Ultimately, beneficial fungi could be more effective than pesticides against nematodes
2021-02-04
(Press-News.org) Over the past 30 years, the use of soil fumigants and nematicides used to protect cole crops, such as broccoli and Brussel sprouts, against cyst nematode pathogens in coastal California fields has decreased dramatically. A survey of field samples in 2016 indicated the nematode population has also decreased, suggesting the existence of a natural cyst nematode controlling process in these fields.
Thanks to California's pesticide-use reporting program, nematologists have been able to follow the amounts of fumigants and nematicides used to control cyst nematodes over the past three decades.
"Application of these pesticides steadily declined until they were completely eliminated in 2014 while, for example, broccoli yields continued to increase each year," said Ole Becker, a scientist with the Department of Nematology at the University of California.
In a study of 152 fields, Borneman, Becker and colleagues detected cyst nematodes in about 38% of them. Only a few of these fields had enough nematodes to potentially damage the crops. This showed that growers had likely reduced their usage of nematicides because of a natural decline in the nematode populations.
To identify the cause of this natural decline, Borneman, Becker and colleagues used cyst nematodes as a bait and found that a diverse population of fungi were likely killing the nematodes. The most abundant genus was Hyalorbilia, which contains species previously described as effective parasites of cyst and root-knot nematodes.
"The results from our baiting analysis combined with advanced molecular tools gave us a detailed depiction of the possible nematode-parasitizing fungi in these soils, which then provided a plausible explanation for this dramatic decrease in pesticide use," said Borneman.
Their research demonstrates the usefulness of monitoring plant-parasitic nematode density before using nematicides and increases the awareness of beneficial fungi in crop protection. These fungi might be considered as possible biological control agents for nematodes.
INFORMATION:
To learn more, read " END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-04
As the coronavirus pandemic continues to devastate communities worldwide, Black Americans who face racial discrimination in hospitals and doctor's offices weather additional stresses that can exacerbate threats from COVID-19. A new University of Georgia study examines the interplay between the perceptions of coronavirus threat and psychological distress among Black Americans.
The additional stresses arise from the prevalent belief among Black Americans worried that they might not recover from how hospitals treat them if they become infected with the coronavirus.
"While the notion has been floated among commentators, this is the first study that uses nationally representative data to assess whether this threat, or feeling, ...
2021-02-04
BOSTON - Tiny particles of air pollution -- called fine particulate matter -- can have a range of effects on health, and exposure to high levels is a known risk factor for cardiovascular disease. New research led by investigators at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) reveals that fine particulate matter has a detrimental impact on cardiovascular health by activating the production of inflammatory cells in the bone marrow, ultimately leading to inflammation of the arteries. The findings are published in the END ...
2021-02-04
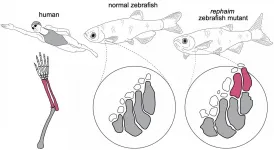
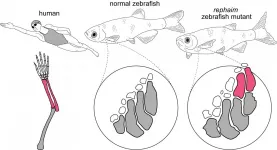
By tweaking a single gene, Harvard scientists engineered zebrafish that show the beginning formation of limb-like appendages. The researchers stumbled upon this mutation, which may shed light on the sea-to-land transition of vertebrates, while screening for various gene mutants and their impact on fish development. Their discovery, outlined February 4th in the journal Cell, marks a fundamental step in our understanding of fin-to-limb evolution and how surprisingly simple genetic changes can create great leaps in the development of complex structures.
"It was a little bit unbelievable that just one mutation was able to create completely new bones and joints," says M. Brent Hawkins (@Homeobox), first author of ...
2021-02-04
Fin-to-limb transition is an icon of key evolutionary transformations. Many studies focus on understanding the evolution of the simple fin into a complicated limb skeleton by examining the fossil record. In a paper published February 4 in Cell, researchers at Harvard and Boston Children's Hospital examined what's occurring at the genetic level to drive different patterns in the fin skeleton versus the limb skeleton.
Researchers, led by M. Brent Hawkins, a recent doctoral recipient in the Department of Organismic and Evolutionary Biology, performed forward genetic screens in zebrafish looking for mutations that affect the fin skeleton. Unlike tetrapod limbs, which have complex skeletons with many bones that articulate ...
2021-02-04
Although scientists knew that some bats could reach heights of over 1,600 meters (or approximately one mile) above the ground during flight, they didn't understand how they managed to do it without the benefit of thermals that aren't typically available to them during their nighttime forays. Now, researchers reporting in the journal Current Biology on February 4th have uncovered the bats' secret to high-flying.
It turns out that the European free-tailed bats they studied--powerful fliers that the researchers documented sometimes reaching speeds of up to 135 kilometers (84 miles) per hour in self-powered flight--do depend on orographic uplift that ...
2021-02-04
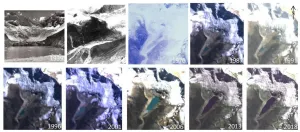
As the planet warms, glaciers are retreating and causing changes in the world's mountain water systems. For the first time, scientists at the University of Oxford and the University of Washington have directly linked human-induced climate change to the risk of flooding from a glacial lake known as one of the world's greatest flood risks.
The study examined the case of Lake Palcacocha in the Peruvian Andes, which could cause flooding with devastating consequences for 120,000 residents in the city of Huaraz. The paper, published Feb. 4 in Nature Geoscience, provides new evidence for an ongoing legal case that hinges on the link between greenhouse gas emissions and particular climate change impacts.
"The scientific challenge was to provide the clearest and cleanest assessment ...
2021-02-04
CHICAGO - A new study by Northwestern University researchers finds involvement with firearms by high-risk youth is associated with firearm violence during adulthood.
"Association of Firearm Access, Use, and Victimization During Adolescence with Firearm Perpetration During Adulthood in a 16-year Longitudinal Study of Youth Involved in the Juvenile Justice System" will publish in JAMA Network Open at 10 a.m. CST, Thursday, Feb. 4. Access the full study online.
The longitudinal study of juvenile justice youth is the first to analyze firearm victimization and access during adolescence and its association with firearm violence in adulthood.
The study is based ...
2021-02-04
Toronto - (February 4, 2021) The results of a Phase III randomized clinical trial have shown that when it comes to detecting clinically significant prostate cancer, Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) with targeted biopsies (MRI-TBx) matches the current standard and brings a multitude of advantages. The PRostate Evaluation for Clinically Important Disease: MRI vs Standard Evaluation Procedures (PRECISE) study will help to make prostate cancer diagnosis more accurate and less invasive.
PRECISE included 453 participants at Canadian academic cancer centres who were either assigned to receive MRI ...
2021-02-04
What The Study Did: Researchers estimated the rate of nurse burnout in the United States and the factors associated with leaving or considering leaving their jobs due to burnout.
Authors: Megha K. Shah, M.D., M.Sc., of the Emory University School of Medicine in Atlanta, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.36469)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, ...
2021-02-04
What The Study Did: Researchers in this randomized clinical trial investigated whether nasopharyngeal application of povidone iodine could reduce the viral load of patients with nonsevere COVID-19 symptoms.
Authors: Olivier Mimoz, M.D., Ph.D., University Hospital of Poitiers in Poitiers, France, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaoto.2020.5490)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Ultimately, beneficial fungi could be more effective than pesticides against nematodes