(Press-News.org) People traditionally think that lungs and limbs are key innovations that came with the vertebrate transition from water to land. But in fact, the genetic basis of air-breathing and limb movement was already established in our fish ancestor 50 million years earlier. This, according to a recent genome mapping of primitive fish conducted by the University of Copenhagen, among others. The new study changes our understanding of a key milestone in our own evolutionary history.
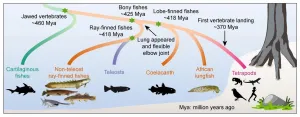
There is nothing new about humans and all other vertebrates having evolved from fish. The conventional understanding has been that certain fish shimmied landwards roughly 370 million years ago as primitive, lizard-like animals known as tetrapods. According to this understanding, our fish ancestors came out from water to land by converting their fins to limbs and breathing under water to air-breathing.
However, limbs and lungs are not innovations that appeared as recent as once believed. Our common fish ancestor that lived 50 million years before the tetrapod first came ashore already carried the genetic codes for limb-like forms and air breathing needed for landing. These genetic codes are still present in humans and a group of primitive fishes.
This has been demonstrated by recent genomic research conducted by University of Copenhagen and their partners. The new research reports that the evolution of these ancestral genetic codes might have contributed to the vertebrate water-to-land transition, which changes the traditional view of the sequence and timeline of this big evolutionary jump. The study has been published in the scientific journal Cell.
"The water-to-land transition is a major milestone in our evolutionary history. The key to understanding how this transition happened is to reveal when and how the lungs and limbs evolved. We are now able to demonstrate that the genetic basis underlying these biological functions occurred much earlier before the first animals came ashore," stated by professor and lead author Guojie Zhang, from Villum Centre for Biodiversity Genomics, at the University of Copenhagen's Department of Biology.
A group of ancient living fishes might hold the key to explain how the tetrapod ultimately could grow limbs and breathe on air. The group of fishes includes the bichir that lives in shallow freshwater habitats in Africa. These fishes differ from most other extant bony fishes by carrying traits that our early fish ancestors might have had over 420 million years ago. And the same traits are also present in for example humans. Through a genomic sequencing the researchers found that the genes needed for the development of lungs and limbs have already appeared in these primitive species.
Our synovial joint evolved from fish ancestor
Using pectoral fins with a locomotor function like limbs, the bichir can move about on land in a similar way to the tetrapod. Researchers have for some years believed that pectoral fins in bichir represent the fins that our early fish ancestors had.
The new genome mapping shows that the joint which connects the socalled metapterygium bone with the radial bones in the pectoral fin in the bichir is homologous to synovial joints in humans - the joints that connect upper arm and forearm bones. The DNA sequence that controls the formation of our synovial joints already existed in the common ancestors of bonefish and is still present in these primitive fishes and in terrestrial vertebrates. At some point, this DNA sequence and the synovial joint was lost in all of the common bony fishes - the socalled teleosts.
"This genetic code and the joint allows our bones move freely, which explains why the bichir can move around on land," says Guojie Zhang.
First lungs, then swim bladder
Moreover, the bichir and a few other primitive fishes have a pair of lungs that anatomically resembles ours. The new study reveals that the lungs in both bichir and alligator gar also function in a similar manner and express same set of genes as human lungs.
At the same time, the study demonstrates that the tissue of the lung and swim bladder of most extant fishes are very similar in gene expression, confirming they are homologous organs as predicted by Darwin. But while Darwin suggested that swim bladders converted to lungs, the study suggests it is more likely that swim bladders evolved from lungs. The research suggests that our early bony fish ancestors had primitive functional lungs. Through evolution, one branch of fish preserved the lung functions that are more adapted to air breathing and ultimately led to the evolution of tetrapods. The other branch of fishes modified the lung structure and evolved with swim bladders, leading the evolution of teleosts. The swim bladders allow these fishes to maintain buoyancy and perceive pressure, thus better survive under water.
"The study enlightens us with regards to where our body organs came from and how their functions are decoded in the genome. Thus, some of the functions related to lung and limbs did not evolve at the time when the water-to-land transition occurred, but are encoded by some ancient gene regulatory mechanisms that were already present in our fish ancestor far before landing. It is interesting that these genetic codes are still present in these 'living-fossil'' fishes, which offer us the opportunity to trace back the root of these genes," concludes Guojie Zhang.
INFORMATION:
FACT BOX 1: Not just limbs and lungs, but also the heart
Primitive fish and humans also share a common and critical function in the cardio-respiratory system: The conus arteriosus, a structure in the right ventricle of our heart which might allow the heart to efficiently deliver the oxygen to the whole body, and which is also found in the bichir. However, the vast majority of bony fish have lost this structure. The researchers discovered a genetic element that appears to control the development of the conus arteriosus. Transgenic experiments with mice showed that when researchers removed this genetic element, the mutated mice died due to thinner, smaller right ventricles, which lead to congenital heart defects and compromised heart function.
FACT BOX 2:
The vast majority of extant fish species belong to the ray-finned fishes, a subclass of bony fish. These are typically fish with gills, fins and a swim bladder.
The terrestrial group of vertebrates are known as tetrapod. The tetrapod includes all vertebrates that descended from the first animals adapted to a life on land by developing four limbs and lungs, i.e., all mammals, birds, reptiles and amphibians.
The researchers' theory is that the air-breathing ability in these primitive fishes allowed them to survive the second mass extinction roughly 375-360 million years ago. At that time, oxygen depletion in Earth's oceans caused a majority of species to be wiped out. Lungs allowed some fish to survive on land.
