Newly discovered subset of brain cells fight inflammation with instructions from the gut
Findings on a novel anti-inflammatory pathway may guide researchers toward innovative multiple sclerosis or brain tumor treatments
2021-01-25
(Press-News.org) Astrocytes are the most abundant type of cells within the central nervous system (CNS), but they remain poorly characterized. Researchers have long assumed that astrocytes' primary function is to provide nutrients and support for the brain's more closely scrutinized nerve cells; over the years, however, increasing evidence has shown that astrocytes can also actively promote neurodegeneration, inflammation, and neurological diseases. Now, a team led by researchers from Brigham and Women's Hospital, has shown that a specific astrocyte sub-population can do the opposite, instead serving a protective, anti-inflammatory function within the brain based on signals regulated by the bacteria that reside in the gut. Findings on the new anti-inflammation pathway are published in Nature.
"Over the years, many labs, including mine, have identified important roles for astrocytes in promoting neurological diseases," said corresponding author Francisco Quintana, PhD, of the Ann Romney Center for Neurologic Diseases at the Brigham. "This is the first case in which we're showing that at least a subset of these cells (astrocytes) can prevent inflammation. The reason we haven't seen this before was because we were studying these cells as if they were uniform, or one single cell type. But now we have the resolution to see the differences between these cells."
The researchers used refined gene- and protein-analysis tools to identify the novel astrocyte subset. The astrocyte population resides close to the meninges (the membrane enclosing the brain) and expresses a protein called LAMP1, along with a protein called TRAIL, which can induce the death of other cells. These features help the LAMP1+TRAIL+ astrocytes limit CNS inflammation by inducing cell death in T-cells that promote inflammation.
To determine what mechanism controls LAMP1+TRAIL+ astrocytes in the brain, the researchers performed a series of tests using the gene-editing tool CRISPR-Cas9. They found that a particular signaling molecule, called interferon-gamma, regulates TRAIL expression. Moreover, they found that the gut microbiome induces the expression of interferon-gamma in cells that circulate through the body and ultimately reach the meninges, where they can promote astrocyte anti-inflammatory activities.
Understanding the mechanisms driving the anti-inflammatory functions of LAMP1+TRAIL+ astrocytes could enable researchers to develop therapeutic approaches to combat neurological diseases, like multiple sclerosis. For example, they are exploring probiotic candidates that can be used to regulate the astrocytes' anti-inflammatory activity. Additionally, the research team's more recent data indicates that certain brain tumors exploit this pathway to evade the body's immune response. The investigators are therefore developing cancer immunotherapies to retaliate against the tumors' attacks.
"Finding microbiome-controlled anti-inflammatory subsets of astrocytes is an important advance in our understanding of CNS inflammation and its regulation," Quintana said. "This is a very novel mechanism by which the gut controls inflammation in the brain. It guides new therapies for neurological diseases, and we believe that this mechanism could contribute to the pathogenesis of brain tumors."
Quintana's lab identified the only other subset of astrocyte known to be regulated by the gut microbiome in 2016, but the investigators believe that there are likely others. "It's becoming clear that the gut flora are important in many diseases," he said. "We're lucky that we've been leading the charge to identify different subsets of astrocytes and the mechanisms that control them. We have a list of other populations of astrocytes, and we're working to see how the gut flora may control them."
INFORMATION:
This work was supported the National Institutes of Health (NS102807, ES02530, ES029136, AI126880, AI149699, DP2AT009499, 1K99NS114111, F32NS101790, and R01AI130019), National MS Society (RG4111A1 and JF2161-A-5), the International Progressive MS Alliance (PA-1604-08459), a Chan-Zuckerberg Initiative Ben Barres Early Career award, the Burroughs Wellcome fund, the Canada Institute of Health Research, Canadian Foundation for Innovation, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute (T32CA207201), Program in Interdisciplinary Neuroscience at BWH, and the Women's Brain Initiative at BWH, an Alfonso Martín Escudero Foundation postdoctoral fellowship, the European Molecular Biology Organization (ALTF 610-2017), the FAPESP BEPE (#2019/13731-0).
Paper cited: Sanmarco, LM, et al. "Gut-licensed IFN-?+ NK cells drive LAMP1+TRAIL+ anti-inflammatory astrocytes" Nature DOI: 10.1038/s41586-020-03116-4
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-25
-Data demonstrate ADG2 binds to all known variants of SARS-CoV-2 and is not impacted by known circulating resistance mutations-
-Company expects to begin clinical studies for a half-life extended version of ADG2 for the treatment and prevention of COVID-19 in early 2021-
Waltham, MA - January 25, 2021- Adagio Therapeutics, Inc., a biotechnology company developing best-in-class antibodies to broadly neutralize coronaviruses, today published in vitro and in vivo data in Science on its lead antibody candidate, ADG2, which demonstrated similar or higher potency against SARS-CoV-2 compared to other monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) in clinical development and strong binding to all known ...
2021-01-25
Working in preclinical models, researchers report that plitidepsin, a drug with limited clinical approval for the treatment of multiple myeloma, is more potent against SARS-CoV-2 than remdesivir, an antiviral that received FDA emergency use authorization for the treatment of COVID-19 in 2020. The results suggest plitidepsin should be further evaluated as a COVID-19 therapy, the authors say; because it targets a host protein rather than a viral protein, if treatment proves successful in humans, the SARS-CoV-2 virus won't be easily able to gain resistance ...
