Study shows flu vaccine lessens COVID-19 symptoms in children
Other vaccines may also prove beneficial in reducing COVID-19 symptoms and complications
2021-02-04
(Press-News.org) Researchers from the University of Missouri School of Medicine have discovered that children who receive a seasonal flu shot are less likely to suffer symptoms from a COVID-19 infection. The finding comes from a review of more than 900 children diagnosed with COVID-19 in 2020.
"It is known that the growth of one virus can be inhibited by a previous viral infection," said Anjali Patwardhan, MD, professor of pediatric rheumatology and child health. "This phenomenon is called virus interference, and it can occur even when the first virus invader is an inactivated virus, such as the case with the flu vaccine."
Patwardhan reviewed records from 905 pediatric patients diagnosed with COVID-19 between February and August 2020 to determine each patient's influenza vaccination history. She discovered the COVID-19 positive children who received the influenza vaccine in the current flu season had lower odds of experiencing symptoms, respiratory problems or severe disease. She also found that children with COVID-19 who received the pneumococcal vaccine also had lower odds of experiencing symptomatic disease.
"Research on the pediatric population is critical because children play a significant role in influencing viral transmission," Patwardhan said. "Understanding the relationship and co-existence of other viruses alongside COVID-19 and knowing the vaccination status of the pediatric patient may help in deploying the right strategies to get the best outcomes."
Patwardhan said it will also be important to explore the connection between vaccinations and COVID-19 symptoms in a larger geographical-multiracial study.
"Based on these findings, we hypothesize that the higher incidence of COVID-19 in minority populations may also reflect their low vaccination rate apart from other health inequalities," Patwardhan said.
INFORMATION:
Patwardhan's co-author is MU School of Medicine colleague Adrienne Ohler, PhD, associate research professor. Their study, "The Flu Vaccination May Have a Protective Effect on The Course of COVID-19 in the Pediatric Population: When Does Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-Cov-2) Meet Influenza," was recently published in the journal Cureus.
The authors declare they have received no financial support for this study and report no conflicts of interest.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-04
Cardiac patients who also have diabetes will be able to do their rehabilitation exercises more safely, thanks to the world's first guidance on the subject, which has been published by international experts including a Swansea University academic.
The guidance will be a crucial resource for healthcare professionals, so they can help the growing number of cardiac rehabilitation patients who also have diabetes.
The guidance, approved by international diabetes organisations, was drawn up by a team including Dr. Richard Bracken of the School of ...
2021-02-04
Scientists at Bielefeld University's Faculty of Physics have succeeded for the first time in imaging the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus with a helium ion microscope. In contrast to the more conventional electron microscopy, the samples do not need a thin metal coating in helium ion microscopy. This allows interactions between the coronaviruses and their host cell to be observed particularly clearly. The scientists have published their findings, obtained in collaboration with researchers from Bielefeld University's Medical School OWL and Justus Liebig University Giessen, in the Beilstein Journal of Nanotechnology.
'The study shows that the helium ion microscope is suitable for imaging coronaviruses - so precisely that the interaction between virus ...
2021-02-04
People undergoing long-term dialysis are almost 4 times more likely to die from COVID-19 and should be prioritized for vaccination, found a new Ontario study published in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal).
"As the COVID-19 pandemic proceeds, focused efforts should be made to protect this population from infection including prioritizing patients on long-term dialysis and the staff treating them for SARS-CoV-2 vaccination," writes Dr. Peter Blake, provincial director, Ontario Renal Network, Ontario Health, and professor, Schulich School of Medicine and Dentistry, Western University, ...
2021-02-04
It is necessary to develop additional COVID-19 vaccines, as different vaccine approaches have their advantages and disadvantages and may work synergistically. Researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden now report that they have developed a prototype vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 using a DNA vaccine platform that is inexpensive, stable, easy to produce, and shows a good safety profile. A study published in Scientific Reports shows that the vaccine induces potent immune responses in mice.
