Preventing COVID-19 and aging: Geroprotector to enhance resilience and vaccine response
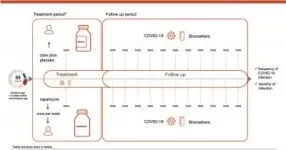
Clinical trial to explore the potential of rapalogs to enhance resilience against SARS-CoV-2 infection and reduce the severity of COVID-19 in biologically aged individuals
2021-02-10
(Press-News.org) 10th of February, Wednesday, Hong Kong - Deep Longevity, a fully-owned subsidiary of Regent Pacific (SEHK:0575.HK), specializing in the development and the application of next-generation artificial intelligence (AI) for aging and longevity research, today announced the publication of an article in Lancet Healthy Longevity titled "The potential of rapalogs to enhance resilience against SARS-CoV-2 infection and reduce the severity of COVID-19".
While the pandemic continues to unfold, targeted therapeutic solutions for COVID-19 are still not established. The extremely rapid development of various vaccines as a preventative approach provides reassurance, but at the same time faces a number of major challenges: insufficient protection against mutated variants, production line limitations, anti-vaccination skeptics etc. At the same time, COVID-19 still disproportionately affects older and comorbid individuals, who mostly suffer from more severe courses of illness, complications and lethal outcomes. Most frequently, advanced age goes hand in hand with comorbidities, which potentiates the adverse effect of the virus drastically.
Vaccines are still far from arriving at a complete protection. Unfortunately, the population least likely to benefit from such solutions are also those at the highest risk: the elderly and individuals with pre-existing age-related conditions. "It is a double-edged sword: the immune system of elderly and multimorbid (any age) patients is compromised. Those individuals are thus more prone to get infected and to develop a more severe disease. On the other hand, their response to a vaccine - which acts on and with the immune system - might be insufficient. We also see reinfections occurring in elderly patients, which then take an even more aggressive course, leading to fatalities." said associate prof. Evelyne Bischof, Harvard, Columbia and Basel trained MD, practicing physician, one of the authors of the paper in Lancet Healthy Longevity today - a joint work of the world-renowned biogerontologists and longevity specialists prof. Alex Zhavoronkov, prof.Matt Kaeberlein, and prof. Richard Siow. 'It is a major problem not only because of the predominantly aged demographics, increased danger in care homes for elderly, but especially because most elderly patients are also comorbid - due to the aging processes causing age-related, mostly chronic diseases." She continues. Such patients are at a significantly enhanced risk of infection and death if they need to be hospitalized for non-COVID-19 reasons.
While most trials exclusively target the infectious component of the disease, the authors outline the rationale behind a double approach: targeting COVID in the biologically aged for better prevention, vaccination efficacy and improved outcomes. The reasoning is complex and interrelated: old age is related with immunosenescence (immune system aging and thus worse function), with age-related diseases that are related with more severe COVID-19 course, e.g. diabetes, hypertension, cancer etc., with frailty and vulnerability (more exposure, e.g. due to homecare or institutionalization). Therefore, in order to efficiently intervene, geroprotective and senoremediative interventions towards mounting the immune response to vaccines are of uttermost importance, both from the medical, as well as the global economic aspect.
AI-based strategies were harnessed for repurposing known geroprotectors such as rapamycin, for the prevention of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Pre-clinical simulation analysis and previous evidence showing paradoxical immunopotentiation effects of rapamycin urge to propose additional clinical trials for these molecules in the broad elderly population.