2021-01-25
A new approach to mapping viral mutations that "escape" leading clinical antibodies has revealed mutations in the SARS-CoV-2 virus that allow it to evade treatments, including a single amino-acid mutation that fully escapes Regeneron's antibody cocktail. These maps, say the authors, demonstrate that prior characterization of escape mutations was incomplete. They will also help to enable immediate interpretation of the effects of the mutations cataloged by viral genomic surveillance, say the authors. Several antibodies are in use or under development as therapies to treat COVID-19. As new SARS-CoV-2 variants emerge, it ...
2021-01-25
Researchers have engineered an antibody that neutralizes SARS-CoV-2 with a potency that "rivals" current lead SARS-CoV-2 clinical neutralizing antibodies, and that also broadly neutralizes a range of clade 1 sarbecoviruses. Their antibody, ADG-2, studied in mice, represents a "promising candidate" for the prevention and treatment of not only COVID-19, they say, but also of future respiratory diseases caused by SARS-related coronaviruses. Although two vaccines and two monoclonal antibody (mAb) therapies have been authorized for emergency use by the FDA, it is unknown whether these vaccines and treatments will provide broad protection against new emerging SARS-CoV-2 strains that originate in humans or animal reservoirs; this is partly ...
2021-01-25
During the first wave of the COVID-19 pandemic, nearly one in four families responded that they would be unlikely to bring their child to the Emergency Department if they had an emergency condition, according to a survey from Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children's Hospital of Chicago published in the journal Academic Emergency Medicine. Greater hesitancy to seek emergency care was found in families living in under-resourced communities, those who rely on public insurance and in families who are Black, Latinx or Asian.
"We observed greater hesitancy to use the Emergency Department among more vulnerable demographic groups who historically showed high utilization of emergency care for their children," ...
2021-01-25
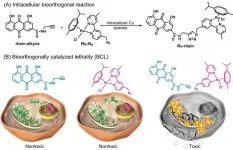
Cancer is the second leading cause of death in the world. The number of deaths and incidences is increasing each year. The metal-based anticancer drugs were used clinically worldwide, but suffer from poor selectivity, serious side effects and drug resistance. Tumor-targeting drug development is the basis for precise cancer treatment.
Recently, Professor Hongke Liu of Nanjing Normal University, Professor Jing Zhao and Academician Zijian Guo of Nanjing University have made breakthrough achievements in anticancer drug development. They proposed a "bio-orthogonally catalyzed lethality" (BCL) strategy ...
2021-01-25
Hernias are one of the most common soft tissue injuries. Hernias form when intra-abdominal content, such as a loop of the intestine, squeezes through weak, defective or injured areas of the abdominal wall.
The condition may develop serious complications, therefore hernia repair may be recommended. Repair consists of surgically implanting a prosthetic mesh to support and reinforce the damaged abdominal wall and facilitate the healing process. However, currently used mesh implants are associated with potentially adverse postsurgical complications.
"Although hernia mesh implants are mechanically strong and support abdominal tissue, making the patient feel comfortable initially, ...
2021-01-25
Musical notes that sound pleasant together can form a harmony. These notes are usually in a special relationship with each other: when expressed as frequencies, their ratios result in simple fractions, such as four-thirds or three-halves. Similarly, a planetary system can also form a kind of harmony when planets, whose orbital period ratios form simple fractions, regularly attract each other with their gravity. When one planet takes three days to orbit its star and its neighbor takes two days, for example. Using the CHEOPS space telescope, scientists, led by astrophysicist Adrien Leleu of the Center for Space and Habitability of the University of Bern, the University of Geneva and ...
2021-01-25
HOUSTON - (Jan. 25, 2021) - A new theory that could explain how unconventional superconductivity arises in a diverse set of compounds might never have happened if physicists Qimiao Si and Emilian Nica had chosen a different name for their 2017 model of orbital-selective superconductivity.
In a study published this month in npj Quantum Materials, Si of Rice University and Nica of Arizona State University argue that unconventional superconductivity in some iron-based and heavy-fermion materials arises from a general phenomenon called "multiorbital singlet pairing."
In superconductors, electrons form pairs and flow without resistance. Physicists cannot fully explain how ...
2021-01-25
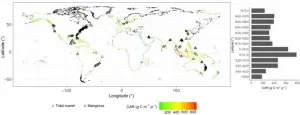
Coastal Blue Carbon (BC), which includes mangrove and saltmarsh tidal wetlands, of which was first coined a decade ago to describe the disproportionately large contribution of coastal vegetated ecosystems to global carbon sequestration. The role of BC in climate change mitigation and adaptation has now reached international prominence. Recent studies have reported BC's unique role in mitigating climate change, projected coastal wetlands area change, carbon stocks in response to historical sea level rise fluctuations, and the future roadmap relative to carbon sequestration studies. However, several questions remain unanswered:
Q1. What is the global extent and spatial distribution ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Newly discovered subset of brain cells fight inflammation with instructions from the gut
Findings on a novel anti-inflammatory pathway may guide researchers toward innovative multiple sclerosis or brain tumor treatments