Fungus that eats fungus could help coffee farmers
2021-02-03
(Press-News.org) Coffee rust is a parasitic fungus and a big problem for coffee growers around the world. A study in the birthplace of coffee - Ethiopia - shows that another fungus seems to have the capacity to supress the rust outbreaks in this landscape.
"Coffee leaf rust is a fungal disease that is a problem for coffee growers around the world, especially on Arabica coffee, which accounts for three quarters of global coffee production and has the finest cup quality. There is a need to learn more about natural solutions instead of just applying pesticides," says Kristoffer Hylander, professor at the Department of Ecology, Environment and Plant Sciences (DEEP) at Stockholm University.
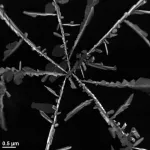
Coffee leaf rust is caused by a parasitic fungus that attacks the leaves of the coffee shrub. In some areas it has previously been known to have a potential natural enemy - a hyperparasitic fungus that grows on top of the rust. However, very little is known about its biology and to what extent it could suppress the rust. This is the first study on the interaction between the rust and its hyperparasite in Ethiopia, the birthplace of Arabica coffee. The coffee plant, the rust and its hyperparasite may have coevolved in Ethiopia for a long time.
Coffee leaf rust generally increases in abundance from the rainy to the dry season. However, it seems like this increase is reduced in places where the hyperparasite is common:
"This is an indication that the hyperparasite may have the potential to reduce outbreaks of the rust in areas where both the rust and the hyperparasite exist together," says Ayco Tack, associate professor at the Department of Ecology, Environment and Plant Sciences (DEEP) at Stockholm University.
It seems like the rust and the hyperparasite thrive in slightly different environments, with the rust adapting well in less humid places and the hyperparasite favouring slightly more humid places such as coffee farms with more shade trees.
"This could be a win-win situation. By increasing the tree cover in coffee plantations with native shade tree species that maintain their leaves during the dry season, we could perhaps benefit both biodiversity and the hyperparasite," says Kristoffer Hylander, professor at the Department of Ecology, Environment and Plant Sciences (DEEP) at Stockholm University.
The authors did not investigate whether the presence of the hyperparasite could lead to better coffee yields, via its effect on rust. The hyperparasite might reduce leaf drop associated with severe rust infection, thus reducing the expected indirect negative effect of the rust on coffee yields.
"This would be one of the next important steps in this research, since yield of coffee (or revenue) matters most for the smallholder coffee farmers. Interestingly, Ethiopia does not seem to have as big a problem with coffee leaf rust as other coffee-producing countries - and it would be interesting to find out if the hyperparasite may be an explanation for this difference. It is also important to note that the effect of coffee leaf rust in this landscape might change with the current global climate change," says Beyene Zewdie, who recently defended his thesis on the ecology of coffee diseases in Ethiopia at the Department of Ecology, Environment and Plant Sciences (DEEP) at Stockholm University.
More detailed experimental studies are needed to explore the relationships between the rust and the hyperparasite. This could enable coffee growers to utilize the hyperparasite as a biological control for the coffee leaf rust in more intensively managed plantations where the rust epidemics are highly problematic.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-03
Many nations place drugs into various schedules or categories according to their risk of being abused and their medical value. At times, drugs are rescheduled to a more restrictive category to reduce misuse by constricting supply. A new study examined lessons from past efforts worldwide to schedule and reschedule drugs to identify general patterns and found that rescheduling drugs can lower use as well as the dangers associated with the drug. The findings have implications for policy.
The study, by researchers at Carnegie Mellon University (CMU), is published in the International Journal of Drug Policy.
"Our review suggests that rescheduling drugs can often disrupt trends in prescribing, use, or harms," says Jonathan Caulkins, professor of operations research and public policy at CMU's ...
2021-02-03
In the first longitudinal study to follow Georgia pre-K students through middle school, Stacey Neuharth-Pritchett, associate dean for academic programs and professor in UGA's Mary Frances Early College of Education, found that participating in pre-K programs positively predicted mathematical achievement in students through seventh grade.
"Students who participated in the study were twice as likely to meet the state standards in their mathematics achievement," said Neuharth-Pritchett. "School becomes more challenging as one progresses through the grades, and so if ...
