Dalian coherent light source reveals the origin of interstellar medium S2 fragments
2021-01-28
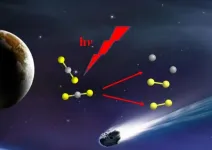
(Press-News.org) Studying the creation and evolution of sulfur-containing compounds in outer space is essential for understanding interstellar chemistry. CS2 is believed to be the most important molecule in comet nuclei, interstellar dust, or ice cores. CS and S2 are the photodissociation fragments of CS2.
Forty years ago, the emission spectra of only CS and S2 species, and not those of CS2 species, were observed from several comets by the International Ultraviolet Explorer satellite. The photodissociation mechanism of CS2 molecules remains unclear, and S2 fragments have not been experimentally observed before.
Recently, a team led by Prof. YUAN Kaijun from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), in cooperation with Prof. WANG Xing'an's group from the University of Science and Technology of China, observed the C+S2 product channel from CS2 photodissociation for the first time using a home-made Time-Sliced Velocity Map Ion Imaging (TS-VMI) experimental setup, based on the Dalian Coherent Light Source (DCLS).
This study, published in The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters on January 11 2021, provided direct experimental evidence for the origin of the interstellar medium S2 fragments observed previously.
The researchers investigated the two-photon ultraviolet (UV) and one-photon vacuum ultraviolet (VUV) photodissociation dynamics of CS2 molecules via the VUV free-electron laser (FEL) at DCLS. They directly observed the C+S2 product channel from CS2 photodissociation and obtained images of the electronically ground/excited states of S2 products with vibrational excitation.
Moreover, the researchers analyzed the product scattering anisotropy parameter β value. The electronically-excited states of the central atom of the CS2 molecule played an important role in the isomerization and photodissociation processes.
This research demonstrated that interstellar medium S2 fragments could be directly generated from CS2 photodissociation.
"Given the similarity of OCS studied in our previous works and CS2 in this work, we believe that the central-atom elimination channel is more general than expected in the photodissociation of triatomic molecules," stated Prof YUAN.
INFORMATION:
This work was supported by the Chemical Dynamics Research Center, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, and the Key Technology Team of CAS.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-28
An ecologist from RUDN University together with colleagues from 14 countries compared three methods for estimating ecosystem transpiration in a study. In the first ever research with such a comprehensive data-set, the team used land-atmosphere water vapor flux data of collected at 251 locations all over the planet, from Australia to Greenland. The outcome of the research help to understand the role of plants in the global water and carbon cycles in the current predicament of global warming. The results of the study were published in the December 2020 issue of the journal Global ...
2021-01-28
Western Carolina University researchers find a disproportionate number of inmates with violent offenses suffer from post-traumatic stress disorder, panic disorder and alcohol use disorder, and published their findings in the Journal of Criminal Psychology.
Alexa Barrett, clinical psychology master's student at WCU, and Al Kopak, associate professor of criminology and criminal justice at WCU, discovered the combination of PTSD, PD and AUD significantly increased the likelihood of violent offenses while conducting research at three county detention centers in North Carolina.
Supported by a Summer Research Assistantship provided by the Graduate School, the purpose of this study was to detail ...
2021-01-28
A PhD student and 'beer scientist' has inadvertently discovered a way to conduct extremely small-scale brewing experiments, potentially leading to better beer.
It came about when University of Queensland PhD candidate Edward Kerr hit a hurdle when he completed a beer brewing experiment for a paper.
"I was looking at barley protein changes during the mashing stage of beer brewing, when one of the paper's reviewers asked if the changes were caused by temperature or time spent mashing the barley," Mr Kerr said.
"It was a good question, but to find out I'd need to brew all over again, with an instrument that would hold at least 23 litres ...
2021-01-28
WASHINGTON, D.C. and SAN DIEGO, CA -- In his inaugural address, President Joe Biden vowed that "help is on the way" to a nation grappling with a pandemic that has already claimed over 420,000 lives and counting. However, despite the promise of a better future, a new survey from West Health and Gallup finds Americans remain largely skeptical that issues as varied as managing the COVID-19 crisis, lowering healthcare costs, improving the economy, fixing immigration and addressing climate change, will improve anytime soon.
The findings from the monthly West Health-Gallup U.S. Healthcare Study are based on a ...
2021-01-28
Pioneering research into how our bodies manufacture the cells that make blood has moved us closer to regrowing tissues and organs. The findings also may let doctors grow the cells for transplantation into people to battle cancer, blood disorders and autoimmune diseases.
Researcher Karen K. Hirschi, PhD, of the Department of Cell Biology and the Robert M. Berne Cardiovascular Research Center at the University of Virginia School of Medicine, has developed a simple and efficient way to generate "hemogenic endothelial cells." These cells are the first step in the production line of blood cells, and Hirschi's new findings provide a blueprint for creating them outside the body.
"By studying how hemogenic endothelial cells develop normally, we gain insights needed ...
2021-01-28
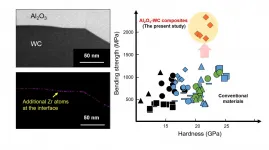
Ceramic matrix composites (CMCs) are incredibly strong materials used in jet engines, gas turbines, and cutting tools for nickel superalloys. Aluminum oxide (Al2O3) is hard and chemically inert, and tungsten carbide (WC) is used as a superhard material, but past efforts to create an Al2O3-WC CMC yielded unsatisfactory results. Recently, a study by Japanese scientists, published in Scientific Reports, shows that adding zirconium atoms results in improved Al2O3-WC CMCs.
Given the potential utility of Al2O3-WC CMCs as superhard materials, researchers around the world have tested several formulations to identify one with a high bending strength, which is a measure of the physical stress a material can be subjected to before it becomes permanently bent or broken. Previously, ...
2021-01-28
In a first-of-its-kind study, researchers discovered that light pollution leads to more than just wasted energy and washed-out starlight--it can increase the likelihood of a preterm birth by almost 13%. Laura Argys, professor of economics at the University of Colorado Denver, collaborated with scientists at Lehigh University and Lafayette College to produce this study.
Skyglow, the brightness of the night sky apart from discrete light sources such as the moon and visible stars, is one of the most pervasive forms of light pollution. When you have increased artificial brightness at night, coming from sources like streetlamps, outdoor advertising, and buildings, it reduces your ability to see the dark ...
2021-01-28
Aging and lifestyle-related metabolic imbalances, such as hyperglycemia, hyperlipidemia, and oxidative-stress, cause the accumulation of advanced glycation end products (AGEs), including pentosidine (PEN, crosslinked type) and carboxymethyl-lysine (CML, non-crosslinked type). Osteoporosis is a widespread metabolic skeletal disease characterized by diminished bone mineral density (BMD) or bone strength, which increases the risk of fractures.
To date, the association of PEN and CML with osteoporotic fracture has been reported, and the accumulation of AGEs in bone ...
2021-01-28
When it comes to drones, the Singapore public is not as keen for them to be used to provide services around their living spaces, finds a study by researchers at the Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore). However, they are more accepting of drones being used in areas like recreational spots or industrial areas.
There is growing global interest in the use of drones to provide a range of applications - from building inspection to last mile commercial delivery - that promise productivity gains and cost reductions.
In Singapore, the use of drones is picking up, with the government adopting them for various projects in the Smart Nation drive, where technology ...
2021-01-28
Cambridge, Massachusetts - They may be the youngest astronomers to make a discovery yet.
This week, 16-year-old Kartik Pinglé and 18-year-old Jasmine Wright have co-authored a peer-reviewed END ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Dalian coherent light source reveals the origin of interstellar medium S2 fragments