To find the right network model, compare all possible histories
2021-01-26
(Press-News.org) Two family members test positive for COVID-19 -- how do we know who infected whom? In a perfect world, network science could provide a probable answer to such questions. It could also tell archaeologists how a shard of Greek pottery came to be found in Egypt, or help evolutionary biologists understand how a long-extinct ancestor metabolized proteins.
As the world is, scientists rarely have the historical data they need to see exactly how nodes in a network became connected. But a new paper published in Physical Review Letters offers hope for reconstructing the missing information, using a new method to evaluate the rules that generate network models.
"Network models are like impressionistic pictures of the data," says physicist George Cantwell, one of the study's authors and a postdoctoral researcher at the Santa Fe Institute. "And there have been a number of debates about whether the real networks look enough like these models for the models to be good or useful."
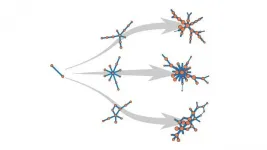
Normally when researchers try to model a growing network -- say, a group of individuals infected with a virus -- they build up the model network from scratch, following a set of mathematical instructions to add a few nodes at a time. Each node could represent an infected individual, and each edge a connection between those individuals. When the clusters of nodes in the model resemble the data drawn from the real-world cases, the model is considered to be representative -- a problematic assumption when the same pattern can result from different sets of instructions.
Cantwell and co-authors Guillaume St-Onge (University Laval, Quebec) and Jean-Gabriel Young (University of Vermont) wanted to bring a shot of statistical rigor to the modeling process. Instead of comparing features from a snapshot of the network model against the features from the real-world data, they developed methods to calculate the probability of each possible history for a growing network. Given competing sets of rules, which could represent real-world processes such as contact, droplet, or airborne transmission, the authors can apply their new tool to determine the probability of specific rules resulting in the observed pattern.
"Instead of just asking 'does this picture look more like the real thing?'" Cantwell says, "We can now ask material questions like, 'did it grow by these rules?'" Once the most likely network model is found, it can be rewound to answer questions such as who was infected first.
In their current paper, the authors demonstrate their algorithm on three simple networks that correspond to previously-documented datasets with known histories. They are now working to apply the tool to more complicated networks, which could find applications across any number of complex systems.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-26
A new paper from UC Santa Cruz researchers, published in END ...
2021-01-26
Overview:
Jihui Yuan (Assistant Professor, Department of Architecture and Civil Engineering, Toyohashi University of Technology) proposed a numerical bead model to predict the upward-to-downward reflection ratio of glass bead retro-reflective (RR) material purposed for urban heat island (UHI) mitigation and reducing energy consumption. It revealed that the retro-reflectivity of glass bead RR material gradually increases from morning to noon, at which time it begins to gradually decrease. These results will contribute to existing research on the absorption or reflection of solar radiation to improve urban thermal and lighting ...
2021-01-26
WASHINGTON--Poor social conditions caused by systemic racism contribute to health disparities in people with diabetes, according to a paper published in the Endocrine Society's Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
Minorities are disproportionately affected by diabetes because of poor social conditions that contribute to negative health outcomes such as poverty, unsafe housing, lack of access to healthy food and safe physical activity, and inadequate employment and educational opportunities. These are known as the social determinants of health and are the result of residential ...
2021-01-26
PITTSBURGH, 26 January 2021 - A vaginal ring containing the antiretroviral drug dapivirine and the contraceptive hormone levonorgestrel delivered sustained levels of each drug when used continuously for 90 days - levels likely sufficient to serve its dual purpose for protecting against both HIV and unwanted pregnancy, according to findings of a new study.
Results of the Phase I study of the 90-day dual-purpose ring are being presented at the HIV Research for Prevention (HIVR4P) Virtual Conference, or HIVR4P // Virtual, which is taking place over the course of ...
2021-01-26
"Shell-crushing" - exactly what it sounds like - is a predatory mode used by numerous marine life from crabs to octopuses to large fishes and mammals when they eat hard-shelled mollusks like clams, oysters and conchs. These predators have to break apart the shell using robust claws or fortified jaws to access the prey's soft tissues.
Despite its prevalence in the marine environment, this feeding behavior has remained elusive to study remotely, particularly for larger marine animals that destroy shells almost completely, leaving behind little trace. Moreover, because they are highly mobile, scientists have difficulty in directly observing their foraging habits, which is why the ecology of shell-crushing (durophagy) remains ...
2021-01-26
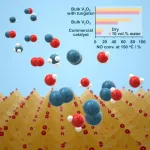
Tokyo, Japan - Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have created a new tungsten-substituted vanadium oxide catalyst for breaking down harmful nitrogen oxides in industrial exhaust. Their new catalyst material works at lower temperatures and does not suffer major drops in performance when processing "wet" exhaust, resolving a major drawback in conventional vanadium oxide catalysts. They found that the unaggregated dispersal of atomic tungsten in the original crystal structure plays a key role in how it functions.
Selective catalytic reduction (SCR) is an essential technology for keeping air clean. Industrial exhaust is passed through catalytic units and reacted with ...
2021-01-26
If we are to prevent the impending environmental crisis, it is imperative that we find efficient and sustainable ways to avoid being wasteful. One area with much room for improvement is the recycling of waste heat from industrial processes and technological devices into electricity. Thermoelectric materials are at the core of research in this field because they allow for clean power generation at little cost.
For thermoelectric materials to be used in vastly different fields such as steel works and transportation, they need to be able to operate in both high and low temperature regimes. In this regard, "half-Heusler Ni-based ...
2021-01-26
VANCOUVER, Wash. -When entrepreneurs dream up ideas for new businesses, cannabis use might help, and hinder, their creativity, according to a new study in the Journal of Business Venturing by Washington State University researchers.
The study found that cannabis-using entrepreneurs generated new business ideas such as a weightless, gravity-free virtual reality workout, that were more original, but less feasible, compared to those who do not use cannabis.
"Originality and feasibility are both crucial in entrepreneurship--one without the other limits potential value creation," said Benjamin Warnick, lead author of the study and assistant professor in the ...
2021-01-26
LONDON, ON - Neurofeedback, also called 'brain training,' consists of exercises where individuals regulate their own brain activity. In a new study from Lawson Health Research Institute and Western University, researchers have found that neurofeedback may be an effective treatment for individuals with post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Published in END ...
2021-01-26
A new study found that talented dogs can learn new words after hearing them only four times.
While preliminary evidence seems to show that most dogs do not learn words (i.e. names of objects), unless eventually very extensively trained, a few individuals have shown some exceptional abilities.
The Family Dog Project research team at the Department of Ethology, Eötvös Loránd University, Budapest is investigating on these exceptionally talented dogs who seem to learn words in the absence of any formal training, but simply by being exposed to playing with their owners in the typical way ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] To find the right network model, compare all possible histories