INFORMATION:
Collapsed glaciers increase third pole uncertainties: Downstream lakes may merge within a decade
2021-02-09
(Press-News.org) Glaciers are not only melting, but also collapsing in the Third Pole region. In 2016, two glaciers in the western Third Pole's Aru Mountains collapsed, one after another. The first collapse caused nine human casualties and the loss of hundreds of livestock. However, that may not be the end of the catastrophe.
According to a study recently published in The Cryosphere, meltwater from ice avalanches has been filling downstream lakes in a way that may cause previously separated lakes to merge within the next decade, thus disrupting the function of ecosystems in the region.
"The collapse of Aru glaciers has both short-term and long-term impacts on downstream lakes," said Dr. LEI Yanbin, lead author of the study and a researcher at the Institute of Tibetan Plateau Research (ITP), Chinese Academy of Sciences.
According to LEI and his team, the first glacier collapse sent at least 7.1 million cubic meters of ice, the volume of approximately 2,840 Olympic-size swimming pools, into the downstream Aru Co Lake. The avalanche of ice lowered the lake's surface temperature by 2-4 degree centigrade for two weeks and reshaped the near-shore lakebed. As the ice from the avalanches started to melt, it contributed 23% to the volume increase of Memar Co Lake, a neighboring terminal lake that has risen three meters from 2016 to 2019 - a rate that is 30% faster than that from 2003 to 2014.
The study was enabled by the glacier-meteorology-lake observation system built by a group of scientists led by Prof. YAO Tandong, co-chair of Third Pole Environment (TPE) and co-author of the study.
YAO and his group were the first scientists to arrive at the scene after the glacier collapse, and have since been working to reveal why and how the glaciers collapsed, as well as trying to understand the impact of the collapses on downstream lakes.
Their research found that ice avalanche debris from the first glacier collapse had nearly melted away by the summer of 2017, but 30% of the ice from the second glacier collapse still remained as of the end of 2019. "If Memar Lake continues to expand at this rate, it will merge with the Aru Co Lake in 7-11 years," said YAO. "A scenario like that could significantly change the regional landscape and disrupt local ecosystems. That's why we need to watch the two lakes more closely in case of such changes."
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Samara Polytech chemists simplify crystal structures
2021-02-09
Science always strives to replace complex natural objects and phenomena with simpler models. Scientists of Samara Center for Theoretical Materials Science (SCTMS) of Samara Polytech have developed methods to simplify the crystal structure of a substance to obtain chemically important knowledge. The main approaches are described in the article published in the Structural Chemistry journal IF 2.081 (doi:10.1007/s11224-020-01724-4).
"The main goal of simplifying any crystal structure is to understand the features of its structure and properties, and the simplification ...
Covid-19 vs conservation - how the northern white rhino rescue programme overcame challenges
2021-02-09
The BioRescue research project, a programme aiming at saving the northern white rhinoceros from extinction, exemplifies the challenges to overcome when conducting research and conservation in an international consortium in times of a global pandemic. COVID-19 hampered communication and travels, prevented or delayed crucial procedures, caused losses in revenues and by that may have lowered the chances of a survival of the northern white rhino. The consortium adjusted strategies, gained valuable knowledge during these challenging times and continued with its mission. The effects of the pandemic on the BioRescue project are described in detail in a scientific paper published in the Journal ...
Known tumour suppressor gene found essential for development, regeneration&stress-response
2021-02-09
Adult progenitor cells are present in the Drosophila fly as early as its larvae stage. These cells are the only ones that are maintained throughout development and they are responsible for giving rise to adult tissues and organs. Headed by Jordi Casanova (also an IBMB-CSIC researcher), the Development and Morphogenesis in Drosophila lab at IRB Barcelona has identified the headcase (hdc) gene as responsible for the unique characteristics of these adult progenitor cells.
"In our study, mainly using the powerful genetic tools available in Drosophila, we were able to show that this gene regulates the development ...
All in the head? Brains adapt to support new species
2021-02-09
Scientists studying forest dwelling butterflies in Central and South America have discovered that changes in the way animals perceive and process information from their environment can support the emergence of new species. The study led by the University of Bristol, and published today [9 February] in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), has implications for how new species might evolve and the underappreciated role of changes in the brain.