In addition, in contrast to current studies, the authors propose to use an objective measurement of the biological rather than the chronological age. In the absence of reliable predictive and prognostic COVID19-biomarkers, minimally-invasive deep aging clocks are suggested as surrogate markers of biological age to track the efficacy of these preventative geroprotective interventions and to stratify the patients by predicted severity of the disease. Moreover, it will allow validation of markers of biological age in the context of viral infections and identification mechanisms by which geroprotectors enhance resilience against infections and reduce the severity of symptoms. This AI based approach in precision medicine was just recently illustrated in Nature Aging
The Lancet Healthy Longevity paper outlined the available evidence and a clinical translation of the geroprotector rapamycin for further research in a clinical trial setting, paving a new perspective: longevity medicine in pandemics. Longevity medicine as AI-based precision medicine aims to assure a healthy lifespan, mitigating and eliminating the risks and development of age-related diseases. Different from the reactive medicine, it uses the latest anticipatory technologies and muti-omics technologies to delay, attenuate or reverse senescence on all levels (cellular, tissue, system, organism, society). The benefits of such an approach in this and future pandemics is obvious, while the publication pioneers the scientific base for a longevity medicine RCT using geroprotective interventions.
INFORMATION:
About Deep Longevity: Originally incubated by Insilico Medicine, Deep Longevity was acquired on 14 December 2020 by Regent Pacific Group Limited (SEHK:0575.HK), a specialist healthcare, wellness and life sciences investment group. Deep Longevity is developing explainable artificial intelligence systems to track the rate of aging at the molecular, cellular, tissue, organ, system, physiological, and psychological levels. It is also developing systems for the emerging field of longevity medicine, enabling physicians to make better decisions on the interventions that may slow down or reverse the aging processes. Deep Longevity developed the Longevity as a Service (LaaS) solution to integrate multiple deep biomarkers of aging dubbed "deep aging clocks" to provide a universal multifactorial measure of human biological age.
https://deeplongevity.com/
About Regent Pacific (SEHK:0575.HK)
Regent Pacific is a diversified investment group based in Hong Kong currently holding various corporate and strategic investments focusing on the healthcare, wellness, and life sciences sectors. The Group has a strong track record of investments and has returned approximately US$298 million to shareholders in the 21 years of financial reporting since its initial public offering.
https://www.regentpac.com/
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-10
New Rochelle, NY, February 9, 2021--The rapid upscaling of a telemonitoring program in which health care providers performed daily telemedicine check-ins on COVID-19 patients faced a unique set of challenges. How these were resolved, and early outcomes are reported in the peer-reviewed journal Telemedicine and e-Health, Click here to read the article now.
"Kaiser Permanente's Virtual Home Care Program (VHCP) was able to rapidly establish a telemedicine-based program for the management of COVID-19 positive patients in the DC and Baltimore Metro regions. Preliminary data suggest that such a program may be effective ...
2021-02-10
Mini-Neptunes and super-Earths up to four times the size of our own are the most common exoplanets orbiting stars beyond our solar system. Until now, super-Earths were thought to be the rocky cores of mini-Neptunes whose gassy atmospheres were blown away. In a new study published in The Astrophysical Journal, astronomers from McGill University show that some of these exoplanets never had gaseous atmospheres to begin with, shedding new light on their mysterious origins.
From observations, we know about 30 to 50 percent of host stars have one or the other, and the two populations appear in about equal proportion. But where did they come from?
One theory is that most exoplanets ...
2021-02-10
Lung ultrasound, considered a simple method for diagnosing lung disease, can also help predict the clinical progression of severe COVID-19 patients, according to a study conducted at the University of São Paulo's Medical School (FM-USP) in São Paulo City, Brazil.
The principal investigator for the study was Heraldo Possolo de Souza, a professor at FM-USP and an attending physician at its teaching and general hospital, Hospital das Clínicas (HC).
The researchers applied an ultrasound examination protocol covering 12 lung regions in 180 COVID-19 patients undergoing treatment at HC. The results showed that the higher the lung ultrasound score, the greater the risk of admission to an intensive care unit (ICU), intubation, and death.
The study was supported ...
2021-02-10
Gulls are one of the main wild birds that act as reservoirs of Campylobacter and Salmonella, two most relevant intestinal antibiotic-resistant bacteria causing gastroenteritis in humans. Therefore, according to an article published in the journal Science of the Total Environment seagulls could act as sentinels of the antibiotic pressure in the environment.
