City, University of London academic tracks COVID-19 dark web marketplace before vaccine
In new research, Dr Andrea Baronchelli and colleagues highlight the importance of the continuous monitoring of dark web marketplaces (DWMs), especially in light of the current shortage and availability of COVID-19 vaccines
2021-02-04
(Press-News.org) New research carried out by City, University of London data scientist, Dr Andrea Baronchelli, and colleagues into the dark web marketplace (DWM) trade in products related to COVID-19, has revealed the need for the continuous monitoring of dark web marketplaces (DWMs) especially in light of the current shortage and availability of coronavirus vaccines.
In their paper, Dark Web Marketplaces and COVID-19: before the vaccine published in the EPJ Data Science, Dr Baronchelli and his colleagues analysed 851,199 listings extracted from 30 DWMs between January 1, 2020 and November 16, 2020 before the advent of the availability of the coronavirus vaccine.
They identify 788 listings directly related to COVID-19 products and monitors the temporal evolution of product categories including Personal Protective Equipment (PPE), medicines (e.g., hydroxychloroquine), and medical fraud.
The authors compare trends in the temporal evolution of trade in these products with variations in public attention, as measured by Twitter posts and Wikipedia page visits.
Among their discoveries, the paper's authors highlight the importance of dark web players such as DarkBay/DBay - the 'eBay of the dark web':
"In our dataset, DarkBay/DBay is featured prominently among DWMs offering COVID-19 specific listings. Ranking in the top 100 sites in the entire dark web, DarkBay/DBay is regarded as the eBay of the dark web because it offers more listings categories than other DWMs. It was also frequently accessible during the period of time monitored during this research, with an uptime of 80%, higher from the 77% uptime of Empire, the largest global DWM at the time of writing".
Critically, the authors highlight the importance of the continuous monitoring of DWMs, especially given shortages in the availability and supply of COVID-19 vaccines in various regions of the world:
"Uninformed citizens exposed to waves of misinformation, such as the ones related to hydroxychloroquine, chloroquine, and azithromycin, may be tempted to shop on DWMs thus exposing themselves to serious health risks. Moreover, the availability of regulated products currently in shortage in the traditional economy undermines anti-price gouging regulations and regulated businesses which sell the same products."
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-04
In data gathered and analyzed over 13 years, the North American Nanohertz Observatory for Gravitational Waves (NANOGrav) Physics Frontiers Center (PFC) has found an intriguing low-frequency signal that may be attributable to gravitational waves.
NANOGrav researchers - including a number from West Virginia University's (WVU's) Department of Physics and Astronomy and the Center for Gravitational Waves and Cosmology - measure the times of arrival of radio pulses from exotic stars called pulsars with large radio telescopes, including the Green Bank Telescope (GBT) in Pocahontas County, ...
2021-02-04
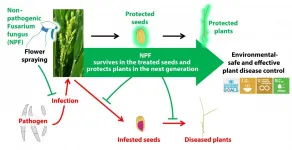
Researchers have developed a new technique to protect rice seeds against fungal infections that can ruin up to half of all rice crops in the world. The biocontrol method, which involves inoculation of flowers with a different fungus that doesn't cause disease and using seeds harvested from the flower to grow crops, is even better at protecting rice plants from diseases than existing fungicide approaches, and could also be used against similar pathogens that affect other staple crops.
The extremely destructive seedborne bakanae disease, which affects rice plants everywhere in the world that the staple crop is grown, is currently typically combatted with either chemical fungicides or ...
2021-02-04
The new therapeutic approach is based on shutting down the viral hepatitis B genome located in the nucleus of infected liver cells. Upon infection of the liver cell, the viral genome is transformed inside the nucleus into a closed circular DNA molecule. This deoxyribonucleic acid is a stable molecule known as covalently closed circular DNA (cccDNA) and serves as the template for the production of new viruses. The cccDNA represents the central reservoir of the hepatitis B viruses and enables their persistence in the liver. The virologist Prof. Dr. Maura Dandri and her team at the UKE managed to prevent the HBV-cccDNA from producing further viruses in the animal model.
The point of attack of their ...