The vaccine, called DREP-S, is administered as DNA and is based on a DNA-launched self-amplifying RNA (DREP) platform developed at Karolinska ...
2021-02-04
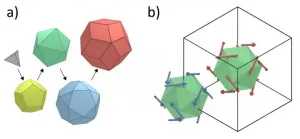
Between chemistry classes, gemstones, and electronics, the idea of crystals, substances with an ordered and periodic arrangement of atoms is quite common. But about 40 years ago, a strange particle was discovered by scientists that hasn't become commonplace in our world yet: quasicrystals. These are structures with curious atomic arrangements, which, while superficially similar to crystals, lack periodicity despite being ordered. Because of their structures, quasicrystals exhibit symmetries forbidden to crystals and are endowed with interesting properties that crystals cannot show, ...
2021-02-04
The unmet HIV prevention and treatment needs of female sex workers and especially their male clients could contribute substantially to ongoing HIV transmission in South Africa, according to a new study led by researchers at the University of Bristol, UK.
The researchers used mathematical modelling to look at the contribution of commercial sex, sex between men, and other heterosexual partnerships to HIV transmission in South Africa.
They found that, over a ten-year period (2010-19), sex between female sex workers and their paying clients contributed 6.9 per cent of new HIV infections, while ...
2021-02-04
In order to fight pathogens, mast cells regulate inflammatory reactions of the immune system. Both mast cells and neutrophils are white blood cells and are critical for the body's immune defense. A team of scientists around the immunologist Prof. Dr. Anne Dudeck and the bioengineer Jan Dudeck has discovered a crucial aspect of the communication between mast cells and neutrophils. These new findings may allow for developing innovative, targeted therapeutic strategies to dampen allergic responses and inflammatory reactions. The results have been published ...
2021-02-04
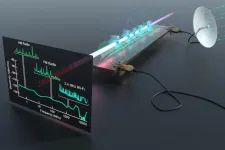
ADELPHI, Md. -- A new quantum sensor can analyze the full spectrum of radio frequency and real-world signals, unleashing new potentials for soldier communications, spectrum awareness and electronic warfare.
Army researchers built the quantum sensor, which can sample the radio-frequency spectrum--from zero frequency up to 20 GHz--and detect AM and FM radio, Bluetooth, Wi-Fi and other communication signals.
The Rydberg sensor uses laser beams to create highly-excited Rydberg atoms directly above a microwave circuit, to boost and hone in on the portion of the spectrum being measured. The Rydberg atoms are sensitive to the circuit's voltage, enabling the device to be used as a sensitive probe for the wide range of signals in the RF spectrum.
"All ...
2021-02-04
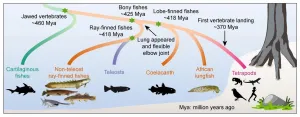
People traditionally think that lungs and limbs are key innovations that came with the vertebrate transition from water to land. But in fact, the genetic basis of air-breathing and limb movement was already established in our fish ancestor 50 million years earlier. This, according to a recent genome mapping of primitive fish conducted by the University of Copenhagen, among others. The new study changes our understanding of a key milestone in our own evolutionary history.
There is nothing new about humans and all other vertebrates having evolved from fish. The conventional understanding has been that certain fish shimmied landwards roughly ...
2021-02-04
A global team of researchers has developed a new strategy for fast and reliable antibody tests, which can quantify the immune response induced by vaccination and reveal the timeline and stage of pathogen infection.
Led by Professor Martin Hegner, Principal Investigator in CRANN and Trinity College Dublin's School of Physics, the team's one-step quantitative antibody tests are conducted using (blood) serum and are on a par with the gold-standard, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) technique.
The major advantage of the newly developed nano technique with respect to ELISA tests is that it is equally ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Study shows flu vaccine lessens COVID-19 symptoms in children
Other vaccines may also prove beneficial in reducing COVID-19 symptoms and complications