CWRU researchers uncover biochemical rules between RNA-protein interactions and expr
Work has potential implications for new therapies to treat cancer and neurodegenerative disorders
2021-02-10
(Press-News.org) CLEVELAND--A team of Case Western Reserve University researchers has found a way to measure key characteristics of proteins that bind to RNA in cells--a discovery that could improve our understanding of how gene function is disturbed in cancer, neurodegenerative disorders or infections.
RNA--short for ribonucleic acid--carries genetic instructions within the body. RNA-binding proteins play an important role in the regulation of gene expression. Scientists already knew that the way these proteins function depends on their "binding kinetics," a term that describes how frequently they latch on to a site in an RNA, and how long they stay there.
Until now, researchers could not measure the kinetics of RNA-binding proteins in cells. But the Case Western Reserve researchers answered this longstanding question in RNA biology. The findings open the door to a biochemical understanding of RNA protein interactions in cells.
By understanding the kinetics, researchers can quantitatively predict how an RNA binding protein regulates the expression of thousands of genes, which is critical for developing strategies that target RNA protein interactions for therapeutic purposes.
"The study marks a major step toward understanding how gene function is regulated and how to devise ways to correct errors in this regulation in diseases such as cancer, neurodegenerative disorders or infections," said Eckhard Jankowsky, the study's principal author and a professor of biochemistry at the university's School of Medicine and director of the school's Center for RNA Science and Therapeutics .
Their study, "The kinetic landscape of an RNA binding protein in cells," was published Feb. 10 in Nature. Funding from the National Institute of General Medical Sciences and the National Science Foundation supported the research.
The co-authors, all from Case Western Reserve, are: research associate Deepak Sharma; graduate students Leah Zagore, Matthew Brister and Xuan Ye; Carlos Crespo-Hernández, a chemistry professor; and Donny Licatalosi, an associate professor of biochemistry and member of the Center for RNA Science and Therapeutics.
To measure the kinetics of RNA binding proteins, the researchers used a laser that sends out extremely short (femtosecond) pulses of ultraviolet light to cross-link the RNA-binding protein known as DAZL to its several thousand binding sites in RNAs. (DAZL, short for Deleted in Azoospermia-Like, is involved in germ cell development.) They then used high throughput sequencing to measure the change of the crosslinked RNA over time and determined the binding kinetics of DAZL at thousands of binding sites.
The resulting "kinetic landscape" allowed the researchers to decode the link between DAZL binding and its effects on RNAs.
INFORMATION:
Case Western Reserve University is one of the country's leading private research institutions. Located in Cleveland, we offer a unique combination of forward-thinking educational opportunities in an inspiring cultural setting. Our leading-edge faculty engage in teaching and research in a collaborative, hands-on environment. Our nationally recognized programs include arts and sciences, dental medicine, engineering, law, management, medicine, nursing and social work. About 5,100 undergraduate and 6,700 graduate students comprise our student body. Visit case.edu to see how Case Western Reserve thinks beyond the possible.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-10
A team of researchers, led by a Texas A&M University professor, has found that some energy drinks have adverse effects on the muscle cells of the heart.
The study, led by Dr. Ivan Rusyn, a professor in the Veterinary Integrative Biosciences (VIBS) Department at the Texas A&M College of Veterinary Medicine & Biomedical Sciences (CVMBS), was published in Food and Chemical Toxicology. In it, researchers observed cardiomyocytes - human heart cells grown in a laboratory - exposed to some energy drinks showed an increased beat rate and other factors affecting cardiac function.
When placed in the context of the human body, ...
2021-02-10
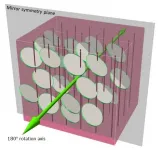
A team at the University of Colorado Boulder has designed new kinds of liquid crystals that mirror the complex structures of some solid crystals--a major step forward in building flowing materials that can match the colorful diversity of forms seen in minerals and gems, from lazulite to topaz.
