New "molecular" tool helps shed light on individual synapses in brain cells
Scientists engineer a light-activated protein that can be used to study single synapses of neurons
2021-02-09
(Press-News.org) Neurons are the primary cells of the nervous system, and the signals that are transmitted between them are responsible for all our actions and our cognitive ability. In particular, learning and memory are believed to be associated with a process called "long-term potentiation," which is the strengthening of connections between specific neurons via continued signal transmission through "synapses" (small gaps between neurons). Long-term potentiation can change the connection between neurons via synapses--by changing their size and composition. Understanding how long-term potentiation occurs can be valuable to clarifying how our brain learns and retains new knowledge. A team of scientists from Japan has now made significant strides in the understanding of long-term potentiation. Read on to know how!
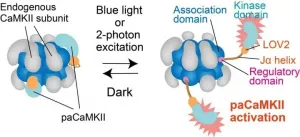
One way to study long-term potentiation is by using "optogenetics," i.e., activating neurons and monitoring their responses upon light stimulation. Optogenetics allows scientists to activate single neurons and dissect how neurons work in neuronal networks. As such, optogenetics is a revolutionary advancement in neuroscience research, but optogenetic tools to modify single synapses (spines) have not been developed until now. This is an issue because neuronal signaling pathways may have spine-specific effects. In particular, the protein "CaMKII," critical for long-term potentiation, is activated by the molecule "glutamate" in a spine-specific way, but exactly what happens at the synapses during activation remains a mystery.
Fortunately, a research team at National Institute of Physiological Sciences, Japan, led by Dr. Hideji Murakoshi, resolved this issue. The team fused CaMKII with a specific domain of a plant photoreceptor (a type of cell that responds to light). This domain called "LOV2-Jα" caused CaMKII to become sensitive to light, after which they expressed this new photoactivatable CaMKII in different types of isolated neurons and in living mice. Their findings are recently published in the journal Nature Communications.
"We were very excited to find that activating CaMKII triggers some important effects, specifically recruiting receptors that cause a chain reaction that then leads to long-term potentiation," Dr. Murakoshi explains. The process physically changes the dendritic spines, expanding them, an outcome that the scientists also observed in their experiments. Importantly, all that was needed for this process to happen was CaMKII activation--to put it in scientific terms, CaMKII activation was sufficient for long-term potentiation of individual dendritic spines, which had not been demonstrated before. The team also used light-based imaging technology and the light-activated CaMKII to determine what signaling molecules are activated during long-term potentiation. All of these findings combine to provide a better picture of how long-term potentiation occurs at the synapse level.
"In addition to the valuable information we uncovered about an important neurological process, our light-activated CaMKII is a major addition to existing optogenetic tools," Dr. Murakoshi comments when asked about the significance of their work. "We've created something that can be used to manipulate neuronal signaling and investigate synaptic plasticity--or the physiological changes that happen at individual synapses during events like memory formation."
The scientists are optimistic that with further development, the ability to manipulate synapses also has important implications for the treatment of brain diseases (such as autism)--a remarkable feat for neuroscience!
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-09
Researchers report that large-scale commercial farms on deforested land in the southern Amazon result in higher temperature increases and less rainfall than small-scale farms.
Deforestation has converted swaths of land in the southern Amazon region from rainforest to farmland. The uses of the deforested land are diverse, and activities can range from small-scale farming in rural settlements to large-scale commodity agriculture. Commercial farms in the Southern Amazon can reach hundreds of thousands of hectares in area, exporting millions of tons in grains and beef every year.
Eduardo Maeda from the University of Helsinki and colleagues used satellite data to compare areas dominated by different land uses and farm sizes to evaluate their impacts on ...
2021-02-09
Li-ion batteries (LIBs) are widely used in various mobile electronics. Concerns of global warming and climate change have recently boosted the demand for LIBs in electric vehicles and solar photovoltaic output smoothing. Si has been studied as an active material with a high theoretical capacity of 3578 mAh/g, which is around ten times higher than that of graphite (372 mAh/g).
Now, a team of researchers at Osaka University has used flake-shaped Si nanopowder wrapped by ultrathin graphite sheets (GSs) to fabricate LIB electrodes with high areal capacity and current density.
Generally ...
2021-02-09
Rivers and lakes at high latitudes are considered to be major sources for greenhouse gas emissions to the atmosphere, but these losses are poorly constrained. In a study published in Nature Communications, Umeå University researchers and collaborators quantify carbon emissions from rivers and lakes across Western Siberia, finding that emission are high and exceed carbon export to the Arctic Ocean.
