(Press-News.org) Mass spectrometers are widely used to analyze highly complex chemical and biological mixtures. Skoltech scientists have developed a new version of a mass spectrometer that uses rotation frequencies of ionized molecules in strong magnetic fields to measure masses with higher accuracy (FT ICR). The team has designed an ion trap that ensures the utmost resolving power in ultra-strong magnetic fields. The research was published in the journal Analytical Chemistry.
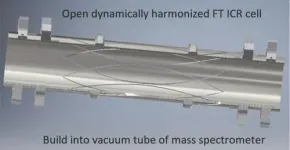
The ion trap is shaped like a cylinder made up of electrodes, with electric and magnetic fields generated inside. The exact masses of the test sample's ions can be determined from their rotation frequencies. The electrodes must create a harmonized field of a particular shape such that the ions rotate predictably. A trap with such a field is called a Dynamically Harmonized Cell (DHC).
The DHC was invented in 2011 by Evgeny Nikolaev, a Professor at the Skoltech Center for Computational and Data-Intensive Science and Engineering (CDISE). Although in reality, the cell's field is of a highly complex nature and is not harmonized, for fast rotating ions in the magnetic field it still appears as harmonized due to the averaging effect, hence the cell's name. So far, the best trap in terms of spectrum measurement accuracy, the DHC has been widely used in research and commercial mass spectrometers with a high demand on accuracy and integrated into the strongest magnetic field mass spectrometer at the National High Magnetic Field Laboratory in Tallahassee, FL.
Super strong magnets cost tens of millions of dollars. Mass measurement accuracy is supposed to increase linearly with magnetic field strength, but it does not: in reality, the pattern is non-linear, and the increase in accuracy is much slower than expected.
The scientists assumed that non-linearity occurs because the level of vacuum in the cell is not sufficient, no matter how advanced are the pumps. They developed a trap with both ends open for easy evacuation of residual gases and named it the 'Zig-Zag Cell'.
"Right now, our lab is manufacturing the new cell which we will use for experiments to check whether our assumptions and theoretical predictions are correct, and if they are, the trap will put the linear relationship between mass spectrum measurement accuracy and magnetic field strength back in place, thus ensuring higher accuracy at very high values of magnetic field strength. The fact that the accuracy increases with an increase in magnetic field strength means that the trap will potentially help create the most accurate mass spectrometer of all," says Anton Lioznov, a PhD student at Skoltech.
According to the study lead, Professor Evgeny Nikolaev, mass spectrometers with a new type of cell will ensure higher accuracy for biological samples and complex mixtures, such as oil, where even existing mass spectrometers of this type with the DHC can detect up to 400,000 compounds.
INFORMATION:
Skoltech is a private international university located in Russia. Established in 2011 in collaboration with the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), Skoltech is cultivating a new generation of leaders in science, technology, and business researching breakthrough fields. It is promoting technological innovation intending to solve critical problems that face Russia and the world. Skoltech is focusing on six priority areas: data science and artificial intelligence, life sciences, advanced materials and modern design methods, energy efficiency, photonics, and quantum technologies, and advanced research. Web: https://www.skoltech.ru/.
Skoltech researchers and their colleagues from Russia and Germany have designed an on-chip printed 'electronic nose' that serves as a proof of concept for low-cost and sensitive devices to be used in portable electronics and healthcare. The paper was published in the journal ACS Applied Materials Interfaces.
The rapidly growing fields of the Internet of Things (IoT) and advanced medical diagnostics require small, cost-effective, low-powered yet reasonably sensitive, and selective gas-analytical systems like so-called 'electronic noses.' These ...
A genetic engineering method makes it possible to observe how woody cell walls are built in plants. The new research in wood formation, conducted by the University of Copenhagen and others, opens up the possibility of developing sturdier construction materials and perhaps more climate efficient trees.
The ability of certain tree species to grow taller than 100 meters is due to complex biological engineering. Besides needing the right amounts of water and light to do so, this incredible ability is also a result of cell walls built sturdily enough to keep a tree both upright and able to withstand the tremendous pressure created as water is sucked up from its roots and into its leaves.
This ability is made possible by what are known as the secondary cell ...
Skoltech scientists have developed an algorithm that can identify various tree species in satellite images. Their research was published in the IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing.
Identifying tree species is essential for efficient forest management and monitoring. Satellite imagery is an easier and cheaper way to deal with this task than other approaches that require ground observations of vast and remote areas.