The international team, led by Dr Stephen Montgomery from the School of Biological Sciences at the University of Bristol, compared ...
In-depth analysis identifies causes and mitigation efforts in COVID-19 cluster
2021-02-09
BOSTON -- Hospitals across the United States have gone to great lengths to implement infection control measures to prevent transmission of SARS-CoV-2. And yet, as the pandemic has unfolded, many health care settings have experienced clusters of cases, with the virus spreading among patients, staff or both. Some clusters have been easily traced back to break rooms and shared meals. But other clusters have been challenging to trace and contain. In September 2020, Brigham and Women's Hospital detected a cluster of infections that would ultimately include 14 patients and 38 staff members. The hospital rapidly activated its incident command structure in order to coordinate a controlled response to contain the cluster. Steps taken included widespread ...
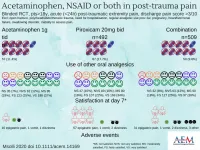
Findings of study comparing analgesics in acute post-trauma pain
2021-02-09
DES PLAINES, IL -- The combination of a high?dose NSAID with paracetamol does not increase the analgesic effect compared to paracetamol alone. Researchers also found that paracetamol alone is superior to high?dose NSAID alone for posttraumatic extremity pain. These are the findings of a study titled Acetaminophen, or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, or combination of both analgesics in acute post-trauma pain: a randomized controlled trial, to be published in the February 2021 issue of Academic Emergency Medicine (AEM), a journal of the Society for Academic Emergency Medicine (SAEM).
According to the study, taking into account its superior efficacy ...
How diseases and history are intertwined
2021-02-09
Today, the average American is unlikely to spend time worrying about malaria. Although the disease is commonly perceived to be restricted to other parts of the world, it played a significant role in shaping American history. It even helped turn the tide of the American Revolutionary War by infecting so many British soldiers that General Cornwallis was forced to surrender at Yorktown.
First-year students in a 2019 introductory seminar class led by Erin Mordecai, an assistant professor of biology in the School of Humanities and Sciences (H&S), delved ...
Samara Polytech scientists proved the anti-cancer properties of a number of plant extracts
2021-02-09
Samara Polytech chemists investigated the potential anticarcinogenic effects of extracts obtained from plant materials of lingonberry, raspberry, black chokeberry, grapes, Krasnodar green tea, ginseng, fireweed and coffee, and also evaluated their effect on the growth and viability of colon cancer cells. The research was carried out within the framework of the state assignment for fundamental research No. 0778-2020-0005, its results were published Dec. 29, 2020 in the journal Proceedings of Universities. Applied Chemistry and Biotechnology (DOI: https://doi.org/10.21285/2227-2925-2020-10-4-613-626).
Prevention is the most cost-effective and long-term strategy for controlling this disease. It is now well known ...
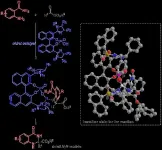
New method for asymmetric N,N-acetal synthesis promises advances in drug development
2021-02-09
A lot of our medicines and other bioactive drugs are based on chemical structures called "enantiomers"-- molecules that are mirror images of each other and are non-superimposable. Notable among them are chiral N,N-acetals contained in diuretic drugs like bendroflumethiazide and thiabutazide, used to treat high blood pressure and edema. Because an enantiomer and its mirror image version often have different biological activities, with only one of them having pharmacological utility, an "enantioselective" or asymmetric synthesis yielding the desired enantiomer in greater amounts is highly desirable.
In the case of N,N-acetals, several studies have demonstrated their enantioselective preparation from aldehydes, aldimines, or enamines. However, in all these cases, ...
Case Western Reserve-led team finds that people with dementia at higher risk for COVID-19
2021-02-09
CLEVELAND (Feb. 9)--A study led by Case Western Reserve University researchers found that patients with dementia were at a significantly increased risk for COVID-19--and the risk was higher still for African Americans with dementia.
Reviewing electronic health records of 61.9 million adults in the United States, researchers found the risk of contracting COVID-19 was twice as high for patients with dementia than for those without it--while among those with dementia, African Americans had close to three times the risk of being infected with COVID-19 as Caucasians did.
In addition, patients with dementia who ...