High latitude regions play a key role in the global carbon cycle and climate system. An important question is the degree of mobilization and atmospheric release of vast soil carbon stocks, partly stored in permafrost, with amplified warming of these regions. A fraction of this carbon is exported to inland waters and emitted to the atmosphere, yet these ...
2021-02-09
Cryopreservation involves preserving biological materials, such as cells, tissues, and organs, at ultra-low temperatures so that they can be revived and used at a later date. To achieve cryopreservation such that the preserved materials are not damaged, scientists use various chemicals called cryoprotectants, which facilitate the freezing process. Unfortunately, many of the existing cryoprotective agents have major limitations. For example, dimethyl sulfoxide is useful for cryopreserving red blood cells, but it is also toxic to the cells.
To overcome these limitations, researchers at the Japan Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (JAIST) and Japan's RIKEN have experimented with a class of chemicals known as polyampholytes, identifying one ...
2021-02-09
In research on solar energy and climatology, "clear sky" or "cloudless" conditions are very important. For instance, the number of clear-sky days (number of days having an average cloud cover less than 10%) is a key parameter of solar resource assessments. The instantaneous surface irradiance is highly affected by cloud variations, based on which clear-sky detection (CSD) methods can be developed. However, a general tendency in common among all CSD methods is the detection accuracy deteriorates when aerosol loading increases.
"The lack of accurate clear-sky detection data makes it difficult to assess existing clear-sky detection methods in polluted areas," explains Liu Mengqi, a PhD student from the group of Prof. Xiang'ao Xia at the Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese ...
2021-02-09
Researchers at the Garvan Institute of Medical Research have developed a computational model to calculate 'skeletal age', a personalised estimate of an individual's risk of bone fracture and premature death.
The skeletal age calculator, which will be accessible to doctors and health professionals, aims to better identify those at risk of a first bone fracture and subsequent fractures, and also estimates how fractures impact life expectancy.
Osteoporosis, a disease which reduces bone strength and increases bone fracture risk, is a major national health issue and estimated to affect over 900,000 Australians. ...
2021-02-09
Research groups at University of Helsinki and Institut Jacques Monod, Paris, discovered a new molecular mechanism that promotes cell migration. The discovery sheds light on the mechanisms that drive uncontrolled movement of cancer cells, and also revises the 'text book view' of cell migration.
The ability of cells to move within our bodies is critical in wound healing, as well as for immune cells to patrol in our tissues to hunt bacterial and viral pathogens. On the flip-side, uncontrolled movement of cells is a hallmark of cancer invasion and metastasis.
The machinery that drives cell migration is a complex network of dynamic filaments composed of a protein actin. Actin exists in monomeric form, but ...
2021-02-09
Glaciers are not only melting, but also collapsing in the Third Pole region. In 2016, two glaciers in the western Third Pole's Aru Mountains collapsed, one after another. The first collapse caused nine human casualties and the loss of hundreds of livestock. However, that may not be the end of the catastrophe.
According to a study recently published in The Cryosphere, meltwater from ice avalanches has been filling downstream lakes in a way that may cause previously separated lakes to merge within the next decade, thus disrupting the function of ecosystems in the region.
"The collapse of Aru glaciers has both short-term and long-term impacts on downstream lakes," said Dr. LEI Yanbin, lead author of the study and a researcher at the Institute of Tibetan Plateau Research ...
2021-02-09
Science always strives to replace complex natural objects and phenomena with simpler models. Scientists of Samara Center for Theoretical Materials Science (SCTMS) of Samara Polytech have developed methods to simplify the crystal structure of a substance to obtain chemically important knowledge. The main approaches are described in the article published in the Structural Chemistry journal IF 2.081 (doi:10.1007/s11224-020-01724-4).
"The main goal of simplifying any crystal structure is to understand the features of its structure and properties, and the simplification ...
2021-02-09
The BioRescue research project, a programme aiming at saving the northern white rhinoceros from extinction, exemplifies the challenges to overcome when conducting research and conservation in an international consortium in times of a global pandemic. COVID-19 hampered communication and travels, prevented or delayed crucial procedures, caused losses in revenues and by that may have lowered the chances of a survival of the northern white rhino. The consortium adjusted strategies, gained valuable knowledge during these challenging times and continued with its mission. The effects of the pandemic on the BioRescue project are described in detail in a scientific paper published in the Journal ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New "molecular" tool helps shed light on individual synapses in brain cells
Scientists engineer a light-activated protein that can be used to study single synapses of neurons