Crystal structures in super slow motion
Physicists from Göttingen first to succeed in filming a phase transition with extremely high spatial and temporal resolution
2021-01-22
(Press-News.org) Laser beams can be used to change the properties of materials in an extremely precise way. This principle is already widely used in technologies such as rewritable DVDs. However, the underlying processes generally take place at such unimaginably fast speeds and at such a small scale that they have so far eluded direct observation. Researchers at the University of Göttingen and the Max Planck Institute (MPI) for Biophysical Chemistry in Göttingen have now managed to film, for the first time, the laser transformation of a crystal structure with nanometre resolution and in slow motion in an electron microscope. The results have been published in the journal Science.
The team, which includes Thomas Danz and Professor Claus Ropers, took advantage of an unusual property of a material made up of atomically thin layers of sulphur and tantalum atoms. At room temperature, its crystal structure is distorted into tiny wavelike structures - a "charge-density wave" is formed. At higher temperatures, a phase transition occurs in which the original microscopic waves suddenly disappear. The electrical conductivity also changes drastically, an interesting effect for nano-electronics.
In their experiments, the researchers induced this phase transition with short laser pulses and recorded a film of the charge-density wave reaction. "What we observe is the rapid formation and growth of tiny regions where the material was switched to the next phase," explains first author Thomas Danz from Göttingen University. "The Ultrafast Transmission Electron Microscope developed in Göttingen offers the highest time resolution for such imaging in the world today." The special feature of the experiment lies in a newly developed imaging technique, which is particularly sensitive to the specific changes observed in this phase transition. The Göttingen physicists use it to take images that are composed exclusively of electrons that have been scattered by the crystal's waviness.
Their cutting-edge approach allows the researchers to gain fundamental insights into light-induced structural changes. "We are already in a position to transfer our imaging technique to other crystal structures," says Professor Claus Ropers, leader of Nano-Optics and Ultrafast Dynamics at Göttingen University and Director at the MPI for Biophysical Chemistry. "In this way, we not only answer fundamental questions in solid-state physics, but also open up new perspectives for optically switchable materials in future, intelligent nano-electronics."
INFORMATION:
Original publication: Thomas Danz et al., Ultrafast nanoimaging of the order parameter in a structural phase transition, Science 2021, doi:10.1126/science.abd2774
Contact:
Thomas Danz
University of Göttingen
Faculty of Physics
Nano-Optics and Ultrafast Dynamics
Friedrich-Hund-Platz 1, 37077 Göttingen, Germany
Email: thomas.danz@uni-goettingen.de
Professor Claus Ropers
University of Göttingen
Faculty of Physics
Nano-Optics and Ultrafast Dynamics
and Max Planck Institute for Biophysical Chemistry - Ultrafast Dynamics
Friedrich-Hund-Platz 1, 37077 Göttingen, Germany
Tel: +49 (0) 551 39-24549
Email: claus.ropers@uni-goettingen.de
http://www.uni-goettingen.de/en/598878.html
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-22
Head and neck cancer is the sixth most common cancer worldwide, and while effective treatments exist, sadly, the cancer often returns.
Researchers at the University of Cincinnati have tested a new combination therapy in animal models to see if they could find a way to make an already effective treatment even better.
Since they're using a Food and Drug Administration-approved drug to do it, this could help humans sooner than later.
These findings are published in the journal END ...
2021-01-22
Washington, DC - January 22, 2021 - New research shows that non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) reduced both antibody and inflammatory responses to SARS-CoV-2 infection in mice. The study appears this week in the Journal of Virology, a publication of the American Society for Microbiology.
The research is important because "NSAIDs are arguably the most commonly used anti-inflammatory medications," said principal investigator Craig B. Wilen, Assistant Professor of Laboratory Medicine and Immunology, Yale University School of Medicine.
In addition to taking NSAIDs for chronic conditions such as arthritis, people take them "for shorter periods of time during infections, and [during] ...
2021-01-22
UPTON, NY - New results from an atmospheric study over the Eastern North Atlantic reveal that tiny aerosol particles that seed the formation of clouds can form out of next to nothingness over the open ocean. This "new particle formation" occurs when sunlight reacts with molecules of trace gases in the marine boundary layer, the atmosphere within about the first kilometer above Earth's surface. The findings, published in the journal Nature Communications, will improve how aerosols and clouds are represented in models that describe Earth's climate so scientists can understand how the particles--and the processes that control them--might ...
