(Press-News.org) Coastal Blue Carbon (BC), which includes mangrove and saltmarsh tidal wetlands, of which was first coined a decade ago to describe the disproportionately large contribution of coastal vegetated ecosystems to global carbon sequestration. The role of BC in climate change mitigation and adaptation has now reached international prominence. Recent studies have reported BC's unique role in mitigating climate change, projected coastal wetlands area change, carbon stocks in response to historical sea level rise fluctuations, and the future roadmap relative to carbon sequestration studies. However, several questions remain unanswered:
Q1. What is the global extent and spatial distribution of BC systems?
Q2. What factors influence BC burial rates?
Q3. How does climate change impact carbon accumulation in mature BC ecosystems?
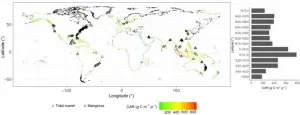
In a recent publication in National Science Review, Prof. Wang and Prof. Sanders lead an international group to go beyond recent soil C stock estimates, to reveal global tidal wetland C accumulation and predict changes under relative sea level rise, temperature and precipitation. They use data from literature study sites (n=563) and new observations (n=49) spanning wide latitudinal gradients and 20 countries (Figure 1). They found that global tidal wetlands accumulate ~54 Tg C yr-1, which is ~30% of the organic C buried on the ocean floor (Figure 1). Modelling based on current climatic drivers and under projected emissions scenarios revealed an increase of up to ~300 g C m-2 yr-1 by 2100 as an average global C accumulation rate (Figure 2). This rapid increase was found here to be driven by sea-level rise in tidal marshes, and higher temperature and precipitation in mangroves. Their results highlight the feedbacks between climate change and C sequestration in tidal wetlands (Figure 2). The findings in this research show that even though these global tidal wetlands only occupy END
Climate change increases coastal blue carbon sequestration
2021-01-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Photocatalytic reaction in the shadow
2021-01-25
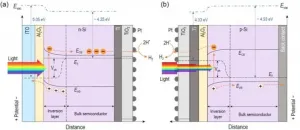
Solar-driven photoelectrochemical (PEC) water splitting is an attractive approach to convert solar energy into chemical energy. Among many photoelectrode materials, crystalline silicon (c-Si) has drawn considerable attention because of its earth abundance, narrow bandgap, and suitable band edge position for hydrogen evolution reaction (HER). However, c-Si suffers from low photovoltage generated from the solid-liquid junction.
Various strategies, such as the construction of p-n homojunctions, metal-insulator-semiconductor (MIS) junctions and p-n heterojunctions, have been adopted to obtain high photovoltage. The MIS junctions have been the focus of attention in PEC water splitting due to their simple fabrication and the potential to achieve higher efficiencies than p-n ...
The public health employment picture: Are graduates meeting the demands of the workforce?
2021-01-25
January 25, 2021 -- In a study to gain understanding of the future public health workforce, researchers at Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health and the Association of Schools and Programs of Public Health (ASPPH), conducted a large-scale analysis of the first employment outcomes of public health graduates and found that 78 percent were employed including 5 percent employed in fellowships and internships. Fifteen percent were continuing their studies; only 5 percent were not employed and job seeking. These indicators may ultimately expand public health's reach and lead to healthier communities overall. The study is the first national analysis of employment outcomes of public health graduates, and one of the only such analyses ...
Boosting the efficiency of carbon capture and conversion systems
2021-01-25
Systems for capturing and converting carbon dioxide from power plant emissions could be important tools for curbing climate change, but most are relatively inefficient and expensive. Now, researchers at MIT have developed a method that could significantly boost the performance of systems that use catalytic surfaces to enhance the rates of carbon-sequestering electrochemical reactions.
Such catalytic systems are an attractive option for carbon capture because they can produce useful, valuable products, such as transportation fuels or chemical feedstocks. This output can help to subsidize the process, offsetting the costs of reducing greenhouse ...
Borderline personality disorder: Don't ignore it
2021-01-25
For many years, clinicians have been hesitant to diagnose adolescents with Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD), believing it was a mental health "death sentence" for a patient because there was no clear treatment. Carla Sharp, professor of psychology and director of the Developmental Psychopathology Lab at the University of Houston, begs to differ.
And her new research, published in Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology backs her up.
