(Press-News.org) LA JOLLA, CA--A big question on people's minds these days: how long does immunity to SARS-CoV-2 last following infection?
Now a research team from La Jolla Institute for Immunology (LJI), The University of Liverpool and the University of Southampton has uncovered an interesting clue. Their new study suggests that people with severe COVID-19 cases may be left with more of the protective "memory" T cells needed to fight reinfection.
"The data from this study suggest people with severe COVID-19 cases may have stronger long-term immunity," says study co-leader LJI Professor Pandurangan Vijayanand, M.D., Ph.D.
The research, published Jan. 21 in Science Immunology, is the first to describe the T cells that fight SARS-CoV-2 in "high resolution" detail.
"This study highlights the enormous variability in how human beings react to a viral challenge," adds co-leader Christian H Ottensmeier, M.D., Ph.D., FRCP, a professor at the University of Liverpool and adjunct professor at LJI.
Since early in the COVID-19 pandemic, scientists at LJI have investigated which antibodies and T cells are important for fighting SARS-CoV-2. As experts in genomics, Vijayanand and Ottensmeier have used sequencing tools to uncover which T cell subsets may control disease severity. In October, the team published the first detailed look at how CD4+ T cells respond to the virus.
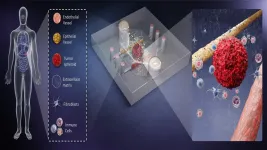
For the new study, the researchers used a technique called single-cell transcriptomics analysis to study the expression of individual genes of more than 80,000 CD8+ T cells isolated from both COVID-19 patients and non-exposed donors. CD8+ T cells are the cells responsible for destroying virus-infected host cells. "Memory" CD8+ T cells are also important for protecting the body from reinfection against many viruses.
The team studied CD8+ T cells from 39 COVID-19 patients and 10 subjects who had never been exposed to the virus (their blood samples were given before the pandemic). Of the COVID-19 patients, 17 patients had a milder case that did not require hospitalization, 13 had been hospitalized, and nine had needed additional ICU support.
To the researchers' surprise, they saw weaker CD8+ T cell responses in patients with milder COVID-19 cases. The researchers saw the strongest CD8+ T cell responses in the severely ill patients who required hospitalization or ICU support.
"There is an inverse link between how poorly T cells work and how bad the infection is," says Ottensmeier. "I think that was quite unexpected."
One could expect to see a stronger CD8+ T cell response in the mild cases, since these are the cases where the immune system was equipped to fight off a severe infection--but the study showed the opposite. In fact, CD8+ T cells in the milder cases showed the molecular signs of a phenomenon called T cell "exhaustion." In cases of T cell exhaustion, cells receive so much immune system stimulation during a viral attack that they are less effective in doing their jobs.
While more research is needed, Vijayanand and Ottensmeier think it is worth studying whether T cell exhaustion in the mild COVID-19 cases may hinder a person's ability to build long-term immunity.
"People who have severe disease are likely to end up with a good number of memory cells," says Vijayanand. "People with milder disease have memory cells, but they seem exhausted and dysfunctional--so they might not be effective for long enough."
The new study provides a valuable window into CD8+ T cell responses, but it is limited because it relies on the CD8+ T cells found in blood samples. As a next step, the researchers hope to shed light on how T cells in tissues hit hardest by SARS-CoV-2, such as the lungs, react to the virus. This step will be important because the memory T cells that provide long-term immunity need to live in the tissues.
"This study is very much a first step in understanding the spectrum of immune responses against infectious agents," says Ottensmeier. Going forward, the researchers hope to use single-cell sequencing techniques to look at CD8+ T cells in cancer patients with COVID-19 infection.
"This research highlights the power of these new tools to understand human immunology," says Vijayanand.
INFORMATION:
The new study, titled "Severely ill COVID-19 patients display impaired exhaustion features in SARS-CoV-2-reactive CD8+ T cells," was supported by the National Institutes of Health (grants U19AI142742, U19AI118626, R01HL114093, R35-GM128938, S10RR027366, S10OD025052, the William K. Bowes Jr Foundation, the Whittaker Foundation, the Wessex Clinical Research Network and the National Institute of Health Research UK.
Additional study authors include co-first authors Anthony Kusnadi, Ciro Ramírez-Suástegui, Vicente Fajardo and Serena J Chee, as well as Benjamin J Meckiff, Hayley Simon, Emanuela Pelosi, Grégory Seumois and Ferhat Ay.
DOI: 10.1126/sciimmunol.abe4782
About La Jolla Institute for Immunology
The La Jolla Institute for Immunology is dedicated to understanding the intricacies and power of the immune system so that we may apply that knowledge to promote human health and prevent a wide range of diseases. Since its founding in 1988 as an independent, nonprofit research organization, the Institute has made numerous advances leading toward its goal: life without disease.
