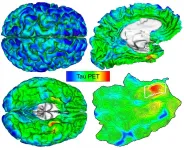
Automated imaging detects and tracks brain protein involved in Alzheimer's disease
The method may lead to earlier diagnoses, when treatments are most effective
2021-02-02
(Press-News.org) BOSTON - Amyloid-beta and tau are the two key abnormal protein deposits that accumulate in the brain during the development of Alzheimer's disease, and detecting their buildup at an early stage may allow clinicians to intervene before the condition has a chance to take hold. A team led by investigators at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) has now developed an automated method that can identify and track the development of harmful tau deposits in a patient's brain. The research, which is published in END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Opioid prescriptions remained elevated two years after critical care
2021-02-02
Nearly 11 percent of people admitted to an intensive care unit in Sweden between 2010 and 2018 received opioid prescriptions on a regular basis for at least six months and up to two years after discharge. That is according to a study by researchers at Karolinska Institutet published in Critical Care Medicine. The findings suggest some may become chronic opioid users despite a lack of evidence of the drugs' long-term effectiveness and risks linked to increased mortality.
"We know that the sharp rise in opioid prescriptions in the U.S. has contributed to a deadly opioid crisis there," says first author Erik von Oelreich, PhD student in the Department of Physiology and ...
Decision-support tool could reduce unnecessary antibiotic prescriptions for child diarrhoea
2021-02-02
A decision-support tool that could be accessed via mobile devices may help clinicians in lower-resource settings avoid unnecessary antibiotic prescriptions for children with diarrhoea, a study published today in eLife shows.
The preliminary findings suggest that incorporating real-time environmental, epidemiologic, and clinical data into an easy-to-access, electronic tool could help clinicians appropriately treat children with diarrhoea even when testing is not available. This could help avoid the overuse of antibiotics, which contributes to the emergence of drug-resistant bacteria.
"Diarrhoea is a common condition among children ...
International research network identifies triggers for severe course of liver cirrhosis
2021-02-02
FRANKFURT. Chronic liver disease and even cirrhosis can go unnoticed for a long time because many patients have no symptoms: the liver suffers silently. When the body is no longer able to compensate for the liver's declining performance, the condition deteriorates dramatically in a very short time: tissue fluid collects in the abdomen (ascites), internal bleeding occurs in the oesophagus and elsewhere, and the brain is at risk of being poisoned by metabolic products. This acute decompensation of liver cirrhosis can develop into acute-on-chronic liver failure with inflammatory reactions throughout the body and failure of several organs.
In the PREDICT study, led ...
Good customer service can lead to higher profits, even for utilities without competition
2021-02-02
BLOOMINGTON, Ind. - In Lily Tomlin's classic SNL comedy sketch, her telephone operator "Ernestine" famously delivers the punchline, "We don't care. We don't have to. We're the Phone Company." But new research finds that satisfied customers mean increased profits even for public utilities that don't face competition.
Little is known about effect of customer satisfaction at utilities. As a result, utility managers are often unsure how much to invest in customer service - if anything at all. The issue also is of interest to regulators responsible for protecting consumers.
The study, in ...
Finding rare birds is never a picnic, contrary to popular Patagonia belief
2021-02-02
CORVALLIS, Ore. - One of birdwatching's most commonly held and colorfully named beliefs, the Patagonia Picnic Table Effect, is more a fun myth than a true phenomenon, Oregon State University research suggests.
Owing its moniker to an Arizona rest area, the Patagonia Picnic Table Effect, often shortened to PPTE, has for decades been cited as a key driver of behavior, and rare-species-finding success, among participants in the multibillion-dollar recreational birding business - an industry that has gotten even stronger during a pandemic that's shut down so many other activities.
But a study led by an OSU College of Science ...
Beyond qubits: Sydney takes next big step to scale up quantum computing
2021-02-02
Scientists and engineers at the University of Sydney and Microsoft Corporation have opened the next chapter in quantum technology with the invention of a single chip that can generate control signals for thousands of qubits, the building blocks of quantum computers.
"To realise the potential of quantum computing, machines will need to operate thousands if not millions of qubits," said Professor David Reilly, a designer of the chip who holds a joint position with Microsoft and the University of Sydney.
"The world's biggest quantum computers currently operate with just 50 or so qubits," he said. "This small scale is partly because of limits to the physical architecture that control the qubits."
"Our ...
Not too big, not too small: Goldilocks analogy found in maze navigation
2021-02-02
New research from the Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology Graduate University (OIST) has found a surprising randomness for how fluids choose their path around obstacles that depends on their spacing. This has important implications for a range of scenarios - from oil recovery and groundwater remediation, to understanding the movement of fluids through biological systems. The research was published in Physical Review Letters.
