INFORMATION:
Title: Cardiac Arrest in COVID-19: Characteristics and outcomes of in- and out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. A report from the Swedish Registry for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation
Raised mortality from cardiac arrest in people with COVID-19
2021-02-05
(Press-News.org) Sudden cardiac arrest is more often fatal in people with COVID-19, a new study shows. Those responsible for the research see the results as a wake-up call for the public and care providers alike.
The survey now published in the
European Heart Journal is a register-based observation study. It covers all 3,026 cases of sudden cardiac arrest that were reported to the Swedish Registry for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation in the period from 1 January to 20 July 2020 -- that is, both before and during the pandemic.
The Registry's statistics show that, in Sweden, there are 6,000 cases of sudden cardiac arrest annually in which the person is not admitted to hospital. Some 600 of these people survive. The corresponding figures for cardiac arrest during inpatient care are 2,500 cases and 900 survivors.
The study results indicate that mortality from sudden cardiac arrest is higher if the person has COVID-19, but that different patient groups show divergent differences in mortality rates.
During the study period, 1,946 cases of sudden cardiac arrest outside of hospitals were registered. In 10 percent of the cases in this group, the person had COVID-19, and the risk of a fatal outcome proved to be 3.4 times higher for these people than for the other group members.
Of the 1,080 cases of sudden cardiac arrest that took place in hospitals, COVID-19 was present in 16 percent. Among the patients with COVID-19, mortality was 2.3 times higher than for the others in this group.
The largest mortality difference was noted in the group of women who were already receiving inpatient care at the time of their cardiac arrest. In these women, ongoing COVID-19 infection was associated with nine times the risk of a fatal outcome during the initial months and a sevenfold risk from April onward.
The study, carried out by researchers at the Swedish Registry for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and the University of Gothenburg, received financial support from the Swedish Heart-Lung Foundation. This Foundation's prompt funding action was crucial for the implementation, emphasizes Araz Rawshani, registrar and researcher at the Faculty of Medicine, Sahlgrenska Academy, who also works at Sahlgrenska University Hospital.
"We hope our results can help to raise awareness of COVID-19 complications among the public, care providers, and decision-makers. That could improve care and mobilize resources for high-risk patients," he says.
Kristina Sparreljung is the Secretary-General of the Swedish Heart-Lung Foundation.
"We hope these results will help to enable more lives to be saved. This study is a direct result of the emergency grant provided by the Heart-Lung Foundation for research on COVID-19 connected with cardiopulmonary disease back in spring 2020," she says.
The survival rate for cardiac arrest has risen successively in recent years, but mortality remains high. Surviving a sudden cardiac arrest outside of hospital requires, pending arrival of an ambulance, immediate action in the form of cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and use of an automated external defibrillator (AED).
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Sensor and detoxifier in one
2021-02-05
Ozone is a problematic air pollutant that causes serious health problems. A newly developed material not only quickly and selectively indicates the presence of ozone, but also simultaneously renders the gas harmless. As reported by Chinese researchers in Angewandte Chemie, the porous "2-in-one systems" also function reliably in very humid air.
Ozone (O(3)) can cause health problems, such as difficulty breathing, lung damage, and asthma attacks. Relevant occupational safety regulations therefore limit the concentrations of ozone allowable in the workplace. Previous methods for the detection of ozone, such as those based on semiconductors, have a variety ...
Energy harvesting: Printed thermoelectric generators for power generation
2021-02-05
Thermoelectric generators, TEGs for short, convert ambient heat into electrical power. They enable maintenance-free, environmentally friendly, and autonomous power supply of the continuously growing number of sensors and devices for the Internet of Things (IoT) and recovery of waste heat. Scientists of Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) have now developed three-dimensional component architectures based on novel, printable thermoelectric materials. This might be a milestone on the way towards use of inexpensive TEGs. The results are reported in npj Flexible Electronics (DOI: 10.1038/s41528-020-00098-1) and ACS Energy Letters (DOI: 10.1021/acsenergylett.0c02159).
"Thermoelectric generators directly convert thermal into electrical energy. This technology enables ...
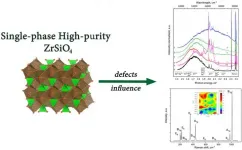
Ural Federal University scientists developed a new way of synthesis of high-purity zircon
2021-02-05
The scientific novelty of the work of scientists from Ural Federal University, Institute of Solid State Chemistry and Geology and Geochemistry of the Ural Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences lies in the fact that for the first time scientists solved the task of creating zircon with certain spectral properties. To this end, they have worked out the so-called sol-gel method.
It is distinguished by its technological simplicity, controllability of processes and allows synthesizing a larger volume of products with high purity than with other ...
