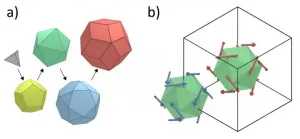
(Press-News.org) Between chemistry classes, gemstones, and electronics, the idea of crystals, substances with an ordered and periodic arrangement of atoms is quite common. But about 40 years ago, a strange particle was discovered by scientists that hasn't become commonplace in our world yet: quasicrystals. These are structures with curious atomic arrangements, which, while superficially similar to crystals, lack periodicity despite being ordered. Because of their structures, quasicrystals exhibit symmetries forbidden to crystals and are endowed with interesting properties that crystals cannot show, such as high resistance to heat flow, current flow, and corrosion.
Since their discovery, quasicrystals have been researched extensively by materials scientists around the world. Due to their rarity, scientists have often resorted to studying models mimicking them, called approximants. Recently, in a class of gold-based approximants, called "Tsai-type approximants", the presence of magnetic order was detected whose type can be controlled by the composition of the approximants--an exciting possibility for material scientists to explore.
In such approximants of increasing complexity, such as that composed of gold (Au), aluminum (Al), and terbium (Tb), the magnetic order was found to be antiferromagnetic, where each ion in the crystal acts as a small magnets with its poles opposite to those of its neighbors. In a new study published in END
Quasicrystal-clear: Material reveals unique shifting surface structure under microscope
Scientists reveal peculiar surface structure in materials resembling quasicrystals with interesting implications for its magnetic properties
2021-02-04
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Clients of female sex workers should be targeted for HIV prevention and treatment in South Africa
2021-02-04
The unmet HIV prevention and treatment needs of female sex workers and especially their male clients could contribute substantially to ongoing HIV transmission in South Africa, according to a new study led by researchers at the University of Bristol, UK.
The researchers used mathematical modelling to look at the contribution of commercial sex, sex between men, and other heterosexual partnerships to HIV transmission in South Africa.
They found that, over a ten-year period (2010-19), sex between female sex workers and their paying clients contributed 6.9 per cent of new HIV infections, while ...
Mast cells: Sentinels and high-speed messengers of the immune defense
2021-02-04
In order to fight pathogens, mast cells regulate inflammatory reactions of the immune system. Both mast cells and neutrophils are white blood cells and are critical for the body's immune defense. A team of scientists around the immunologist Prof. Dr. Anne Dudeck and the bioengineer Jan Dudeck has discovered a crucial aspect of the communication between mast cells and neutrophils. These new findings may allow for developing innovative, targeted therapeutic strategies to dampen allergic responses and inflammatory reactions. The results have been published ...
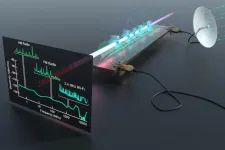
New quantum receiver the first to detect entire radio frequency spectrum
2021-02-04
ADELPHI, Md. -- A new quantum sensor can analyze the full spectrum of radio frequency and real-world signals, unleashing new potentials for soldier communications, spectrum awareness and electronic warfare.
Army researchers built the quantum sensor, which can sample the radio-frequency spectrum--from zero frequency up to 20 GHz--and detect AM and FM radio, Bluetooth, Wi-Fi and other communication signals.
The Rydberg sensor uses laser beams to create highly-excited Rydberg atoms directly above a microwave circuit, to boost and hone in on the portion of the spectrum being measured. The Rydberg atoms are sensitive to the circuit's voltage, enabling the device to be used as a sensitive probe for the wide range of signals in the RF spectrum.
"All ...
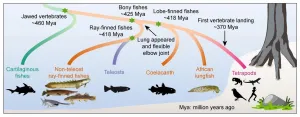
Surprising new research: We're more like primitive fishes than once believed
2021-02-04
People traditionally think that lungs and limbs are key innovations that came with the vertebrate transition from water to land. But in fact, the genetic basis of air-breathing and limb movement was already established in our fish ancestor 50 million years earlier. This, according to a recent genome mapping of primitive fish conducted by the University of Copenhagen, among others. The new study changes our understanding of a key milestone in our own evolutionary history.
There is nothing new about humans and all other vertebrates having evolved from fish. The conventional understanding has been that certain fish shimmied landwards roughly ...
New technique rapidly quantifies immune response following vaccination
2021-02-04
A global team of researchers has developed a new strategy for fast and reliable antibody tests, which can quantify the immune response induced by vaccination and reveal the timeline and stage of pathogen infection.