Vaccinating people over 60 is the most effective way to mitigate mortality from COVID-19, a new age-based modeling study suggests. Although vaccination of younger adults is projected to avert the greatest incidence of disease, vaccinating older adults will most effectively reduce deaths, the analysis shows. Less than one year after SARS-CoV-2 was identified, deployment of multiple vaccines against the virus has been initiated in several countries. Although vaccine production is being rapidly scaled up, demand will exceed supply for the next several months. An urgent challenge is the optimization of vaccine allocation to maximize public health benefit. To quantify the impact of COVID-19 vaccine ...
Vaccinating older adults for COVID-19 first will save substantially more U.S. lives than prioritizing other age groups, and the slower the vaccine rollout and more widespread the virus, the more critical it is to bring them to the front of the line.
That's one key takeaway from a new University of Colorado Boulder paper, published today in the journal Science, which uses mathematical modeling to make projections about how different distribution strategies would play out in countries around the globe.
The research has already informed policy recommendations by the Centers for Disease ...
It is no secret that over the last few decades, humans have changed nature at an ever-increasing rate. A growing collection of research covers the many ways this is impacting our quality of life, from air quality to nutrition and income. To better understand how which areas are most at risk, scientists have combed through volumes of literature to present global trends in the relationship between human wellbeing and environmental degradation.
Their work, which included Fabrice DeClerck from the Alliance of Bioversity International and CIAT, was summarized in "Global trends in nature's contributions to people", which was recently published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
This systematic ...
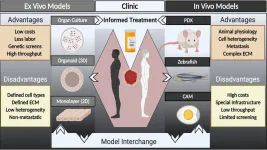
WASHINGTON, January 21, 2021 -- Despite cancer being a leading cause of death worldwide, treatment options for many types of cancers remain limited. This is partly due to the in vitro tools used to model cancers, which cannot adequately predict the behavior of a cancer or its sensitivity to drugs.
Further, animal models, like mice, biologically differ from humans in ways that play a critical role in immunotherapy, and results from animal studies do not always translate well to human disease.
These shortcomings point to a clear need for a better, patient-specific model to improve the understanding of cancer cells and their impacts.
Researchers from the University of Wisconsin and the University ...
Medicated drops may help close small macular holes over a two- to eight-week period, allowing some people to avoid surgery to fix the vision problem, a new study suggests.
The findings, based on a retrospective multicenter case series published Dec. 15, 2020, in Ophthalmology Retina, could lead to a better understanding of which patients may benefit from the treatment, as well as the timeline of the treatment's effectiveness.
"For certain patients, medicated drops may heal their macular hole by decreasing inflammation and increasing fluid absorption in the retina," said ophthalmologist and retinal surgeon Dimitra Skondra, MD, PhD, senior author of the study. Skondra is an associate professor of ophthalmology and visual ...
WASHINGTON, January 21, 2021 -- Cancer is a major, worldwide challenge, and its impact is projected to escalate due to aging and growth of the population. Researchers recognize that new approaches to diagnose and treat deadly cancers, including identifying new drugs to treat cancer, will be essential to curbing the growing impact of the disease.
While decades of investment in research have resulted in substantial improvements in surviving cancer, a key challenge remains in identifying new drugs that improve outcomes for cancer patients, particularly for cancers when tumors have spread throughout the body.
In APL Bioengineering, by AIP Publishing, researchers suggest a major hurdle to identifying new drugs is the paucity of models -- organisms ...
EUGENE, Ore. -- Jan. 21, 2021 -- Developing economies suffer from a paradox: they don't receive investment flows from developed economies because they lack stability and high-quality financial and lawmaking institutions, but they can't develop those institutions without foreign funds.
A study co-authored by Brandon Julio, a professor in the Department of Finance at the University of Oregon's Lundquist College of Business, found that bilateral investment treaties, commonly known as BITs, can help developing economies overcome this paradox, but only as long as those ...
Researchers at Vanderbilt University Medical Center and colleagues have identified genetic factors that increase the risk for developing pneumonia and its severe, life-threatening consequences.
Their findings, published recently in the American Journal of Human Genetics, may aid efforts to identify patients with COVID-19 at greatest risk for pneumonia, and enable earlier interventions to prevent severe illness and death.
Despite the increasing availability of COVID-19 vaccines, it will take months to inoculate enough people to bring the pandemic under control, experts predict. In the meantime, thousands of Americans are hospitalized and die from COVID-19 each ...
A new study from researchers at MIT uncovers the kinds of infrastructure improvements that would make the biggest difference in increasing the number of electric cars on the road, a key step toward reducing greenhouse gas emissions from transportation.
The researchers found that installing charging stations on residential streets, rather than just in central locations such as shopping malls, could have an outsized benefit. They also found that adding on high-speed charging stations along highways and making supplementary vehicles more easily available to people who need to travel beyond the single-charge range of their electric vehicles could greatly increase the vehicle electrification potential.
The findings are reported today in the journal Nature Energy, in a paper by MIT associate ...
DAVIS, Calif., January 21, 2020 - A new peer-reviewed study reveals that the vast majority of U.S. infants may be suffering from a substantial deficiency in an important bacterium key to breast milk utilization and immune system development, as well as protection against gut pathogens linked to common newborn conditions such as colic and diaper rash.
According to the study published today in END ...