2021-02-04
Treating equine donor stem cells with a growth factor called TGF-β2 may allow them to avoid "tripping" the immune response in recipients, according to new research from North Carolina State University. The work could simplify the stem cell treatment process for ligament and tendon injuries in horses, and may also have implications for human stem cell therapies.
Mesenchymal stem cell therapy is a promising avenue for treating musculoskeletal injuries - particularly tendon and ligament injuries - in horses. Mesenchymal stem cells are adult stem cells found in bone marrow that act as repair directors, producing secretions that recruit paracrine, or healing, factors to the site of injury.
Just as blood cells have "types," ...
2021-02-04
Gels are formed by mixing polymers into fluids to create gooey substances useful for everything from holding hair in place to enabling contact lenses to float over the eye.
Researchers want to develop gels for healthcare applications by mixing in medicinal compounds, and giving patients injections so that the gel releases the active pharmaceutical ingredient over a period of months to avoid weekly or daily needle sticks.
But standing in the way is a problem that's as easily understandable as the difference between using hair gel on a beach versus in a ...
2021-02-04
Virtual 'exergaming' has become a popular way to exercise - especially among younger people - since the release of virtual reality (VR) fitness games on consoles such as Nintendo and Playstation.
But while VR is undoubtedly raising fitness games to a whole new level, researchers at the University of South Australia are cautioning players about the potential side effects of VR, particularly in the first hour after playing.
In a new study published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research, UniSA researchers investigated the consequences of playing one of the most popular VR exergames - Beat Saber* - finding that one in seven players still ...
2021-02-04
Catalysts are key materials in modern society, enabling selective conversion of raw materials into valuable products while reducing waste and saving energy. In case of industrially relevant oxidative dehydrogenation reactions, most known catalyst systems are based on transition metals such as Iron, Vanadium, Molybdenum or Silver. Due to intrinsic drawbacks associated with the use of transition metals, such as rare occurrence, environmentally harmful mining processes, and toxicity, the fact that pure carbon exhibits catalytic activity in this type of reaction and thus has high potential as a sustainable substitution material is of high interest.
To date, the development of carbon-based catalysts for oxidative dehydrogenation reactions may be divided into two ...
2021-02-04
UCC palaeontologists have discovered new evidence that the fate of vertebrate animals over the last 400 million years has been shaped by microscopic melanin pigments.
This new twist in the story of animal evolution is based on cutting-edge analyses of melanin granules - melanosomes - in many different fossil and modern vertebrates, including fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds and mammals. Melanin and melanosomes have traditionally been linked to outermost body tissues such as skin, hair and feathers, with important roles in UV protection and stiffening of tissues. Analyses of where different animals store melanin in the body, however, show that different vertebrate groups concentrate melanin in different organs, revealing ...
2021-02-04
Ultrasound is not only used as an imaging technique but targeted pulses of ultrasound can be used as a highly accurate treatment for a range of brain diseases, for which there were previously only limited treatment options. Over the last few years, several revolutionary techniques of this kind have been developed, primarily in Toronto but also at MedUni Vienna. The Viennese technique improves brain functions by externally activating neurons that are still functional. Improvements can be expected in various neuropsychiatric brain diseases such as Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, stroke, Multiple Sclerosis, and neuralgia. A review jointly written by ...
2021-02-04
Researchers at NUI Galway have identified genomic signatures in women developing the most common type of breast cancer that can be associated with long-term survival. The NUI Galway team analysed the genomes of breast cancer patients to look for associations with survival rates using advanced statistical techniques.
Carried out by Lydia King during her studies in NUI Galway's MSc in Biomedical Genomics programme, the research has been published in the international journal PLOS ONE.
Early detection by national screening programmes and timely treatment for patients diagnosed with "luminal" types of breast cancer have resulted in excellent prognoses with survival rates of over 80% within five years of treatment. The challenge of long-term survival ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] City, University of London academic tracks COVID-19 dark web marketplace before vaccine
In new research, Dr Andrea Baronchelli and colleagues highlight the importance of the continuous monitoring of dark web marketplaces (DWMs), especially in light of the current shortage and availability of COVID-19 vaccines