INFORMATION:
The findings, published in the Journal of Medical Engineering and Technology, suggest additional experimentation is still needed to confirm the valve's effectiveness. The researchers are now in the process of developing 3D-printed, carbon and aluminum prototypes of the valve for further testing. The research is funded by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada.
Breakthrough design at UBCO vastly improves mechanical heart valve
A twist on the decade's-old design improves blood flow, prevents clots
2021-01-26
(Press-News.org) New research coming out of UBC's Okanagan campus may take the current 'gold standard' for heart valves to a new level of reliability.
A team of researchers at UBCO's Heart Valve Performance Lab (HVPL) has developed a way to improve overall blood flow through the valves, so the design of mechanical heart valves will more closely match the real thing.
"Despite more than 40 years of research, we are still chasing the goal of creating mechanical heart valves that perform consistently and seamlessly inside the human body," explains Dr. Hadi Mohammadi, an associate professor at the School of Engineering and lead researcher for the HVPL. "The way blood travels through the body is very unique to a person's physiology, so a 'one-size fits all' valve has always been a real challenge."
Mohammadi, along with doctoral student Arpin Bhullar, has developed an innovative mechanical bileaflet that enables the mechanical heart valve to function just like the real thing. A bileaflet valve--two semicircular leaflets that pivot on hinges--is a mechanical gateway that allows consistent blood-flow and ensures the flow is in one direction.
While developed decades ago and used regularly to improve a patient's blood flow, artificial valves have never been perfect, says Mohammadi. With existing versions of bileaflets, there is a small risk of blood clots or even a backflow of blood.
The design of the bileaflet is crucial for maintaining blood flow in order to eliminate risk to the patient. Mohammadi believes he's found a way to fix the problem, by adding a slight twist to the design.
"Our findings show our apex heart valve maintains consistent flow as a result of its breakthrough design--specifically the valve's curvature which mitigates clotting."
The initial design was confirmed by Dr. Guy Fradet, head of Kelowna General Hospital's cardiothoracic surgery program. Mohammadi says it takes decades for innovations in mechanical heart valves before they are used on humans, but he is confident his novel leaflet-shaped valve is the way of the future.
"The work we're doing has resulted in the design of a valve which may serve as the foundation for the next generation of bileaflet mechanical heart valves," he says. "Our research, with computer simulation and in-vitro studies, helped evaluate the performance of the proposed valve and also compare it to the industry gold standard."
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Research shows people with high omega-3 index less likely to die from COVID-19
2021-01-26
Researchers with the Fatty Acid Research Institute (FARI) and collaborators at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center in Los Angeles and in Orange County, CA, have published the first direct evidence that higher omega-3 blood levels may reduce risk for death from COVID-19 infection. The report was published in the journal Prostaglandins, Leukotrienes and Essential Fatty Acids on January 20, 2021.
There are several papers in the medical literature hypothesizing that omega-3 fatty acids should have beneficial effects in patients with COVID-19 infection, but up until now, there have been no published peer-reviewed studies supporting that hypothesis.
This study included ...
Keeping a clean path: Doubling the capacity of solid-state lithium batteries
2021-01-26
Scientists at Tokyo Institute of Technology (Tokyo Tech), Tohoku University, National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology, and Nippon Institute of Technology, demonstrated by experiment that a clean electrolyte/electrode interface is key to realizing high-capacity solid-state lithium batteries. Their findings could pave the way for improved battery designs with increased capacity, stability, and safety for both mobile devices and electric vehicles.
Liquid lithium-ion batteries are everywhere, being found in the majority of everyday mobile devices. While they possess a fair share of advantages, liquid-based batteries carry notable risks as well. This has become clear to the public in recent years after ...
Air pollution linked to higher risk of sight loss from AMD
2021-01-26
Air pollution is linked to a heightened risk of progressive and irreversible sight loss, known as age related macular degeneration (AMD), reveals a large long term study led by UCL researchers.
They found that people in the most polluted areas were at least 8% more likely to report having AMD, according to the findings published in the British Journal of Ophthalmology.
Lead author Professor Paul Foster (UCL Institute of Ophthalmology) said: "Here we have identified yet another health risk posed by air pollution, strengthening the evidence that improving the air we breathe should ...
In ED patients with chest and abdominal pain, care delivered by physicians and APPs is similar
2021-01-25
DES PLAINES, IL -- In patients matched on complexity and acuity presenting to the emergency department with chest pain and abdominal pain, the care delivered by advanced practice providers (APPs) and emergency physicians is largely similar with respect to diagnostic test ordering and admission decisions. That is the finding of a study just published in the January 2021 issue of Academic Emergency Medicine (AEM), a journal of the Society for Academic Emergency Medicine (SAEM).
The lead author of the study is Jesse M. Pines, MD, MBA, MSCE of US Acute Care Solutions, Canton, Ohio and the Department of Emergency Medicine, Allegheny Health Network, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. ...
Governments need to set clear rules for vaccinating health care workers against COVID-19
2021-01-25
An analysis undertaken by Faculty of Law professors and a physician-researcher from the Faculty of Medicine at the University of Ottawa feels provincial and territorial governments should set clear rules for vaccinating health care workers against SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, in public and private settings.
