INFORMATION:
Mapping mutations that escape antibodies against COVID-19 suggests prior mapping incomplete
2021-01-25
(Press-News.org) A new approach to mapping viral mutations that "escape" leading clinical antibodies has revealed mutations in the SARS-CoV-2 virus that allow it to evade treatments, including a single amino-acid mutation that fully escapes Regeneron's antibody cocktail. These maps, say the authors, demonstrate that prior characterization of escape mutations was incomplete. They will also help to enable immediate interpretation of the effects of the mutations cataloged by viral genomic surveillance, say the authors. Several antibodies are in use or under development as therapies to treat COVID-19. As new SARS-CoV-2 variants emerge, it is important to predict whether they will remain susceptible to antibody treatment. Most leading anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies target the viral receptor-binding domain (RBD), which facilitates binding to the ACE2 receptor on host cells. Tyler Starr and colleagues recently developed a scanning method to map how mutations to the RBD affect its recognition by antibodies. Here, Starr and colleagues leveraged this approach to show how mutations to SARS-CoV-2's RBD affect binding by the antibodies in the REGN-COV2 cocktail and by Eli Lilly's antibody LY-CoV016. The authors focused on mutations to the SARS-CoV-2 RBD that do not strongly disrupt binding to the host receptor (ACE-2), to map how these mutations impact binding to the three anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies. The maps identified mutations that escape antibody binding, including, surprisingly, a single mutation that escapes both antibodies in the Regeneron antibody cocktail. To determine if the escape maps could inform analysis of viral evolution in infected humans, the authors examined deep sequencing data from a persistently infected patient who was treated with REGN-COV2 at day 145 after diagnosis with COVID-19. The analysis identified resistance mutations that arose in this patient. Three of the four escape mutations identified by Starr and team had not been identified in Regeneron's viral cell-culture selections, say the authors, illustrating an advantage of complete maps as used here. The complete maps also permitted the researchers to assess what escape mutations are already present among circulating SARS-CoV-2. After examining all human-derived SARS-CoV-2 sequences available as of 11 January 2021, they report a substantial number of RBD mutations that escaped one or more of the antibodies are in circulation.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Researchers engineer antibody that acts against multiple SARS-like viruses
2021-01-25
Researchers have engineered an antibody that neutralizes SARS-CoV-2 with a potency that "rivals" current lead SARS-CoV-2 clinical neutralizing antibodies, and that also broadly neutralizes a range of clade 1 sarbecoviruses. Their antibody, ADG-2, studied in mice, represents a "promising candidate" for the prevention and treatment of not only COVID-19, they say, but also of future respiratory diseases caused by SARS-related coronaviruses. Although two vaccines and two monoclonal antibody (mAb) therapies have been authorized for emergency use by the FDA, it is unknown whether these vaccines and treatments will provide broad protection against new emerging SARS-CoV-2 strains that originate in humans or animal reservoirs; this is partly ...
Nearly one in four families hesitant to take their child to ER during COVID-19 pandemic
2021-01-25
During the first wave of the COVID-19 pandemic, nearly one in four families responded that they would be unlikely to bring their child to the Emergency Department if they had an emergency condition, according to a survey from Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children's Hospital of Chicago published in the journal Academic Emergency Medicine. Greater hesitancy to seek emergency care was found in families living in under-resourced communities, those who rely on public insurance and in families who are Black, Latinx or Asian.
"We observed greater hesitancy to use the Emergency Department among more vulnerable demographic groups who historically showed high utilization of emergency care for their children," ...
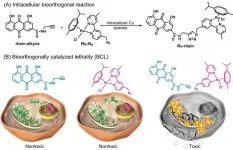
Bioorthogonally catalyzed lethality strategy generates targeting drugs within tumor
2021-01-25
Cancer is the second leading cause of death in the world. The number of deaths and incidences is increasing each year. The metal-based anticancer drugs were used clinically worldwide, but suffer from poor selectivity, serious side effects and drug resistance. Tumor-targeting drug development is the basis for precise cancer treatment.
Recently, Professor Hongke Liu of Nanjing Normal University, Professor Jing Zhao and Academician Zijian Guo of Nanjing University have made breakthrough achievements in anticancer drug development. They proposed a "bio-orthogonally catalyzed lethality" (BCL) strategy ...
3-D printed Biomesh minimizes hernia repair complications
2021-01-25
Hernias are one of the most common soft tissue injuries. Hernias form when intra-abdominal content, such as a loop of the intestine, squeezes through weak, defective or injured areas of the abdominal wall.
