(Press-News.org) A new study has shown that, while there is limited evidence for overall increased mortality in patients with atopic eczema, those with severe atopic eczema may have a greater risk of dying from several health issues compared with those without eczema, according to a new study in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology.
The research team, led by the London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine (LSHTM) and funded by the Wellcome Trust, compared the risk of dying in over 500,000 adults with atopic eczema with more than 2.5 million without eczema. Patients with severe atopic eczema had a 62% higher risk of dying compared to individuals without atopic eczema, due to several causes - the strongest links of which were seen for infections, lung problems and kidney or bladder disorders.
There was limited evidence of increased 'all-cause' mortality in patients with non-severe atopic eczema, and the absolute risk of death was modest, with low overall mortality rates (1435 per 100,000 people per year in those without atopic eczema, and 1496 per 100,000 people per year in those with atopic eczema).
The researchers did not set out to find the reasons behind the increases in risk of death in severe or predominantly active atopic eczema. Previous studies have suggested that the elevated risk may be linked to reduced physical activity and reduced sleep quality, as well as immunological dysfunction due to the disease itself or the drug treatments the patients might be on. They urge for more research into the causes to help develop intervention strategies.
The research was conducted in collaboration with Health Data Research UK, Aarhus University Hospital, Nottingham Support Group for Carers of Children with Eczema and the University of California San Francisco School of Medicine.
Atopic eczema affects up to 10% of adults and is becoming more common globally. The disease is characterised by itch, sleeplessness and adverse effects on quality of life. Around 30% of people with atopic eczema have moderate to severe disease.
Sinéad Langan, Professor of Clinical Epidemiology at LSHTM, said: "Recent evidence has led to a paradigm shift in how atopic eczema is perceived, from focusing on skin symptoms and associated allergic diseases, to understanding that the disease may be associated with a range of important medical outcomes. Recently, we found atopic eczema to be associated with an increased risk of myocardial infarction, ischemic stroke, angina and heart failure.
"However, few studies have assessed if atopic eczema increases the risk of death, a research question we aimed to address in this study."
This new research used the healthcare records from UK general practices alongside hospitalisation records and mortality data from the Office for National Statistics spanning 1998 to 2016. More than 500,000 people with atopic eczema, of which nearly 35,000 were classified as having severe atopic eczema, were matched with up to five individuals without eczema, based on their age (within 15 years), sex and general practice. This resulted in more than three million individuals were successfully matched, with a median age of 41.8 years.
The researchers found that patients with atopic eczema had 8% to 14% increased risk of death due to infectious, digestive and genitourinary causes.
Crucially, they noted that increased mortality risk was mainly in those with the most severe or more active atopic eczema. Patients with severe atopic eczema had 62% higher overall risk of death. These findings are consistent with previous studies.
Long-standing patient collaborator, Amanda Roberts, said: "Forewarned is fore-armed. Now we eczema patients can be more aware of potential harms and complications associated with lungs, kidneys or bladder. This research team is adding so much to our understanding of eczema."
Professor Langan added: "Although the absolute risk of death from severe eczema is low, our findings suggest that those with severe or more active forms of the disease do face a higher risk of dying from associated health issues. We hope that this new information will help inform further research to better understand this pattern and the underlying mechanisms of these associations, and subsequently inform and improve treatment processes for those with severe eczema."
The researchers acknowledge the limitations of this study, including a lack of standardised measures of disease severity. Severity had to be identified based on hospital referral or receiving of specific therapies, prevent the researchers from disentangling the effects of treatment and severity.
INFORMATION:
For more information or interviews, please contact press@lshtm.ac.uk.
A copy of the embargoed paper is available upon request.
Notes to Editors
Publication
Richard J Silverwood, Kathryn E Mansfield, Amy Mulick, Angel YS Wong, Sigrún AJ Schmidt, Amanda Roberts, Liam Smeeth, Katrina Abuabara, Sinéad M Langan. Atopic eczema in adulthood and mortality: UK population-based cohort 1 study, 1998-2016. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology.
The London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine (LSHTM) is a world-leading centre for research, postgraduate studies and continuing education in public and global health. LSHTM has a strong international presence with over 3,000 staff and 4,000 students working in the UK and countries around the world, and an annual research income of £180 million.
LSHTM is one of the highest-rated research institutions in the UK, is partnered with two MRC University Units in The Gambia and Uganda, and was named University of the Year in the Times Higher Education Awards 2016. Our mission is to improve health and health equity in the UK and worldwide; working in partnership to achieve excellence in public and global health research, education and translation of knowledge into policy and practice.
http://www.lshtm.ac.uk
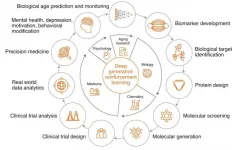
27th of January, Wednesday, Hong Kong - Deep Longevity, a fully-owned subsidiary of Regent Pacific (HKEX: 0575), specializing in the development and the application of next-generation artificial intelligence (AI) for aging and longevity research, today announced the publication of an article in END ...