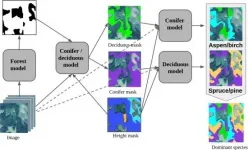
Researchers from the Skoltech Center for Computational and Data-Intensive Science and Engineering (CDISE) and Skoltech Space Center used a neural network to automate dominant tree species' identification in high and medium resolution images. A hierarchical classification model and additional data, such as vegetation height, helped ...
People with combined vision and hearing loss are nearly four times more likely to experience depression and more than three times more likely to suffer chronic anxiety, according to a new study published in the journal Frontiers in Psychology and led by Anglia Ruskin University (ARU).
Researchers analysed a health survey of 23,089 adults in Spain and found that while people suffering either vision or hearing loss both were more likely to report depression as those that were not, that risk increased to 3.85 times higher when respondents reported problems with both senses combined.
The study also found people with combined vision and hearing loss were 3.38 times more likely than the general population to report chronic anxiety.
It is understood to be the first study looking at ...
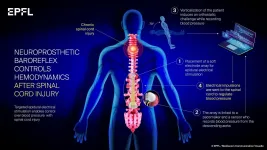
An international team of scientists headed by Grégoire Courtine at EPFL and CHUV and Aaron Phillips at the University of Calgary has developed a treatment that can dramatically improve the lives of patients with a spinal cord injury.
VIDEO: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UGXnuHgDWFU
"A serious and underrecognized result of these injuries is unstable blood pressure, which can have devastating consequences that reduce quality of life and are life threatening. Unfortunately, there are no effective therapies for unstable blood pressure after spinal cord injury". said Dr. Aaron Phillips, co-lead author of the study (see affiliations below). ...
Thursday, 28 January 2021: A study has found that adolescents who frequently use cannabis may experience a decline in Intelligence Quotient (IQ) over time. The findings of the research provide further insight into the harmful neurological and cognitive effects of frequent cannabis use on young people.
The paper, led by researchers at RCSI University of Medicine and Health Sciences, is published in Psychological Medicine.
The results revealed that there were declines of approximately 2 IQ points over time in those who use cannabis frequently compared to those who didn't use cannabis. Further analysis suggested that this decline in IQ points was primarily related to reduction in verbal IQ.
The research involved systematic review and statistical analysis on seven longitudinal studies ...
New insight into how human brains detect and perceive different types of touch, such as fluttery vibrations and steady pressures, has been revealed by UCL scientists with the help of the ancient Chinese cooking ingredient, Szechuan pepper.
Humans have many different types of receptor cells in the skin that allow us to perceive different types of touch. For more than a century, scientists have puzzled over whether touch signals from each type of receptor are processed independently by the brain, or whether these different signals interact before reaching conscious perception.
For the study, published in Proceedings of the Royal Society B, UCL researchers took a novel approach to this question by stimulating one type of touch receptor chemically, and another type mechanically. ...
Investors' moods are affected by gloomy weather. New research from Copenhagen Business School recommends entrepreneurs looking for finance should be aware of the weather forecast at the time they want to launch their crowdfunding campaigns.
The researchers wanted to explore whether weather-induced moods can explain crowdfunders' contributions and focused on the role of investors' moods and emotions including day-to-day decisions on the crowdfunding platform Companisto.
"Financial investment plays a vital role in the success of an entrepreneurial venture ...
Molecules consisting of many atoms are complex structures. The outer electrons are distributed among the different orbitals, and their shape and occupation determine the chemical behaviour and reactivity of the molecule. The configuration of these orbitals can be analysed experimentally. Synchrotron sources such as BESSY II provide a method for this purpose: Resonant inelastic X-ray scattering (RIXS). However, to obtain information about the orbitals from experimental data, quantum chemical simulations are necessary. Typical computing times for larger molecules take weeks, even on high-performance computers.
Speeding up the evaluation
"Up to now, these calculations have mostly been carried out subsequent to the measurements", explains theoretical chemist Dr. Vinicius Vaz da Cruz, ...
Researchers at Lund University in Sweden believe they have identified a gene variant that can cause cerebral small vessel disease and stroke. The study is published in Neurology Genetics.
"The patients we have studied are from the same extended family, and several of them have been diagnosed with cerebral small vessel disease and suffered strokes. After tissue examination and using genetic sequencing methods, we found that they were carriers of a new gene variant that could be connected to their diagnoses," says Andreea Ilinca, researcher at Lund University ...