Scientists from OIST's Micro/Bio/Nanofluidics Unit created a tiny set up comprised of two microscopic cylinders, each around the width of a human hair, placed side-by-side in a channel. This created a choice of three possible paths for a fluid to take past the pair of obstacles. A viscoelastic fluid, which is like that ...
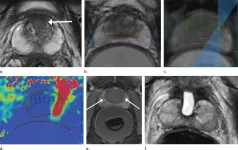
Ultrasound technique treats prostate cancer with minimal side effects
2021-02-02
OAK BROOK, Ill. - A technique that delivers high-intensity focused ultrasound to targeted tissue under MRI guidance effectively treats intermediate-risk prostate cancer with minimal side effects, according to a study published in Radiology.
Prostate cancer is the most common cancer among men, aside from non-melanoma skin cancers. Common treatments to the entire gland, such as surgery and radiation therapy, are effective in eliminating the cancer, but they often leave patients with incontinence and sexual dysfunction.
A class of treatments called focal therapy offers an alternative for some men with intermediate-risk disease that is still confined to the prostate. In focal therapy, the cancer is ablated, or destroyed, by either ...
Age groups that sustain resurging COVID-19 epidemics in the United States
2021-02-02
By late summer 2020, the resurgence of COVID-19 in the United States was largely driven by adults between the ages of 20 and 49, a new study finds. The results indicate that in locations where novel highly transmissible SARS-CoV-2 lineages have not yet established, additional interventions among adults of these ages could bring resurgent COVID-19 epidemics under control and avert deaths. Following initial declines in the number of reported SARS-CoV-2 infections and deaths - a result largely attributed to non-pharmaceutical interventions - a resurgence in transmission of COVID-19 occurred in the United States and Europe beginning in August 2020. Understanding the age demographics that drove this is crucial. For example, between August ...
Tracking cells with omnidirectional visible laser particles
2021-02-02
Laser particles are micrometre and nanometre lasers in the form of particles dispersible in aqueous solution, which have attracted considerable interest in the life sciences as a promising new optical probe. Laser particles emit highly bright light with extremely narrow spectral bandwidth. By transferring laser particles into live cells as shown in Figure 1, individual cells in a heterogeneous population can be tracked using each intracellular particle's specific spectral fingerprint as an optically readable barcode. However, laser particles emit directional light (Figure 2) and freely tumble inside living cells, their orientation varying randomly over time. Therefore optical readout of these labels results ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Black soldier fly larvae show promise for safe organic waste removal
People with COPD commonly misuse medications
How periodontitis-linked bacteria accelerate osteoporosis-like bone loss through the gut
Understanding how cells take up and use isolated ‘powerhouses’ to restore energy function
Ten-point plan to deliver climate education unveiled by experts
Team led by UC San Diego researchers selected for prestigious global cancer prize
Study: Reported crop yield gains from breeding may be overstated
Stem cells from human baby teeth show promise for treating cerebral palsy
Chimps’ love for crystals could help us understand our own ancestors’ fascination with these stones
Vaginal estrogen therapy not linked to cancer recurrence in survivors of endometrial cancer
How estrogen helps protect women from high blood pressure
Breaking the efficiency barrier: Researchers propose multi-stage solar system to harness the full spectrum
A new name, a new beginning: Building a green energy future together
From algorithms to atoms: How artificial intelligence is accelerating the discovery of next-generation energy materials
Loneliness linked to fear of embarrassment: teen research
New MOH–NUS Fellowship launched to strengthen everyday ethics in Singapore’s healthcare sector
Sungkyunkwan University researchers develop next-generation transparent electrode without rare metal indium
What's going on inside quantum computers?: New method simplifies process tomography
This ancient plant-eater had a twisted jaw and sideways-facing teeth
Jackdaw chicks listen to adults to learn about predators
Toxic algal bloom has taken a heavy toll on mental health
Beyond silicon: SKKU team presents Indium Selenide roadmap for ultra-low-power AI and quantum computing
Sugar comforts newborn babies during painful procedures
Pollen exposure linked to poorer exam results taken at the end of secondary school
7 hours 18 mins may be optimal sleep length for avoiding type 2 diabetes precursor
Around 6 deaths a year linked to clubbing in the UK
Children’s development set back years by Covid lockdowns, study reveals
Four decades of data give unique insight into the Sun’s inner life
Urban trees can absorb more CO₂ than cars emit during summer
Fund for Science and Technology awards $15 million to Scripps Oceanography
[Press-News.org] Automated imaging detects and tracks brain protein involved in Alzheimer's diseaseThe method may lead to earlier diagnoses, when treatments are most effective