The thought of eating insects is stomach turning for many, but new Edith Cowan University (ECU) research is shedding light on allergy causing proteins which could pose serious health risks for those suffering from shellfish allergy.
The research, published in the journal Food Chemistry, identified 20 proteins found in cricket food products which could cause serious allergic reactions.
The project was led by Professor Michelle Colgrave from ECU's School of Science and the CSIRO.
Professor Colgrave said crickets and other insects could be the key to feeding ...
DALLAS (January 26, 2021) - Many people believe that they can't change their brains, or that their brain health will inevitably decline as they age. But the Strategic Memory Advanced Reasoning Tactics (SMART) training protocol, created by researchers and clinicians at the Center for BrainHealth®, has been demonstrated over the past two decades to improve cognitive function and psychological well-being in laboratory participants. Recent research suggests that SMART can even make long-lasting improvements to people's brain health when given outside of the lab in short, informal training sessions.
A paper detailing these findings was recently published in Military Medicine. The research was a collaboration between Leanne R. Young, PhD, of Applied Research Associates, ...
The widespread use of cashless payments including credit cards, debit cards, and mobile apps has made transactions more convenient for consumers. However, results from previous research have shown that such cashless payments can increase consumers' spending on unhealthy food. "Why Do Cashless Payments Increase Unhealthy Consumption? The Decision-Risk Inattention Hypothesis," a newly published article in the Journal of the Association for Consumer Research, explains this phenomenon by showing how changes in bodily responses to cashless payments influence consumers responses.
Authors Joowon Park, Clarence Lee, and Manoj Thomas propose that cash and cashless payments elicit different levels of negative arousal when making shopping ...
The development of small hydropower dams is widespread throughout Brazil and elsewhere in the world, vastly overshadowing large hydropower projects. The proliferation of these smaller dams is a response to growing energy and security needs. Their expansion, however, threatens many of the remaining free-flowing rivers and biodiverse tropical regions of the world -- interrupting the migrations of freshwater fishes, on which millions of peoples' livelihoods depend.
A new University of Washington paper published Jan. 11 in Nature Sustainability quantifies these tradeoffs between hydroelectric generation capacity and the impacts on river connectivity ...
Popular folklore and anecdotal evidence suggest that people in a hypnotic or suggestible state can experience sensory hallucinations, such as perceiving sounds and sights that are not actually there. Reliable scientific evidence of these experiences, however, has been notoriously challenging to obtain because of their subjective nature.
New research published in the journal Psychological Science provides compelling evidence that hypnotic suggestions can help highly susceptible people "see" imaginary objects, equipping them with the missing details needed to solve an otherwise challenging visual puzzle.
"Hypnosis holds intriguing effects on human behavior," said Amir Raz, a researcher at McGill University and coauthor on the paper. "The careful, systematic study of hypnotic phenomena can ...
BUFFALO, N.Y. - A new study led by a University at Buffalo researcher has identified how specific communication among different brain regions, known as brain connectivity, can serve as a biomarker for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
The research relied on a deep architecture using machine-learning classifiers to identify with 99% accuracy those adults who had received a childhood diagnosis of ADHD many years earlier.
"This suggests that brain connectivity is a stable biomarker for ADHD, at least into childhood, even when an individual's ...
Amid a sharp economic downturn in 2008, police departments around the United States experienced budget shortfalls that required them to enact cutbacks. A new study examined the effects on crime of budget shortfalls in two New Jersey cities--one of which laid off more than 10 percent of its police force while the other averted layoffs. The study found that the police layoffs were associated with significant increases in overall crime, violent crime, and property crime.
The study, by researchers at John Jay College of Criminal Justice and Rutgers University, appears in Justice Evaluation Journal, a publication of the Academy of Criminal Justice Sciences.
"Our study suggests that sudden and drastic reductions in the size of a police force via layoffs of police officers ...
A new machine learning algorithm based on mammograms can estimate the risk of breast cancer in women more accurately than current risk models, according to a study from Adam Yala and colleagues. The algorithm, which was tested with datasets from three large hospitals located worldwide, could help clinicians design guidelines for breast cancer screening that meet the need for early detection while reducing false-positives, test costs, and other issues associated with overscreening. Mammograms are the most common method to screen for breast cancer, as more than 39 million procedures are performed in the U.S. annually. However, their widespread adoption has not gone without ...
Working to develop new treatments for osteoarthritis, researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have genetically engineered cartilage to deliver an anti-inflammatory drug in response to activity similar to the bending of a knee or other motions that put stress on joints.
Among the early symptoms of osteoarthritis is pain in response to such movements -- motions that involve the so-called mechanical loading of a joint. Joint pain that accompanies bending or lifting can make it difficult to perform normal activities. But by altering genes in cartilage cells in the laboratory, the researchers have been able to program them to respond to the mechanical stress associated with movement and weight-bearing ...