The study has been published in the scientific journal Cell. Access the research article END
A global team of researchers has developed a new strategy for fast and reliable antibody tests, which can quantify the immune response induced by vaccination and reveal the timeline and stage of pathogen infection.
Led by Professor Martin Hegner, Principal Investigator in CRANN and Trinity College Dublin's School of Physics, the team's one-step quantitative antibody tests are conducted using (blood) serum and are on a par with the gold-standard, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) technique.
The major advantage of the newly developed nano technique with respect to ELISA tests is that it is equally ...
ATLANTA - Researchers at Yerkes National Primate Research Center, Emory University, have developed a COVID-19 vaccine that has proven safe and effective in mice and monkeys. Results from this National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID)-funded study are published online today in Immunity.
The Emory MVA COVID-19 vaccine approaches inducing protective immunity via modified vaccinia Ankara (MVA), a harmless version of a poxvirus that is well-known for its use in HIV/AIDS vaccines. Like the Moderna and Pfizer COVID-19 vaccines, the Emory MVA COVID-19 vaccine ...
New research carried out by City, University of London data scientist, Dr Andrea Baronchelli, and colleagues into the dark web marketplace (DWM) trade in products related to COVID-19, has revealed the need for the continuous monitoring of dark web marketplaces (DWMs) especially in light of the current shortage and availability of coronavirus vaccines.
In their paper, Dark Web Marketplaces and COVID-19: before the vaccine published in the EPJ Data Science, Dr Baronchelli and his colleagues analysed 851,199 listings extracted from 30 DWMs between January 1, 2020 and November 16, 2020 before the advent of the availability of the coronavirus vaccine.
They identify 788 listings directly related to COVID-19 ...
In data gathered and analyzed over 13 years, the North American Nanohertz Observatory for Gravitational Waves (NANOGrav) Physics Frontiers Center (PFC) has found an intriguing low-frequency signal that may be attributable to gravitational waves.
NANOGrav researchers - including a number from West Virginia University's (WVU's) Department of Physics and Astronomy and the Center for Gravitational Waves and Cosmology - measure the times of arrival of radio pulses from exotic stars called pulsars with large radio telescopes, including the Green Bank Telescope (GBT) in Pocahontas County, ...
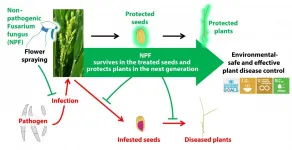
Researchers have developed a new technique to protect rice seeds against fungal infections that can ruin up to half of all rice crops in the world. The biocontrol method, which involves inoculation of flowers with a different fungus that doesn't cause disease and using seeds harvested from the flower to grow crops, is even better at protecting rice plants from diseases than existing fungicide approaches, and could also be used against similar pathogens that affect other staple crops.
The extremely destructive seedborne bakanae disease, which affects rice plants everywhere in the world that the staple crop is grown, is currently typically combatted with either chemical fungicides or ...
The new therapeutic approach is based on shutting down the viral hepatitis B genome located in the nucleus of infected liver cells. Upon infection of the liver cell, the viral genome is transformed inside the nucleus into a closed circular DNA molecule. This deoxyribonucleic acid is a stable molecule known as covalently closed circular DNA (cccDNA) and serves as the template for the production of new viruses. The cccDNA represents the central reservoir of the hepatitis B viruses and enables their persistence in the liver. The virologist Prof. Dr. Maura Dandri and her team at the UKE managed to prevent the HBV-cccDNA from producing further viruses in the animal model.
The point of attack of their ...
Treating equine donor stem cells with a growth factor called TGF-β2 may allow them to avoid "tripping" the immune response in recipients, according to new research from North Carolina State University. The work could simplify the stem cell treatment process for ligament and tendon injuries in horses, and may also have implications for human stem cell therapies.
Mesenchymal stem cell therapy is a promising avenue for treating musculoskeletal injuries - particularly tendon and ligament injuries - in horses. Mesenchymal stem cells are adult stem cells found in bone marrow that act as repair directors, producing secretions that recruit paracrine, or healing, factors to the site of injury.
Just as blood cells have "types," ...
Gels are formed by mixing polymers into fluids to create gooey substances useful for everything from holding hair in place to enabling contact lenses to float over the eye.
Researchers want to develop gels for healthcare applications by mixing in medicinal compounds, and giving patients injections so that the gel releases the active pharmaceutical ingredient over a period of months to avoid weekly or daily needle sticks.
But standing in the way is a problem that's as easily understandable as the difference between using hair gel on a beach versus in a ...
Virtual 'exergaming' has become a popular way to exercise - especially among younger people - since the release of virtual reality (VR) fitness games on consoles such as Nintendo and Playstation.
But while VR is undoubtedly raising fitness games to a whole new level, researchers at the University of South Australia are cautioning players about the potential side effects of VR, particularly in the first hour after playing.
In a new study published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research, UniSA researchers investigated the consequences of playing one of the most popular VR exergames - Beat Saber* - finding that one in seven players still ...
Catalysts are key materials in modern society, enabling selective conversion of raw materials into valuable products while reducing waste and saving energy. In case of industrially relevant oxidative dehydrogenation reactions, most known catalyst systems are based on transition metals such as Iron, Vanadium, Molybdenum or Silver. Due to intrinsic drawbacks associated with the use of transition metals, such as rare occurrence, environmentally harmful mining processes, and toxicity, the fact that pure carbon exhibits catalytic activity in this type of reaction and thus has high potential as a sustainable substitution material is of high interest.
To date, the development of carbon-based catalysts for oxidative dehydrogenation reactions may be divided into two ...