The study was carried out by experts of the Faculty of Biology and the Biodiversity Research Institute (IRBio) of the University of Barcelona, and the Institute of Agrifood Research and Technology (IRTA).
Resistant bacteria to antibiotics represent a serious problem for human health and other species since they can harden the treatment ...
2021-02-10
BOSTON - How often a person takes daytime naps, if at all, is partly regulated by their genes, according to new research led by investigators at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) and published in Nature Communications. In this study, the largest of its kind ever conducted, the MGH team collaborated with colleagues at the University of Murcia in Spain and several other institutions to identify dozens of gene regions that govern the tendency to take naps during the day. They also uncovered preliminary evidence linking napping habits to cardiometabolic health.
"Napping is somewhat controversial," says Hassan Saeed Dashti, PhD, RD, of the MGH Center for Genomic Medicine, co-lead author of the report with Iyas Daghlas, a medical student at ...
2021-02-10
Alongside the effects of lifestyle, including physical exercise and diet, on ageing, research has increasingly turned its attention to the potential cognitive benefits of musical hobbies. However, such research has mainly concentrated on hobbies involving musical instruments.
The cognitive benefits of playing an instrument are already fairly well known: such activity can improve cognitive flexibility, or the ability to regulate and switch focus between different thought processes. However, the cognitive benefits of choir singing have so far been investigated very little.
Now, a study recently ...
2021-02-10
BOSTON - When patients arrive in emergency departments and hospitals with symptoms consistent with COVID-19, it's critical to isolate them to avoid the potential spread of infection, but keeping patients isolated longer than needed could delay patient care, take up hospital beds needed for other patients, and unnecessarily use up personal protective equipment. A team led by investigators at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) has now created a tool to guide frontline clinicians through diagnostic evaluations of such patients so that they'll know when it's safe to discontinue precautions. The tool was developed and validated in a study published in Clinical Infectious Diseases.
In the spring of 2020, due to the risk of false-negative ...
2021-02-10
UPTON, NY--Scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy's Brookhaven National Laboratory, Stony Brook University (SBU), and other collaborating institutions have uncovered dynamic, atomic-level details of how an important platinum-based catalyst works in the water gas shift reaction. This reaction transforms carbon monoxide (CO) and water (H2O) into carbon dioxide (CO2) and hydrogen gas (H2)--an important step in producing and purifying hydrogen for multiple applications, including use as a clean fuel in fuel-cell vehicles, and in the production of hydrocarbons.
But because ...
2021-02-10
A team of Russian scientists from NUST MISIS, Tomsk Polytechnic University (TPU) and Boreskov Institute of Catalysis has suggested a new approach to modifying the combustion behavior of coal. The addition of copper salts reduces the content of unburnt carbon in ash residue by 3.1 times and CO content in the gaseous combustion products by 40%, the scientists found. The research was published in Fuel Processing Technology.
According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), coal is the predominant energy resource used as the primary fuel for power generation. According to reports, coal supplied over one-third of global electricity generation in ...
2021-02-10
Oncotarget published "Combination of copanlisib with cetuximab improves tumor response in cetuximab-resistant patient-derived xenografts of head and neck cancer" which reported that HNSCC is frequently associated with either amplification or mutational changes in the PI3K pathway, making PI3K an attractive target, particularly in cetuximab-resistant tumors.
Here, the authors explored the antitumor activity of the selective, pan-class I PI3K inhibitor copanlisib with predominant activity towards PI3Kα and δ in monotherapy and in combination with cetuximab using a mouse clinical trial set-up with 33 patient-derived xenograft models with known HPV and PI3K mutational status and available data ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Preventing COVID-19 and aging: Geroprotector to enhance resilience and vaccine response
Clinical trial to explore the potential of rapalogs to enhance resilience against SARS-CoV-2 infection and reduce the severity of COVID-19 in biologically aged individuals