Led by Professor Martin Hegner, Principal Investigator in CRANN and Trinity College Dublin's School of Physics, the team's one-step quantitative antibody tests are conducted using (blood) serum and are on a par with the gold-standard, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) technique.
The major advantage of the newly developed nano technique with respect to ELISA tests is that it is equally ...
Emory MVA COVID-19 vaccine safe and effective in animal models
2021-02-04
ATLANTA - Researchers at Yerkes National Primate Research Center, Emory University, have developed a COVID-19 vaccine that has proven safe and effective in mice and monkeys. Results from this National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID)-funded study are published online today in Immunity.
The Emory MVA COVID-19 vaccine approaches inducing protective immunity via modified vaccinia Ankara (MVA), a harmless version of a poxvirus that is well-known for its use in HIV/AIDS vaccines. Like the Moderna and Pfizer COVID-19 vaccines, the Emory MVA COVID-19 vaccine ...
City, University of London academic tracks COVID-19 dark web marketplace before vaccine
2021-02-04
New research carried out by City, University of London data scientist, Dr Andrea Baronchelli, and colleagues into the dark web marketplace (DWM) trade in products related to COVID-19, has revealed the need for the continuous monitoring of dark web marketplaces (DWMs) especially in light of the current shortage and availability of coronavirus vaccines.
In their paper, Dark Web Marketplaces and COVID-19: before the vaccine published in the EPJ Data Science, Dr Baronchelli and his colleagues analysed 851,199 listings extracted from 30 DWMs between January 1, 2020 and November 16, 2020 before the advent of the availability of the coronavirus vaccine.
They identify 788 listings directly related to COVID-19 ...
NANOGrav finds possible 'first hints' of low-frequency gravitational wave background
2021-02-04
In data gathered and analyzed over 13 years, the North American Nanohertz Observatory for Gravitational Waves (NANOGrav) Physics Frontiers Center (PFC) has found an intriguing low-frequency signal that may be attributable to gravitational waves.
NANOGrav researchers - including a number from West Virginia University's (WVU's) Department of Physics and Astronomy and the Center for Gravitational Waves and Cosmology - measure the times of arrival of radio pulses from exotic stars called pulsars with large radio telescopes, including the Green Bank Telescope (GBT) in Pocahontas County, ...
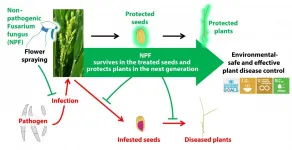
New eco-friendly technique protects rice plants against devastating fungal infection
2021-02-04
Researchers have developed a new technique to protect rice seeds against fungal infections that can ruin up to half of all rice crops in the world. The biocontrol method, which involves inoculation of flowers with a different fungus that doesn't cause disease and using seeds harvested from the flower to grow crops, is even better at protecting rice plants from diseases than existing fungicide approaches, and could also be used against similar pathogens that affect other staple crops.
The extremely destructive seedborne bakanae disease, which affects rice plants everywhere in the world that the staple crop is grown, is currently typically combatted with either chemical fungicides or ...
New combination therapy offers chance of healing hepatitis B
2021-02-04
The new therapeutic approach is based on shutting down the viral hepatitis B genome located in the nucleus of infected liver cells. Upon infection of the liver cell, the viral genome is transformed inside the nucleus into a closed circular DNA molecule. This deoxyribonucleic acid is a stable molecule known as covalently closed circular DNA (cccDNA) and serves as the template for the production of new viruses. The cccDNA represents the central reservoir of the hepatitis B viruses and enables their persistence in the liver. The virologist Prof. Dr. Maura Dandri and her team at the UKE managed to prevent the HBV-cccDNA from producing further viruses in the animal model.
The point of attack of their ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Does online sports gambling affect substance use behaviors?
How do rapid socio-environmental transitions reshape cancer risk?
Do abortion bans affect birth rates and food-assistance costs?
Can artificial intelligence help reduce the carbon footprint of weather forecasting models?
Mangrove forests are short of breath
Low testosterone, high fructose: A recipe for liver disaster
SKKU research team unravels the origin of stochasticity, a key to next-generation data security and computing
Flexible polymer‑based electronics for human health monitoring: A safety‑level‑oriented review of materials and applications
Could ultrasound help save hedgehogs?
attexis RCT shows clinically relevant reduction in adult ADHD symptoms and is published in Psychological Medicine
Cellular changes linked to depression related fatigue
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
[Press-News.org] Quasicrystal-clear: Material reveals unique shifting surface structure under microscopeScientists reveal peculiar surface structure in materials resembling quasicrystals with interesting implications for its magnetic properties