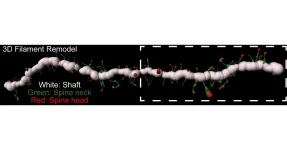
A new study in Biological Psychiatry, published by Elsevier, now shows that players in the extracellular environment - not just at neuronal interfaces - contribute to addiction plasticity. Neurons in a brain area called the nucleus accumbens are known to undergo addiction-related plasticity. Specifically, changes at synapses of medium spiny neurons (MSN), which sense the neurotransmitter dopamine, have been associated with drug-seeking and extinction behaviors.
Previous research had shown that plasticity at MSNs expressing the D1-type of dopamine receptor is linked to drug-seeking, whereas extinction of drug-seeking involves plasticity at MSNs containing the D2-type dopamine receptor. Now, research led by Peter Kalivas, PhD, and Vivian Chioma, PhD, shows that distinct enzymes working at D1- and D2-type MSNs underlie drug-seeking and extinction behaviors.
The researchers trained rats to self-administer heroin by pushing a lever for 10 days, followed by a 10-day withdrawal period. They then carefully examined the rats' brains under a microscope to detect enzymatic activity around the MSN synapses.
The study focused on the activity of extracellular enzymes called metalloproteinases (MMP). MMPs break down proteins that constitute the extracellular matrix around nerve cells. This matrix of proteins supports synaptic connections, but it also constrains the remodeling of synaptic connections in response to experience. Therefore, MMP activity directly impacts cells' ability to manifest neuroplastic changes.
To assess activity of the MMPs, the researchers used a technique called in vivo zymography, in which the rats' brains were injected with a fluorescent dye encapsulated in a protective gelatin coat at various points during the drug-training regimen. Once broken open by MMP enzymes, the dye becomes visible, allowing the investigators to observe cells' morphology as well as the enzymes' activity around specific cell types and sub-cellular locations.
"We found that drug cues increased MMP activity on one cell type in the nucleus accumbens," said Dr. Kalivas, referring to D1-type MSNs, "and they decreased activity on another cell type," the D2-type MSNs. "By showing this cellular specificity of MMP activation and inactivation by cues, we have identified novel molecules that may be potential targets for drug development in treating drug addiction," he added.
"This paper highlights the exquisite selectivity of addiction-related neuroplasticity," said John Krystal, MD, Editor of Biological Psychiatry. "In this study, cues associated with heroin delivery activated MMPs near dopamine D1 receptor-containing MSNs in the nucleus accumbens, promoting plasticity in key cells implicated in addiction. Rather than reducing this addiction-related effect on plasticity, extinction training instead increased MMP activity close to neighboring dopamine D2 receptor-containing MSNs - cells implicated in protection against addiction."
Importantly, the researchers also saw MMP activity associated with cells adjacent to the MSNs called astrocytes, a type of glial cell. The astrocytes, the extracellular matrix, and the two neurons forming a synapse are all part of what is termed the tetrapartite, or four-part, synaptic complex.
"Our work investigating cell-type specific synaptic neuroadaptations in the nucleus accumbens provides evidence of novel advances in our understanding of tetrapartite synaptic activity during heroin seeking," said Dr. Chioma. "This research demonstrates how integration of components of the tetrapartite synapse regulate specific addiction phenotypes."
Dr. Krystal added, "This finding suggests that recovery from addiction is not simply a reversal of addiction-related changes in the brain, but rather it also involves the laying down of new anti-addiction changes that protect against substance use."
INFORMATION:
Notes for editors
The article is "Heroin Seeking and Extinction from Seeking Activate Matrix Metalloproteinases at Synapses on Distinct Subpopulations of Accumbens Cells," by Vivian Chioma, Anna Kruyer, Ana-Clara Bobadilla, Ariana Angelis, Zachary Ellison, Ritchy Hodebourg, Michael Scofield, Peter Kalivas (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2020.12.004). It appears as an Article in Press in Biological Psychiatry, published by Elsevier.
Copies of this paper are available to credentialed journalists upon request; please contact Rhiannon Bugno at Biol.Psych@sobp.org or +1 254 522 9700. Journalists wishing to interview the authors may contact Peter Kalivas at kalivasp@musc.edu or +11 843-991-2627.
The authors' affiliations and disclosures of financial and conflicts of interests are available in the article.
John H. Krystal, MD, is Chairman of the Department of Psychiatry at the Yale University School of Medicine, Chief of Psychiatry at Yale-New Haven Hospital, and a research psychiatrist at the VA Connecticut Healthcare System. His disclosures of financial and conflicts of interests are available here.
About Biological Psychiatry
Biological Psychiatry is the official journal of the Society of Biological Psychiatry, whose purpose is to promote excellence in scientific research and education in fields that investigate the nature, causes, mechanisms and treatments of disorders of thought, emotion, or behavior. In accord with this mission, this peer-reviewed, rapid-publication, international journal publishes both basic and clinical contributions from all disciplines and research areas relevant to the pathophysiology and treatment of major psychiatric disorders.
The journal publishes novel results of original research which represent an important new lead or significant impact on the field, particularly those addressing genetic and environmental risk factors, neural circuitry and neurochemistry, and important new therapeutic approaches. Reviews and commentaries that focus on topics of current research and interest are also encouraged.
Biological Psychiatry is one of the most selective and highly cited journals in the field of psychiatric neuroscience. It is ranked 7th out of 155 Psychiatry titles and 12th out of 271 Neurosciences titles in the Journal Citations Reports® published by Clarivate Analytics. The 2019 Impact Factor score for Biological Psychiatry is 12.095. http://www.sobp.org/journal
About Elsevier
As a global leader in information and analytics, Elsevier helps researchers and healthcare professionals advance science and improve health outcomes for the benefit of society. We do this by facilitating insights and critical decision-making for customers across the global research and health ecosystems.
In everything we publish, we uphold the highest standards of quality and integrity. We bring that same rigor to our information analytics solutions for researchers, health professionals, institutions and funders.
Elsevier employs 8,100 people worldwide. We have supported the work of our research and health partners for more than 140 years. Growing from our roots in publishing, we offer knowledge and valuable analytics that help our users make breakthroughs and drive societal progress. Digital solutions such as ScienceDirect, Scopus, SciVal, ClinicalKey and Sherpath support strategic research management, R&D performance, clinical decision support, and health education. Researchers and healthcare professionals rely on our 2,500+ digitized journals, including The Lancet and Cell, our 40,000 eBook titles; and our iconic reference works, such as Gray's Anatomy. With the Elsevier Foundation and our external Inclusion & Diversity Advisory Board, we work in partnership with diverse stakeholders to advance inclusion and diversity in science, research and healthcare in developing countries and around the world.
Elsevier is part of RELX, a global provider of information-based analytics and decision tools for professional and business customers. http://www.elsevier.com
Media contact
Rhiannon Bugno, Editorial Office
Biological Psychiatry
+1 254 522 9700
END