A third of Americans say they are unlikely or hesitant to get COVID-19 vaccine
UC Davis nationwide survey
2021-01-29
(Press-News.org) News reports indicate COVID-19 vaccines are not getting out soon enough nor in adequate supplies to most regions, but there may be a larger underlying problem than shortages. A University of California, Davis, study found that more than a third of people nationwide are either unlikely or at least hesitant to get a COVID-19 vaccine when it becomes available to them.
The results are from public polling of more than 800 English-speaking adults nationwide in a study published online earlier this month in the journal Vaccine.
"Our research indicates that vaccine uptake will be suboptimal ... with 14.8 percent of respondents being unlikely to get vaccinated and another 23 percent unsure," said Jeanette B. Ruiz, assistant professor of teaching communication at UC Davis and lead author of the study.
"Even though vaccination remains one of the most effective public health initiatives, some still doubt the efficacy and safety of vaccines. Unfortunately, the seemingly rushed process of the COVID-19 vaccine may have further fueled these doubts."
Co-author is Robert Bell, emeritus professor of communication, UC Davis.
Respondents cited vaccine safety and effectiveness assessments as the primary basis for hesitancy, authors said.
In the study, compensated participants were recruited from the United States through an Internet survey panel of 2.5 million residents developed by a commercial survey firm. Recruitment was based on quota sampling to produce a U.S. census-matched sample representative of the nation, and was representative of the U.S. population in terms of region of residence, sex and age, but also diverse with regard to all demographic variables assessed.
Researchers measured the respondents' intention to vaccinate; demographic and health status profile of individuals least likely to vaccinate; general vaccine knowledge and vaccine conspiracy beliefs; and the role of media and partisan politics played in their resistance to vaccination.
Political party, health risk factors, media contribute to attitudes
Authors indicated demographic characteristics, vaccine knowledge, perceived vulnerability to COVID-19, risk factors for COVID-19, and politics likely contribute to vaccination hesitancy. The study was conducted relatively early in the pandemic outbreak during two days in June 2020.
Demographic predictors of likelihood of being vaccinated against COVID-19 included having an income of $120,000 or higher, or being a Democrat (in comparison to the reference category Republican). The members of three political groups -- Democrat, Republican or Independent -- did not differ in their reported vaccine knowledge, however. One fourth of those identifying with no political party reported they were not likely to get vaccinated.
Media had an effect too. Respondents relying primarily on social media for information about COVID-19 anticipated a lower likelihood of COVID-19 vaccine acceptance. Those reporting getting their information from various other media did not show significant differences in vaccine acceptance, but viewers of Fox News did report being more hesitant than viewers of other broadcast news, the research showed. Authors noted that it is possible that individuals gravitate toward the cable news networks that present a view on the pandemic that is aligned with their own opinions.
Media reports have regularly noted that men, adults age 65 and over, and individuals with pre-existing conditions are most vulnerable to COVID-19, and respondents from these groups said they were more likely to accept a future vaccine in this survey. A majority of the least-educated respondents did not expect to get vaccinated against COVID-19, researchers said.
The top four reasons given for vaccination hesitancy were as follows: concerns about vaccine side effects, worries about allergic responses to the vaccine, doubts about vaccine effectiveness and a preference for developing immunity through infection. Other reasons were less frequently cited -- including being healthy, fear of needles, being immune from past infection, being young and lack of concern about developing a serious illness.
Unfortunately, the health disparities present in the spread and treatment of COVID-19 were reflected in survey participants' vaccination hesitancy estimations," researchers said in the paper. "The pandemic has especially burdened the African American, Latino and Native American communities, who account for a disproportionate number of COVID-19 cases and deaths. Greater likelihood of COVID-19 vaccine acceptance was associated with more knowledge about vaccines, less acceptance of vaccine conspiracies, elevated COVID-19 threat appraisals and being current with influenza immunization."
Primary Findings Summary
Male, older, white, married, and those from higher-income households more likely to vaccinate.
Republicans and Fox News viewers were less likely to vaccinate.
Being currently immunized against influenza predicted COVID-19 vaccination intent.
A better understanding of COVID-19 vaccination hesitancy is needed.
INFORMATION:
Link to study:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0264410X21000141
Additional Media Resources
Vaccine Myths in Social Media Can Be Effectively Reduced
https://www.ucdavis.edu/news/vaccine-myths-social-media-can-be-effectively-reduced-credible-fact-checking
UC Davis Live: Combating Vaccine Misinformation
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4OrGUI3IXis
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-29
WOODS HOLE, Mass. -- The most powerful substance in the human brain for neuronal communication is glutamate. It is by far the most abundant, and it's implicated in all kinds of operations. Among the most amazing is the slow restructuring of neural networks due to learning and memory acquisition, a process called synaptic plasticity. Glutamate is also of deep clinical interest: After stroke or brain injury and in neurodegenerative disease, glutamate can accumulate to toxic levels outside of neurons and damage or kill them.
Shigeki Watanabe of Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, a familiar face at the Marine Biological Laboratory (MBL) as a faculty member and researcher, is hot on the ...
2021-01-29
RIVERSIDE, Calif. -- When we step on the car brake upon seeing a red traffic light ahead, a sequence of events unfolds in the brain at lightning speed.