2021-01-22
Millions of students around the world could benefit if their educators adopted a more flexible and practical approach, say Swansea University experts.
After analysing the techniques current being used in higher education, the researchers are calling for a pragmatic and evidence-based approach instead.
Professor Phil Newton, director of learning and teaching at of Swansea University Medical School, said: "Higher education is how we train those who carry out important professional roles in our society. There are now more than 200 million students in HE worldwide and this number is likely to double again over the next decade.
"Given the size, impact, importance and cost of ...
2021-01-22
Researchers at the Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas (CONICET) in Argentina have found that, since the 1990s, up to 25% of reported bee species are no longer being reported in global records, despite a large increase in the number of records available. While this does not mean that these species are all extinct, it might indicate that these species have become rare enough that no one is observing them in nature. The findings appear January 22 in the journal One Earth.
"With citizen science and the ability to share data, records are going up exponentially, but the number of species reported in these records is going down," says first ...
2021-01-22
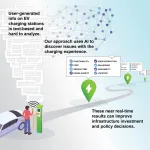
Although electric vehicles that reduce greenhouse gas emissions attract many drivers, the lack of confidence in charging services deters others. Building a reliable network of charging stations is difficult in part because it's challenging to aggregate data from independent station operators. But now, researchers reporting January 22 in the journal Patterns have developed an AI that can analyze user reviews of these stations, allowing it to accurately identify places where there are insufficient or out-of-service stations.
"We're spending billions ...
2021-01-22
On January 22 in Current Biology, a team of Harvard-led researchers presented the most complete genome yet assembled of one of the major Rafflesiaceae lineages, Sapria himalayana.
The species is found in Southeast Asia and its mottled red and white flower is about the size of a dinner plate. (It's more famous cousin, Rafflesia arnoldii, produces blossoms nearly three feet in diameter, the largest in the world.)
The genetic analysis revealed an astonishing degree of gene loss and surprising amounts of gene theft from its ancient and modern hosts. These findings bring unique perspectives into the number and kind of genes it takes to be an endoparasite (an organism that is completely dependent on its host for all nutrients), along ...
2021-01-22
What The Study Did: In this observational study, the spread of SARS-CoV-2 infection during a period of lockdown in southwest Germany was particularly low in children ages 1 to 10 years old. Overall, this large SARS-CoV-2 prevalence study in children is instructive for how ad hoc mass testing provides the basis for rational political decision-making in a pandemic setting.
Authors: Burkhard Tönshoff, M.D., of the University Children's Hospital in Heidelberg, Germany, and Klaus-Michael Debatin, M.D., of Ulm University Medical Center in Ulm, Germany, are the corresponding authors.
To ...
2021-01-22
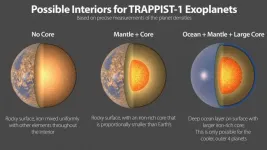
A new international study led by astrophysicist Eric Agol from the University of Washington has measured the densities of the seven planets of the exoplanetary system TRAPPIST-1 with extreme precision, the values obtained indicating very similar compositions for all the planets. This fact makes the system even more remarkable and helps to better understand the nature of these fascinating worlds. This study has just been published in the Planetary Science Journal.
The TRAPPIST-1 system is home to the largest number of planets similar in size to our Earth ever found outside our solar system. Discovered in 2016 by a research team led by Michaël Gillon, astrophysicist at the University of Liège, the system offers an insight into the immense ...
2021-01-22
ITHACA, NY - Biologists have long wondered how complex organisms contain a variety of dramatically different types of cells with specialized functions, even though all of those cells are genetically identical.
New research reveals how proteins, called "pioneer transcription factors," help turn on key genes that give cell types their unique properties and functions.
These pioneer factors, it turns out, help unspool tightly wound coils of DNA so that genetic blueprints in genes can be read and proteins that play roles in biological processes can be made.
The study in fruit flies, "Pioneer-like Factor GAF Cooperates with PBAP (SWI/SNF) and NURF (ISWI) to Regulate Transcription," was published Dec. 10 in the journal Genes & Development.
"We know pretty ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Crystal structures in super slow motion
Physicists from Göttingen first to succeed in filming a phase transition with extremely high spatial and temporal resolution