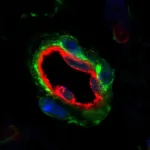
Moffitt researchers discover mechanism that regulates anti-tumor activity of immune cells
IgA regulates immune cell activity by inhibiting RAS signaling and recognizing tumor markers
2021-02-03
(Press-News.org) TAMPA, Fla. -- The prognosis of ovarian cancer is poor, with an estimated five-year survival of only 40% for advanced disease, the stage at which most ovarian carcinomas are diagnosed. These poor outcomes are partly due to the lack of effective therapies for advanced disease and recurrence. Immunotherapies hold promise for many types of cancer; however, studies have shown that patients with ovarian cancer do not have strong responses to existing drugs. In a new article published in Nature, Moffitt Cancer Center researchers demonstrate why some ovarian cancer patients evolve better than others and suggest possible approaches to improve patient outcomes.
Immunotherapeutic drugs activate T cells, a type of immune cell, to put up a defense against tumor cells. Immunotherapies are approved to treat several different types of cancer and have greatly changed the standard of care and improved patient outcomes. However, in ovarian cancer, clinical studies using immunotherapies aimed at stimulating T cells resulted in modest response rates. Studies have suggested that cancer patients who have a higher presence of other immune cells, such as plasma and memory B cells, could respond better to immunotherapies, but how these cell types promote better outcomes is unclear. Moffitt researchers wanted to confirm whether antibodies produced by these cells are associated with better outcomes and assess how these cells contribute to the spontaneous anti-tumor immune response against ovarian cancer.
The researchers analyzed a panel of 534 samples from ovarian cancer patients and found that patients who had a higher infiltration of B cells or B cell-derived plasma cells had better outcomes. B cells are a type of immune cell that produce antibodies and express one of five types of B cell receptors on their surface: IgM, IgD, IgG, IgE or IgA. These isotypes regulate different B cell signaling pathways and control B cell processes.
The surprise came when, upon further analysis of the samples, the Moffitt team discovered that the antibodies produced by B and plasma cells were predominantly of the IgA subtype, followed by IgG.
"We found that the presence of IgA regulated downstream signaling pathways of the ovarian cancer cells. Specifically, IgA resulted in inhibition of the RAS signaling pathway, which is known to contribute to ovarian cancer development," said Jose Conejo-Garcia, M.D., Ph.D., chair of Moffitt's Immunology Department.
This inhibition of RAS sensitized the tumor cells to T cell mediated cell killing, produced by both novel CAR T cells and tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes. The team also assessed that IgA and IgG secreted by the B cells recognized specific ovarian tumor cell surface markers and stimulated other immune cells called myeloid cells to target ovarian cancer cells for destruction.
These data provide new insights into how components of the immune system regulate ovarian cancer progression and offer new opportunities to develop improved targeted agents. This includes a repertoire of tumor-derived antibodies that can be effectively used as novel immunotherapeutic agents. In addition, the study provides a mechanistic rationale for integrated antibody responses in the development of novel immunotherapies, which until now have been based on T cell-centric approaches.
"The findings indicate that immunotherapies that boost both coordinated B and T cell responses against ovarian cancer, an immunogenic disease currently resistant to checkpoint inhibitors, are likely to show superior therapeutic benefit," said Subir Biswas, Ph.D., first author and postdoctoral fellow in the Conejo-Garcia lab.
INFORMATION:
The study finally paves the way for the use of antibodies different from IgG as immunotherapeutic agents for at least tumors currently resistant to conventional immune checkpoint blockade.
This study was supported by the National Institutes of Health (P30CA076292, R01CA240434, R01CA157664, R01CA124515, T32CA009140, U01CA200495) and the American Cancer Society (PF-18-041-1-LIB).
About Moffitt Cancer Center
Moffitt is dedicated to one lifesaving mission: to contribute to the prevention and cure of cancer. The Tampa-based facility is one of only 51 National Cancer Institute-designated Comprehensive Cancer Centers, a distinction that recognizes Moffitt's scientific excellence, multidisciplinary research, and robust training and education. Moffitt is the No. 11 cancer hospital and has been nationally ranked by U.S. News & World Report since 1999. Moffitt's expert nursing staff is recognized by the American Nurses Credentialing Center with Magnet® status, its highest distinction. With more than 7,000 team members, Moffitt has an economic impact in the state of $2.4 billion. For more information, call 1-888-MOFFITT (1-888-663-3488), visit MOFFITT.org, and follow the momentum on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-03
There is an impassioned debate taking place in medicine on whether race-based considerations should be a factor in research, diagnoses, or treatments. Those on one side assert that race should be ignored entirely because it is a societal construct with no biological basis, and accordingly many hospitals are abandoning long-established "race corrections" in medical algorithms and diagnostics. Others, like Meghan McGarry, MD, MS, assistant professor of pediatrics at UC San Francisco, say that we can't completely ignore race, precisely because science is rarely free of societal influence - the structural inequality ...