The condition may develop serious complications, therefore hernia repair may be recommended. Repair consists of surgically implanting a prosthetic mesh to support and reinforce the damaged abdominal wall and facilitate the healing process. However, currently used mesh implants are associated with potentially adverse postsurgical complications.
"Although hernia mesh implants are mechanically strong and support abdominal tissue, making the patient feel comfortable initially, ...
CHEOPS finds unique planetary system
2021-01-25
Musical notes that sound pleasant together can form a harmony. These notes are usually in a special relationship with each other: when expressed as frequencies, their ratios result in simple fractions, such as four-thirds or three-halves. Similarly, a planetary system can also form a kind of harmony when planets, whose orbital period ratios form simple fractions, regularly attract each other with their gravity. When one planet takes three days to orbit its star and its neighbor takes two days, for example. Using the CHEOPS space telescope, scientists, led by astrophysicist Adrien Leleu of the Center for Space and Habitability of the University of Bern, the University of Geneva and ...
What's in a name? A new class of superconductors
2021-01-25
HOUSTON - (Jan. 25, 2021) - A new theory that could explain how unconventional superconductivity arises in a diverse set of compounds might never have happened if physicists Qimiao Si and Emilian Nica had chosen a different name for their 2017 model of orbital-selective superconductivity.
In a study published this month in npj Quantum Materials, Si of Rice University and Nica of Arizona State University argue that unconventional superconductivity in some iron-based and heavy-fermion materials arises from a general phenomenon called "multiorbital singlet pairing."
In superconductors, electrons form pairs and flow without resistance. Physicists cannot fully explain how ...
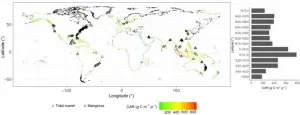
Climate change increases coastal blue carbon sequestration
2021-01-25
Coastal Blue Carbon (BC), which includes mangrove and saltmarsh tidal wetlands, of which was first coined a decade ago to describe the disproportionately large contribution of coastal vegetated ecosystems to global carbon sequestration. The role of BC in climate change mitigation and adaptation has now reached international prominence. Recent studies have reported BC's unique role in mitigating climate change, projected coastal wetlands area change, carbon stocks in response to historical sea level rise fluctuations, and the future roadmap relative to carbon sequestration studies. However, several questions remain unanswered:
Q1. What is the global extent and spatial distribution ...
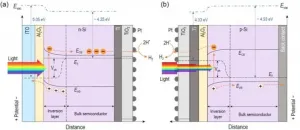
Photocatalytic reaction in the shadow
2021-01-25
Solar-driven photoelectrochemical (PEC) water splitting is an attractive approach to convert solar energy into chemical energy. Among many photoelectrode materials, crystalline silicon (c-Si) has drawn considerable attention because of its earth abundance, narrow bandgap, and suitable band edge position for hydrogen evolution reaction (HER). However, c-Si suffers from low photovoltage generated from the solid-liquid junction.
Various strategies, such as the construction of p-n homojunctions, metal-insulator-semiconductor (MIS) junctions and p-n heterojunctions, have been adopted to obtain high photovoltage. The MIS junctions have been the focus of attention in PEC water splitting due to their simple fabrication and the potential to achieve higher efficiencies than p-n ...
The public health employment picture: Are graduates meeting the demands of the workforce?
2021-01-25
January 25, 2021 -- In a study to gain understanding of the future public health workforce, researchers at Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health and the Association of Schools and Programs of Public Health (ASPPH), conducted a large-scale analysis of the first employment outcomes of public health graduates and found that 78 percent were employed including 5 percent employed in fellowships and internships. Fifteen percent were continuing their studies; only 5 percent were not employed and job seeking. These indicators may ultimately expand public health's reach and lead to healthier communities overall. The study is the first national analysis of employment outcomes of public health graduates, and one of the only such analyses ...
Boosting the efficiency of carbon capture and conversion systems
2021-01-25
Systems for capturing and converting carbon dioxide from power plant emissions could be important tools for curbing climate change, but most are relatively inefficient and expensive. Now, researchers at MIT have developed a method that could significantly boost the performance of systems that use catalytic surfaces to enhance the rates of carbon-sequestering electrochemical reactions.
Such catalytic systems are an attractive option for carbon capture because they can produce useful, valuable products, such as transportation fuels or chemical feedstocks. This output can help to subsidize the process, offsetting the costs of reducing greenhouse ...