Mandatory vaccination for health care workers: an analysis of law and policy, published in the Canadian Medical Association Journal (CMAJ), describes legal precedents from attempts to mandate influenza vaccines for health care workers and ...
Finding a way to stop chemotherapy from damaging the heart
2021-01-25
COLUMBUS, Ohio - There could be an intervention on the horizon to help prevent heart damage caused by the common chemotherapy drug doxorubicin, new research suggests.
Scientists found that this chemo drug, used to treat many types of solid tumors and blood cancers, is able to enter heart cells by hitchhiking on a specific type of protein that functions as a transporter to move a drug from the blood into heart cells.
By introducing another anti-cancer drug in advance of the chemo, the researchers were able to block the transporter protein, effectively stopping the delivery of doxorubicin to those cardiac ...
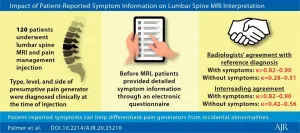
Impact of patient-reported symptom information on lumbar spine MRI Interpretation
2021-01-25
Leesburg, VA, January 25, 2021--According to an open-access article in ARRS' American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), in lumbar spine MRI, presumptive pain generators diagnosed using symptom information from brief electronic questionnaires showed almost perfect agreement with pain generators diagnosed using symptom information from direct patient interviews.
"Using patient-reported symptom information from a questionnaire, radiologists interpreting lumbar spine MRI converged on diagnoses of presumptive pain generators and distinguished these from incidental abnormalities," wrote Rene Balza of the ...
When -- not what -- obese mice ate reduced breast cancer risk
2021-01-25
Restricting eating to an eight-hour window, when activity is highest, decreased the risk of development, growth and metastasis of breast cancer in mouse models, report researchers at University of California San Diego School of Medicine, Moores Cancer Center and Veterans Affairs San Diego Healthcare System (VASDSH).
The findings, published in the January 25, 2021 edition of Nature Communications, show that time-restricted feeding -- a form of intermittent fasting aligned with circadian rhythms -- improved metabolic health and tumor circadian rhythms in mice with obesity-driven postmenopausal breast cancer.
"Previous research has shown that obesity increases the risk of a variety of cancers by negatively affecting how the body ...
Major discovery helps explain coral bleaching
2021-01-25
Corals, like all animals, must eat to live. The problem is that most corals grow in tropical waters that are poor in nutrients, sort of like ocean deserts; it's this lack of nutrients that makes the water around coral reefs so crystal clear. Because food is not readily available, corals have developed a remarkable feeding mechanism that involves a symbiotic relationship with single-celled algae. These algae grow inside the corals, using the coral tissue as shelter and absorbing the CO2 that the corals produce. In exchange, the algae provide corals with nutrients they produce through photosynthesis. These algae contain a variety of pigments, which give the coral reefs the ...
Light pollution linked to preterm birth increase
2021-01-25
Scientists conducted the first study to examine the fetal health impact of light pollution based on a direct measure of skyglow, an important aspect of light pollution. Using an empirical regularity discovered in physics, called Walker's Law, a team from Lehigh University, Lafayette College and the University of Colorado Denver in the U.S., found evidence of reduced birth weight, shortened gestational length and preterm births.
Specifically, the likelihood of a preterm birth could increase by approximately 1.48 percentage points (or 12.9%), according to the researchers, as a result of increased nighttime brightness. Nighttime brightness is characterized by being able to see only one-fourth ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
$3.4 million grant to improve weight-management programs
Higher burnout rates among physicians who treat sickle cell disease
Wetlands in Brazil’s Cerrado are carbon-storage powerhouses
Brain diseases: certain neurons are especially susceptible to ALS and FTD
Father’s tobacco use may raise children’s diabetes risk
Structured exercise programs may help combat “chemo brain” according to new study in JNCCN
The ‘croak’ conundrum: Parasites complicate love signals in frogs
Global trends in the integration of traditional and modern medicine: challenges and opportunities
Medicinal plants with anti-entamoeba histolytica activity: phytochemistry, efficacy, and clinical potential
What a releaf: Tomatoes, carrots and lettuce store pharmaceutical byproducts in their leaves
Evaluating the effects of hypnotics for insomnia in obstructive sleep apnea
A new reagent makes living brains transparent for deeper, non-invasive imaging
Smaller insects more likely to escape fish mouths
Failed experiment by Cambridge scientists leads to surprise drug development breakthrough
Salad packs a healthy punch to meet a growing Vitamin B12 need
Capsule technology opens new window into individual cells
We are not alone: Our Sun escaped together with stellar “twins” from galaxy center
Scientists find new way of measuring activity of cell editors that fuel cancer
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
PsyMetRiC – a new tool to predict physical health risks in young people with psychosis
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Research presented at international urology conference in London shows how far prostate cancer screening has come
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
[Press-News.org] Breakthrough design at UBCO vastly improves mechanical heart valveA twist on the decade's-old design improves blood flow, prevents clots