The image of the traffic light is transferred from our eyes to the visual cortex, which, in turn, communicates to the premotor cortex -- a section of the brain involved in preparing and executing limb movements. A signal is then sent to our foot to step on the brake. However, brain region that helps the body go from "seeing" to "stepping" is still a mystery, frustrating neuroscientists and psychologists.
To unpack this "black box," a team of neuroscientists at the University of California, Riverside, has ...
2021-01-29
A new report combining forecasting and expert prediction data, predicts that 125,000 lives could be saved by the end of 2021 if 50% or more of the U.S. population initiated COVID vaccination by March 1, 2021.
"Meta and consensus forecast of COVID-19 targets," developed by Thomas McAndrew, a computational scientist and faculty member at Lehigh University's College of Health, and colleagues, incorporates data from experts and trained forecasters, combining their predictions into a single consensus forecast. In addition McAndrew and his team produce a metaforecast, which is a combination of an ensemble of computational models and their consensus forecast.
In addition to predictions related to the impact of vaccinations, ...
2021-01-29
Researchers at Linköping University, Sweden, have developed a proton trap that makes organic electronic ion pumps more precise when delivering drugs. The new technique may reduce drug side effects, and in the long term, ion pumps may help patients with symptoms of neurological diseases for which effective treatments are not available. The results have been published in Science Advances.
Approximately 6% of the world's population suffer from neurological diseases such as epilepsy, Parkinson's disease, and chronic pain. However, currently available drug delivery methods - mainly tablets and injections - place the drug in locations where it is not required. This can lead to side effects ...
2021-01-29
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- In many ways, our brain and our digestive tract are deeply connected. Feeling nervous may lead to physical pain in the stomach, while hunger signals from the gut make us feel irritable. Recent studies have even suggested that the bacteria living in our gut can influence some neurological diseases.
Modeling these complex interactions in animals such as mice is difficult to do, because their physiology is very different from humans'. To help researchers better understa nd the gut-brain axis, MIT researchers have developed an "organs-on-a-chip" system that replicates interactions between the brain, liver, and colon.
Using that system, the researchers were able to model the influence that microbes living in the gut have on both healthy brain tissue and tissue samples derived ...
2021-01-29
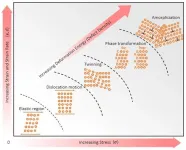
An international team of researchers produced islands of amorphous, non-crystalline material inside a class of new metal alloys known as high-entropy alloys.
This discovery opens the door to applications in everything from landing gears, to pipelines, to automobiles. The new materials could make these lighter, safer, and more energy efficient.
The team, which includes researchers from the University of California San Diego and Berkeley, as well as Carnegie Mellon University and University of Oxford, details their findings in the Jan. 29 issue of Science Advances.
"These present ...
2021-01-29
In 2017, the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine went to three scientists who uncovered the molecular mechanisms that control the circadian rhythm, otherwise known as the "wake-sleep" cycle. To carry out their work, the scientists used the common fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster, making this the sixth Nobel to be awarded to research involving it.
Fruitful fruit flies
Life scientists have been using Drosophila for over a century now. First proposed by entomologist Charles W. Woodworth as a model organism, its use in research was pioneered by geneticist Thomas H. Morgan who ran his famous ...
2021-01-29
As any cook knows, some liquids mix well with each other, but others do not. For example, when a tablespoon of vinegar is poured into water, a brief stir suffices to thoroughly combine the two liquids. However, a tablespoon of oil poured into water will coalesce into droplets that no amount of stirring can dissolve. The physics that governs the mixing of liquids is not limited to mixing bowls; it also affects the behavior of things inside cells. It's been known for several years that some proteins behave like liquids, and that some liquid-like proteins don't mix together. However, very little is known about how these liquid-like proteins behave on cellular surfaces.
"The separation between two liquids that won't mix, like oil and water, is known as ...
2021-01-29
January 29, 2021 -- A study at Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health and Columbia University Irving Medical Center has found that Medicaid expansion in 2014 in New York State was associated with a statistically significant reduction in severe maternal morbidity in low-income women during delivery hospitalizations compared with high-income women. The decrease was even more pronounced in racial and ethnic minority women than in White women. Until now there was little research on the link between ACA Medicaid expansion and maternal health outcomes. The findings are published online in the journal of the International Anesthesia Research Society, Anesthesia & Analgesia.
"Our findings indicate that the 2014 ...
2021-01-29
LA JOLLA--(January 29, 2021) As scientists learn more about the microorganisms that colonize the body--collectively called the microbiota--one area of intense interest is the effect that these microbes can have on the brain. A new study led by Salk Institute scientists has identified a strain of E. coli bacteria that, when living in the guts of female mice, causes them to neglect their offspring.
The findings, published January 29, 2021, in the journal Science Advances, show a direct link between a particular microbe and maternal behavior. Although the research was done in mice, it adds to the growing body of science demonstrating that microbes in the gut are important for brain health and can affect development and behavior.
"To our knowledge, this is the first demonstration ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] A third of Americans say they are unlikely or hesitant to get COVID-19 vaccine
UC Davis nationwide survey