Computer can determine whether you'll die from COVID
2021-02-05
Using patient data, artificial intelligence can make a 90 percent accurate assessment of whether a person will die from COVID-19 or not, according to new research at the University of Copenhagen. Body mass index (BMI), gender and high blood pressure are among the most heavily weighted factors. The research can be used to predict the number of patients in hospitals, who will need a respirator and determine who ought to be first in line for a vaccination.
Artificial intelligence is able to predict who is most likely to die from the coronavirus. In doing so, it can also help decide who should be at the front of the line for the precious vaccines now being administered across Denmark.
The result is from a newly published study by researchers at the University of Copenhagen's Department ...
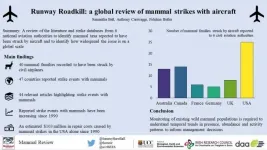
'Runway Roadkill' rapidly increasing at airports across the world, UCC study finds
2021-02-05
- World's wildlife, from giraffes to voles, kangaroos to coyotes being hit by aircraft.
- Study identifies incidences at airports in 47 countries across the globe.
- 'Runway Roadkill' increasing by up to 68% annually and has caused damage that has cost in excess of $103 million in the United States alone over a 30 year period.
- It is hoped study could pave way for international efforts to protect wildlife and reduce costly aircraft damage.
From giraffes to the world's smallest mammals, the world's wildlife is being increasingly struck by aircraft, a global study finds.
Airports from Sydney to London and the USA to Germany were examined by researchers who ...
Dartmouth-invented technology allows doctors to see beam field during radiation treatment
2021-02-05
LEBANON, NH - Dartmouth's and Dartmouth-Hitchcock's Norris Cotton Cancer Center (NCCC) is the first cancer center in the world to install BeamSite Cherenkov imaging cameras in its radiotherapy treatment rooms. The camera system, invented, validated and commercialized by entrepreneurs from NCCC and Dartmouth spinoff biomed tech company, DoseOptics, LLC, captures imaging and real-time video of the beam directly on the patient, allowing the radiation oncology team to visualize treatment delivery.
Cherenkov imaging makes radiation treatment a visual process. The Cherenkov effect occurs when photon or electron radiation beams interact with tissue, such as skin, producing a small light ...
UTA engineers develop programming technology to transform 2D materials into 3D shapes
2021-02-05
University of Texas at Arlington researchers have developed a technique that programs 2D materials to transform into complex 3D shapes.
The goal of the work is to create synthetic materials that can mimic how living organisms expand and contract soft tissues and thus achieve complex 3D movements and functions. Programming thin sheets, or 2D materials, to morph into 3D shapes can enable new technologies for soft robotics, deployable systems, and biomimetic manufacturing, which produces synthetic products that mimic biological processes.
Kyungsuk Yum, an associate professor in the Materials ...
Ensuring healthy family mealtimes is important - and complicated
2021-02-05
URBANA, Ill. ¬- Mealtimes are a central aspect of family life, affecting the health and wellbeing of both children and adults. Although the benefits of healthy mealtimes are straightforward, helping all families realize those benefits is quite complicated, new research from University of Illinois shows.
The study highlights ways in which some solutions - such as an exclusive focus on improving food access or on improving mealtime preparation and organization skills - may be less effective if done in isolation, says Allen Barton, assistant professor in the Department of Human Development and Family Studies at ...
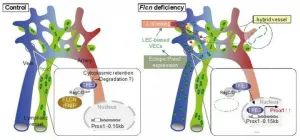
How blood and lymph vessels remain separated after development
2021-02-05
Researchers from Kumamoto University (Japan) have clarified the mechanism by which blood and lymph vessels remain segregated from one another after development. The characteristics and structures of these two vessel types are very similar, and how they maintain separation has remained unexplained for many years. In this study, researchers found that the molecule Folliculin (FLCN) in vascular endothelial cells acts as a gatekeeper to maintain that separation.
Blood and lymphatic vessels form independent networks until the final confluence at the left and right venous angles in the neck. Blood vessels act as a pipeline that ...
Signs of burnout can be detected in sweat
2021-02-05
We've all felt stressed at some point, whether in our personal or professional lives or in response to exceptional circumstances like the COVID-19 pandemic. But until now there has been no way to quantify stress levels in an objective manner.
That could soon change thanks to a small wearable sensor developed by engineers at EPFL's Nanoelectronic Devices Laboratory (Nanolab) and Xsensio. The device can be placed directly on a patient's skin and can continually measure the concentration of cortisol, the main stress biomarker, in the patient's sweat.
Cortisol: A double-edged sword
Cortisol is a steroid hormone ...