Addressing health disparities in diabetes requires a broader look at systemic racism
2021-01-26
(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON--Poor social conditions caused by systemic racism contribute to health disparities in people with diabetes, according to a paper published in the Endocrine Society's Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
Minorities are disproportionately affected by diabetes because of poor social conditions that contribute to negative health outcomes such as poverty, unsafe housing, lack of access to healthy food and safe physical activity, and inadequate employment and educational opportunities. These are known as the social determinants of health and are the result of residential racial segregation and a lack of economic investment in Black communities. Unethical practices and experimentation in minority communities have also caused racial bias in our medical systems and a lack of trust between minority patients and health care providers.
"Traditionally, physicians have focused on the biological contributors to disparities in diabetes, obesity and other chronic diseases; however, given the bright light shone on health disparities during the COVID-19 pandemic, we need to view the contributing factors and solutions more broadly," said study author Sherita Golden, M.D., M.H.S., of Johns Hopkins Medicine in Baltimore, Md. "This will give us agency in contributing to and advocating for health system, public health and policy-level interventions to address the structural and institutional racism embedded in our medical and social systems."
To address health disparities in diabetes, the authors recommend health systems implement the National Standards for Culturally and Linguistically Appropriate Services in Health and Health Care. These standards ensure interpretation services are available to all patients and that patient education materials are at a literacy level most people can understand. They also recommend more training among health care providers on unconscious bias, anti-racism, and the value of diversity in clinical care settings.
INFORMATION:
Other authors of the study include: Joshua J. Joseph of the Ohio State University College of Medicine in Columbus, Ohio and Felicia Hill-Briggs of the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine.
The manuscript received no external funding.
The manuscript, "Casting a Health Equity Lens on Endocrinology and Diabetes," was published online, ahead of print.
Endocrinologists are at the core of solving the most pressing health problems of our time, from diabetes and obesity to infertility, bone health, and hormone-related cancers. The Endocrine Society is the world's oldest and largest organization of scientists devoted to hormone research and physicians who care for people with hormone-related conditions.
The Society has more than 18,000 members, including scientists, physicians, educators, nurses and students in 122 countries. To learn more about the Society and the field of endocrinology, visit our site at http://www.endocrine.org. Follow us on Twitter at @TheEndoSociety and @EndoMedia.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-26
PITTSBURGH, 26 January 2021 - A vaginal ring containing the antiretroviral drug dapivirine and the contraceptive hormone levonorgestrel delivered sustained levels of each drug when used continuously for 90 days - levels likely sufficient to serve its dual purpose for protecting against both HIV and unwanted pregnancy, according to findings of a new study.
Results of the Phase I study of the 90-day dual-purpose ring are being presented at the HIV Research for Prevention (HIVR4P) Virtual Conference, or HIVR4P // Virtual, which is taking place over the course of ...
2021-01-26
"Shell-crushing" - exactly what it sounds like - is a predatory mode used by numerous marine life from crabs to octopuses to large fishes and mammals when they eat hard-shelled mollusks like clams, oysters and conchs. These predators have to break apart the shell using robust claws or fortified jaws to access the prey's soft tissues.
Despite its prevalence in the marine environment, this feeding behavior has remained elusive to study remotely, particularly for larger marine animals that destroy shells almost completely, leaving behind little trace. Moreover, because they are highly mobile, scientists have difficulty in directly observing their foraging habits, which is why the ecology of shell-crushing (durophagy) remains ...
2021-01-26
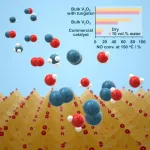
Tokyo, Japan - Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have created a new tungsten-substituted vanadium oxide catalyst for breaking down harmful nitrogen oxides in industrial exhaust. Their new catalyst material works at lower temperatures and does not suffer major drops in performance when processing "wet" exhaust, resolving a major drawback in conventional vanadium oxide catalysts. They found that the unaggregated dispersal of atomic tungsten in the original crystal structure plays a key role in how it functions.
Selective catalytic reduction (SCR) is an essential technology for keeping air clean. Industrial exhaust is passed through catalytic units and reacted with ...
2021-01-26
If we are to prevent the impending environmental crisis, it is imperative that we find efficient and sustainable ways to avoid being wasteful. One area with much room for improvement is the recycling of waste heat from industrial processes and technological devices into electricity. Thermoelectric materials are at the core of research in this field because they allow for clean power generation at little cost.
For thermoelectric materials to be used in vastly different fields such as steel works and transportation, they need to be able to operate in both high and low temperature regimes. In this regard, "half-Heusler Ni-based ...
2021-01-26
VANCOUVER, Wash. -When entrepreneurs dream up ideas for new businesses, cannabis use might help, and hinder, their creativity, according to a new study in the Journal of Business Venturing by Washington State University researchers.
The study found that cannabis-using entrepreneurs generated new business ideas such as a weightless, gravity-free virtual reality workout, that were more original, but less feasible, compared to those who do not use cannabis.
"Originality and feasibility are both crucial in entrepreneurship--one without the other limits potential value creation," said Benjamin Warnick, lead author of the study and assistant professor in the ...
2021-01-26
LONDON, ON - Neurofeedback, also called 'brain training,' consists of exercises where individuals regulate their own brain activity. In a new study from Lawson Health Research Institute and Western University, researchers have found that neurofeedback may be an effective treatment for individuals with post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Published in END ...
2021-01-26
A new study found that talented dogs can learn new words after hearing them only four times.
While preliminary evidence seems to show that most dogs do not learn words (i.e. names of objects), unless eventually very extensively trained, a few individuals have shown some exceptional abilities.
The Family Dog Project research team at the Department of Ethology, Eötvös Loránd University, Budapest is investigating on these exceptionally talented dogs who seem to learn words in the absence of any formal training, but simply by being exposed to playing with their owners in the typical way ...
2021-01-26
Toddlers with high daily touchscreen use are quicker to look at objects when they appear and are less able to resist distraction compared to toddlers with no or low touchscreen use - according to new research from Birkbeck, University of London, King's College London and University of Bath.
The research team say the findings are important for the growing debate around the role of screen time on toddlers' development especially given the increased levels of screen time seen during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Lead researcher Professor Tim Smith, from Birkbeck's ...
2021-01-26
New research from Queen Mary University of London and the University of Maryland, has reignited the debate around the behaviour of the giant dinosaur Spinosaurus.
Since its discovery in 1915, the biology and behaviour of the enormous Spinosaurus has puzzled palaeontologists worldwide. It was recently argued that the dinosaur was largely an aquatic predator, using its large tail to swim and actively pursue fish in the water.
The new study, published today in Palaeontologia Electronica, challenges this recent view of Spinosaurus suggesting that whilst it likely fed ...
2021-01-26
Philadelphia, January 26, 2021 - Addiction, or substance use disorder (SUD), is a complex neurological condition that includes drug-seeking behavior among other cognitive, emotional and behavioral features. Synaptic plasticity, or changes in the way neurons communicate with one another, drives these addictive behaviors. These lasting brain changes are at the crux of why addiction is so hard to treat.
A new study in Biological Psychiatry, published by Elsevier, now shows that players in the extracellular environment - not just at neuronal interfaces - contribute to addiction plasticity. Neurons in a brain area called the nucleus accumbens are known to undergo addiction-related plasticity. Specifically, changes at synapses of medium spiny neurons (MSN), which sense the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Addressing health disparities in diabetes requires a broader look at systemic racism