2021-02-03
Since element 99 - einsteinium - was discovered in 1952 at the Department of Energy's Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) from the debris of the first hydrogen bomb, scientists have performed very few experiments with it because it is so hard to create and is exceptionally radioactive. A team of Berkeley Lab chemists has overcome these obstacles to report the first study characterizing some of its properties, opening the door to a better understanding of the remaining transuranic elements of the actinide series.
Published in the journal Nature, the study, "Structural and Spectroscopic Characterization of an Einsteinium Complex," was co-led by Berkeley Lab scientist Rebecca Abergel and Los ...
2021-02-03
The Arctic Ocean was covered by up to 900 m thick shelf ice and was filled entirely with freshwater at least twice in the last 150,000 years. This surprising finding, reported in the latest issue of the journal Nature, is the result of long-term research by scientists from the Alfred Wegener Institute and the MARUM. With a detailed analysis of the composition of marine deposits, the scientists could demonstrate that the Arctic Ocean as well as the Nordic Seas did not contain sea-salt in at least two glacial periods. Instead, these oceans were filled with large amounts of freshwater under a thick ice shield. This water could then be released into the North Atlantic in very short periods of time. Such sudden freshwater inputs could explain rapid climate oscillations for which no satisfying ...
2021-02-03
What The Study Did: Data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention were used to look at changes in emergency department visits for mental health, suicide attempts, drug and opioid overdoses and outcomes of violence before and during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Authors: Kristin M. Holland, Ph.D., M.P.H., of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in Atlanta, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2020.4402)
Editor's Note: Please see the article for additional information, ...
2021-02-03
What The Study Did: COVID-19 outcomes including hospitalization and in-hospital death were compared between people living with or without diagnosed HIV in New York State.
Authors: Eli S. Rosenberg, Ph.D., of the State University of New York in Rensselaer, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.37069)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and ...
2021-02-03
Mechanism for control of antibiotic production in soil bacteria is visualised for the first time by scientists at University of Warwick and Monash University
Research reported in Nature could lead to improved manufacturing of existing antibiotics, and open up opportunities to discover new ones
The majority of clinically used antibiotics are derived from soil bacteria, but can be hard to find because their production is switched off in laboratory cultures
The discovery of how hormone-like molecules turn on antibiotic production in soil bacteria could unlock the untapped opportunities for medicines that are under our very feet.
An international team of scientists working at the University of Warwick, UK, and Monash ...
2021-02-03
ANN ARBOR, Mich. - The suicide rate among American adolescents has rose drastically over the last decade, but many at-risk youths aren't receiving the mental health services they need.
In fact, one of the greatest challenges is identifying the young people who need the most help.
Now, researchers have developed a personalized system to better detect suicidal youths. The novel, universal screening tool helps caregivers reliably predict an adolescent's suicide risk - alerting them to which ones need follow-up interventions - according to Michigan Medicine-led findings published in JAMA Psychiatry.
"Too many young people are dying by suicide and many at high risk go completely unrecognized and untreated," says lead author Cheryl King, Ph.D., ...
2021-02-03
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- Twenty years ago this month, the first draft of the human genome was publicly released. One of the major surprises that came from that project was the revelation that only 1.5 percent of the human genome consists of protein-coding genes.
Over the past two decades, it has become apparent that those noncoding stretches of DNA, originally thought to be "junk DNA," play critical roles in development and gene regulation. In a new study published today, a team of researchers from MIT has published the most comprehensive map yet of this noncoding DNA.
This map provides in-depth annotation of epigenomic marks -- modifications indicating which genes are turned on or off in different types of cells -- across 833 tissues and cell types, a significant increase over ...
2021-02-03
DALLAS - Feb. 3, 2021 - Gaining more fat cells is probably not what most people want, although that might be exactly what they need to fight off diabetes and other diseases. How and where the body can add fat cells has remained a mystery - but two new studies from UT Southwestern provide answers on the way this process works.
The studies, both published online today in Cell Stem Cell, describe two different processes that affect the generation of new fat cells. One reports how fat cell creation is impacted by the level of activity in tiny organelles inside cells called mitochondria. The other outlines a process that prevents new fat cells from developing in one fat storage area in ...
2021-02-03
People with severe mental disorders have a significantly increased risk of dying from COVID-19. This has been shown in a new study from Umeå University and Karolinska Institutet in Sweden. Among the elderly, the proportion of deaths due to COVID-19 was almost fourfold for those with severe mental disorders compared to non-mentally ill people in the same age.
"We see a high excess mortality due to COVID-19 among the elderly with severe mental disorders, which gives us reason to consider whether this group should be given priority for vaccines," says Martin Maripuu, associate professor at Umeå University.
In the current study, the researchers studied data covering the entire Swedish population over the age of 20 during the period from 11 March to 15 June 2020. Among citizens ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Moffitt researchers discover mechanism that regulates anti-tumor activity of immune cells
IgA regulates immune cell activity by inhibiting RAS signaling and recognizing tumor markers