsy sample to monitor biological processes. This reduces any concern about the translatability of findings, since all the associated models are developed directly from human material. In addition, BMOMs can be integrated with microscopes and miniaturized sensors to watch the response of the cell culture to test treatments in high resolution and real time.
"BMOMs attempt to merge the best of in vivo and in vitro models," said David Beebe, one of the authors. "These models place human cells in a more realistic environment context, where they are more likely to respond to treatment in a way more reflective of the patient response.
"The 3D and multicellular attributes of BMOMs capture more of the myriad and complex cell-cell and cell-matrix interactions that regulate treatment response."
Though promising, these devices have several limitations. They are difficult to fabricate in large quantities, and they require specialized training to use. Beyond these hurdles, BMOMs are also restricted in their capacity to consider human behavioral responses and fall short in modeling the interactions that occur between multiple organs in complex diseases.
With additional research and clinical trials, the authors are optimistic about the applications of BMOMs. Their use with primary cells taken directly from patient tissue can help with patient-specific cancer treatments and drug testing.
INFORMATION:
The article "Towards improved in vitro models of human cancer" is authored by Jose M. Ayuso, Keon-Young Park, María Virumbrales-Muñoz, and David J. Beebe. The article appears in APL Bioengineering (DOI: 10.1063/5.0026857) and can be accessed at https://aip.scitation.org/doi/full/10.1063/5.0026857.
See also: Personalizing cancer care with improved tumor models at https://publishing.aip.org/publications/latest-content/personalizing-cancer-care-with-improved-tumor-models/
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
APL Bioengineering is an open access journal publishing significant discoveries specific to the understanding and advancement of physics and engineering of biological systems. See http://aip.scitation.org/journal/apb.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-21
Medicated drops may help close small macular holes over a two- to eight-week period, allowing some people to avoid surgery to fix the vision problem, a new study suggests.
The findings, based on a retrospective multicenter case series published Dec. 15, 2020, in Ophthalmology Retina, could lead to a better understanding of which patients may benefit from the treatment, as well as the timeline of the treatment's effectiveness.
"For certain patients, medicated drops may heal their macular hole by decreasing inflammation and increasing fluid absorption in the retina," said ophthalmologist and retinal surgeon Dimitra Skondra, MD, PhD, senior author of the study. Skondra is an associate professor of ophthalmology and visual ...
2021-01-21
WASHINGTON, January 21, 2021 -- Cancer is a major, worldwide challenge, and its impact is projected to escalate due to aging and growth of the population. Researchers recognize that new approaches to diagnose and treat deadly cancers, including identifying new drugs to treat cancer, will be essential to curbing the growing impact of the disease.
While decades of investment in research have resulted in substantial improvements in surviving cancer, a key challenge remains in identifying new drugs that improve outcomes for cancer patients, particularly for cancers when tumors have spread throughout the body.
In APL Bioengineering, by AIP Publishing, researchers suggest a major hurdle to identifying new drugs is the paucity of models -- organisms ...
2021-01-21
EUGENE, Ore. -- Jan. 21, 2021 -- Developing economies suffer from a paradox: they don't receive investment flows from developed economies because they lack stability and high-quality financial and lawmaking institutions, but they can't develop those institutions without foreign funds.
A study co-authored by Brandon Julio, a professor in the Department of Finance at the University of Oregon's Lundquist College of Business, found that bilateral investment treaties, commonly known as BITs, can help developing economies overcome this paradox, but only as long as those ...
2021-01-21
Researchers at Vanderbilt University Medical Center and colleagues have identified genetic factors that increase the risk for developing pneumonia and its severe, life-threatening consequences.
Their findings, published recently in the American Journal of Human Genetics, may aid efforts to identify patients with COVID-19 at greatest risk for pneumonia, and enable earlier interventions to prevent severe illness and death.
Despite the increasing availability of COVID-19 vaccines, it will take months to inoculate enough people to bring the pandemic under control, experts predict. In the meantime, thousands of Americans are hospitalized and die from COVID-19 each ...
2021-01-21
A new study from researchers at MIT uncovers the kinds of infrastructure improvements that would make the biggest difference in increasing the number of electric cars on the road, a key step toward reducing greenhouse gas emissions from transportation.
The researchers found that installing charging stations on residential streets, rather than just in central locations such as shopping malls, could have an outsized benefit. They also found that adding on high-speed charging stations along highways and making supplementary vehicles more easily available to people who need to travel beyond the single-charge range of their electric vehicles could greatly increase the vehicle electrification potential.
The findings are reported today in the journal Nature Energy, in a paper by MIT associate ...
2021-01-21
DAVIS, Calif., January 21, 2020 - A new peer-reviewed study reveals that the vast majority of U.S. infants may be suffering from a substantial deficiency in an important bacterium key to breast milk utilization and immune system development, as well as protection against gut pathogens linked to common newborn conditions such as colic and diaper rash.
According to the study published today in END ...
2021-01-21
Sex-specific chromosomes are a dangerous place to be, if you're a gene. Because these chromosomes -- Y chromosomes, in humans -- do not have a matching chromosome with which to exchange genetic information, they are prone to losing non-essential genes left and right in a process called genetic decay.
Now, a new study from research scientist Daniel Winston Bellott in the lab of Whitehead Institute Member David Page broadens our understanding of what makes a gene able to survive on a sex-specific chromosome by looking at one especially slithery branch of the evolutionary tree: snakes.
Comparing surviving genes on snake ...
2021-01-21
PHILADELPHIA -- (Jan. 21, 2021) -- Researchers at The Wistar Institute have discovered a new enzymatic function of the Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) protein EBNA1, a critical factor in EBV's ability to transform human cells and cause cancer. Published in Cell, this study provides new indications for inhibiting EBNA1 function, opening up fresh avenues for development of therapies to treat EBV-associated cancers.
EBV establishes life-long, latent infection in B lymphocytes, which can contribute to development of different cancer types, including Burkitt's lymphoma, nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) and Hodgkin's lymphoma.
The Epstein-Barr Nuclear Antigen 1 (EBNA1) serves as an attractive therapeutic ...
2021-01-21
Two out of five individuals delayed or missed medical care in the early phase of the pandemic--from March through mid-July 2020--according to a new survey from researchers at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health.
The survey of 1,337 U.S. adults found that 544, or 41 percent, delayed or missed medical care during the survey period. Among the 1,055 individuals who reported needing medical care, 29 percent (307 respondents), indicated fear of transmission of COVID-19 as the main reason. Seven percent (75 respondents) reported financial concerns as the main reason for delaying ...
2021-01-21
Researchers from the University Hospitals in Zurich and Basel, ETH Zurich, University of Zurich and the pharmaceutical company Roche have set out to improve cancer diagnostics by developing a platform of state-of-the-art molecular biology methods. The "Tumor Profiler" project aims to derive the comprehensive molecular profile of tumours in cancer patients, which has the potential to predict the efficacy of a host of new cancer medications. It will therefore make it possible to offer treating physicians personalised and improved therapy recommendations.
Three years ago, the researchers began a large-scale clinical study involving ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Combining best of both worlds for cancer modeling
Tiny devices use samples taken directly from patients to combine in vivo and in vitro testing.