2021-02-03
Russian enterprises have limited opportunities to carry out technological modernisation on their own. Their technological portfolios reveal a high dependence on imported solutions and a limited deployment of their own developments, HSE University researchers discovered.
In recent years, there has been a growing demand for the use of advanced manufacturing technologies (AMT) in Russia. Between 2011 and 2018, the number of AMT used increased by 33%, and in 2018 they amounted to almost 255,000 units in absolute terms. Meanwhile, innovation strategies focused on independent development of novel manufacturing solutions are not widespread in Russia. Fewer than ...
2021-02-03
GROUND-BREAKING research from the University of Huddersfield, announced ahead of World Cancer Day 2021, proves that scalp cooling physically protects hair follicles from chemotherapy drugs. It is the world's first piece of biological evidence that explains how scalp cooling actually works and the mechanism behind its protection of the hair follicle.
The study, entitled 'Cooling-mediated protection from chemotherapy drug-induced cytotoxicity in human keratinocytes by inhibition of cellular drug uptake', has been published in the peer-reviewed journal PLOS ONE .
The data was part of an innovative hair follicle research project carried out by the dedicated Scalp Cooling ...
2021-02-03
Antimicrobial packaging is being developed to extend the shelf life and safety of foods and beverages. However, there is concern about the transfer of potentially harmful materials, such as silver nanoparticles, from these types of containers to consumables. Now, researchers reporting in ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces illustrate that silver embedded in an antimicrobial plastic can leave the material and form nanoparticles in foods and beverages, particularly in sweet and sugary ones.
Some polymers containing nanoparticles or nanocomposites can slow ...
2021-02-03
In the Namib Desert in southwestern Africa, the Kuiseb River, an ephemeral river which is dry most of the year, plays a vital role to the region. It provides most of the vegetation to the area and serves as a home for the local indigenous people, and migration corridor for many animals. The overall vegetation cover increased by 33% between 1984 and 2019, according to a Dartmouth study published in Remote Sensing .
The study leveraged recent drone imagery and past satellite imagery to estimate past vegetation cover in this linear oasis of the Kuiseb River, a fertile area in the middle of one of the driest deserts ...
2021-02-03
Some of the most commonly used drugs for treating hereditary breast and ovarian cancers may not work the way we thought they did, according to new University of Colorado Boulder research.
The paper, published February 2 in the journal Nature Communications, sheds new light on how they do work and could open the door to new next-generation medications that work better, the authors said.
"Despite the success of these drugs which sell in the billions of dollars per year and treat many thousands of patients, there are many unknowns about their potency and efficacy that if better understood ...
2021-02-03
BUFFALO, N.Y. - A popular streaming service boasts a film inventory approaching 4,000 titles. When it's time to pick a movie, are you more likely to quickly make a decision or meticulously sift through the possibilities?
Psychologists refer to those who search minimally for something to arrive at an adequate choice as "satisficers." It's the "maximizers," meantime, who search exhaustively for what might be considered as the perfect option.
Previous studies exploring both strategies after making a choice often present satisficing as a more psychologically ...
2021-02-03
An important bacterial disease that affects citrus trees and causes lesions, citrus canker has been effectively controlled by spraying copper. However standard management techniques involve spraying excessive amounts of copper and water without consideration for the size of the trees.
"This technique resulted in a waste of resources as well as higher costs, detrimental environmental impact, and risk for development of copper resistant strains," explained plant pathologist Franklin Behlau, who recently published an article discussing a more sustainable approach to managing citrus canker.
Behlau and his colleagues showed that it is possible to control citrus canker by spraying ...
2021-02-03
The instrumental climate record is the cultural heritage of humankind, the result of the diligent work of many generations of people all over the world. However, the changes in the way in which temperature is measured, as well as the environment in which weather stations are located can produce spurious trends. An international study carried out by researchers from the Universitat Rovira i Virgili (URV), the State Meteorology Agency and the University of Bonn (Germany) have succeeded in identifying the most reliable methods that help correct these trends. These "homogenization methods" are a key step in converting the enormous effort made by observers into reliable data about climate change. The results of this research, funded by ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Fungus that eats fungus could help coffee farmers