"Like adult BPD, adolescent BPD appears to be not as intractable and treatment resistant as previously thought," reports Sharp. "That means we should not shy away from identifying BPD in adolescents and we shouldn't ...
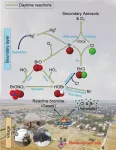
Reactive halogen from domestic coal burning aggravates winter air pollution
2021-01-25
Halogen atoms (Cl and Br) strongly influence the atmospheric chemical composition. Since 1970s, scientists discovered that these atoms were responsible for depletion of ozone in the stratosphere and ground-level ozone of the Arctic. In the past decade, there is emerging recognition that halogen atoms also play important roles in tropospheric chemistry and air quality. However, the knowledge of halogen atoms in continental regions is still incomplete.
"In the troposphere, halogen atoms can kick start hydrocarbon oxidation that makes ozone, modify the oxidative capacity, perturb ...
Survey: barriers, not demographics, affect willingness to pursue veterinary care
2021-01-25
A survey of dog owners from across the U.S. shows that when it comes to seeking veterinary care for dogs, barriers to access - including a lack of trust - have more effect on the decision-making process than differences in race, gender or socioeconomic status. The results could aid veterinarians in developing outreach strategies for underserved communities.
"I was interested in how different demographic groups viewed health care and how those views might affect relationships between veterinarians and their clients," says Rachel Park, a Ph.D. student at North Carolina State University and first author of a paper describing the work. "The existing literature wasn't national in scope and hadn't accounted for multiple identities held, such as one's socioeconomic status or ...
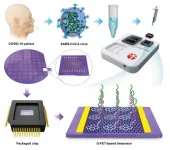
How fast could SARS-CoV-2 be detected?
2021-01-25
In the past 20 years, humans have suffered several serious epidemics from emerging viruses, such as SARS, swine flu, Ebola, MERS and (most recently) SARS-CoV-2. During each epidemic, an accurate, rapid, and accessible molecular diagnostic test is highly essential for the control and prevention of viral diseases. In particular, coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is spreading rapidly in most countries, resulting in a severe global pandemic, which has a profound impact on the world economy and people's normal life. Accurate and rapid diagnosis of COVID-19 has been the most crucial measure for controlling the ...
Study finds shorter radiation regimen safe, effective for men with advanced prostate cancer
2021-01-25
FINDINGS
A study led by researchers at the UCLA Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center found shortening a traditional 45-day course of radiation to a five-day course delivered in larger doses is safe and as effective as conventional radiation for men with high-risk forms of prostate cancer.
The findings show the five-day regimen of stereotactic body radiotherapy, a form of external beam radiation therapy that uses a higher dose of radiation, had a four-year cure rate of 82%. Severe side effects were also rare. Around 2% experienced urinary issues and less than 1% had bowel side effects.
BACKGROUND
Building on previous UCLA research that provided significant evidence that a shortened regimen of radiation could be ...
Opportunities to better detect, manage and treat patients with undiagnosed atrial fibrillation
2021-01-25
(Boston)--Atrial fibrillation (AF) is associated with a higher risk of complications including ischemic stroke, cognitive decline, heart failure, myocardial infarction and death. AF frequently is undetected until complications such as stroke or heart failure occur.
While the public and clinicians have an intense interest in detecting AF earlier, the most appropriate strategies to detect undiagnosed AF and medical prognosis and therapeutic implications of AF detected by screening are uncertain.
A new report led by Boston University School of Medicine (BUSM) researcher Emelia J. Benjamin, MD, ScM, builds upon a recently conducted National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute's virtual workshop that focused on identifying key research priorities related to AF screening.
Global experts reviewed ...
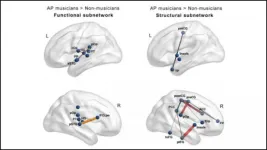
Musicians have more connected brains than non-musicians
2021-01-25
The brains of musicians have stronger structural and functional connections compared to those of non-musicians, regardless of innate pitch ability, according to new research from JNeurosci.
Years of musical training shape the brain in dramatic ways. A minority of musicians -- with Mozart and Michael Jackson in their ranks -- also possess absolute pitch, the ability to identify a tone without a reference. But, it remains unclear how this ability impacts the brain.
In the biggest sample to date, Leipold et al. compared the brains of professional musicians, some with absolute pitch and some without, to non-musicians. To the team's surprise, there were no strong differences ...