The group's findings, published today in the journal Nature, may one day lead to new types of smart windows and television or computer displays that can bend and control light like never before.
The results come down to a property of solid crystals that will be familiar to many chemists and gemologists: Symmetry.
Ivan Smalyukh, ...
2021-02-10
Israelis across the political spectrum prefer the status quo to the two-state solution, and Palestinians are only willing to accept a two-state solution that Israelis will be unable to accept, according to a new RAND Corporation report that assesses whether there are any alternative solutions to the conflict that average Israelis and Palestinians would support.
Derived from a series of innovative, structured focus group discussions, the report suggests that the Biden Administration's recent reaffirmation of U.S. policy to support a "mutually agreed two-state solution, one in which Israel lives in peace ...
2021-02-10
The number of people who own electric vehicles (EVs) is increasing, but they face a conundrum: Unlike those who own gasoline-burning cars, EV owners can't just pop down to the corner gas station for a fill-up. Particularly in rural areas, charging stations can be few and far between.
Joshua Pearce, Richard Witte Endowed Professor of Materials Science and Engineering and professor of electrical and computer engineering at Michigan Technological University, hopes to change that.
In a model outlined in a paper in the journal Renewable Energy, Pearce and his co-author, graduate student Swaraj Sanjay Deshmukh, note the untapped potential of retail parking lot solar photovoltaic awnings.
The study investigates the energy-related benefits ...
2021-02-10
A team of researchers from Immanuel Kant Baltic Federal University obtained magnetic nanoparticles using sweet flag (Acorus calamus). Both the roots and the leaves of this plant have antioxidant, antimicrobial, and insecticide properties. The extract of sweet flag was used as a non-toxic reagent for the manufacture of coated particles. The authors of the work also showed the efficiency of the new nanoparticles against several types of pathogenic fungi that damage cultivated plants. A technology developed by the team provides for the manufacture of nanoparticles from a cheap plant-based raw material and reduces the harmful effect of reagents on the environment.
Because of their unique properties, nanoparticles are used in many areas, from medicine to oil production. ...
2021-02-10
The gram-negative bacteria Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) colonize the stomachs of the majority of the world's population. Although most people may never experience major complications due to the pathogen, H. pylori infections increase the risk of certain types of gastric cancer, as well as other illnesses such as peptic ulcers and gastritis.
Currently, H. pylori infections are treatable with a cocktail of antibiotics, but the rapid emergence of antibiotic resistance in H. pylori is a significant concern. To counter these threats, Pushkar Lele, assistant professor in the Artie McFerrin Department of Chemical Engineering at Texas A&M University, investigated how ...
2021-02-10
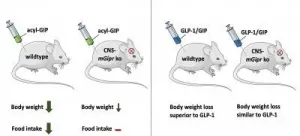
The GIP receptor in the central nervous system plays a crucial role in the regulation of body weight and food intake. This is shown by a recent study by Helmholtz Zentrum München, ETH Zurich and the German Center for Diabetes Research (DZD). The study, which has now been published in 'Cell Metabolism', identifies new targets for the development of a drug treatment for obesity and type 2 diabetes.
Dual-agonists targeting the receptors for Glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) are promising novel drug candidates for the treatment of obesity and diabetes. The new study shows how GIP decreases body weight. GIP is a hormone produced by ...
2021-02-10
With the recent development of foldable mobile phone screens, research on foldable electronics has never been so intensive. One particularly useful application of the foldable technology is in solar panels.
Current solar cells are restricted to rigid, flat panels, which are difficult to store in large numbers and integrate into everyday appliances, including phones, windows, vehicles, or indoor devices. But, one problem prevents this formidable technology from breaking through: to be integrated into these items, solar cells need to be foldable, to bend at will repeatedly without breaking. Traditional conducting materials used in ...
2021-02-10
MAX-phases are the new promising class of artificially created compounds that started to be extensively studied in the last two decades. They are a family of ternary layered compounds with the general formula Mn+1AXn (n = 1, 2, 3 ...), where M is an early transition metal (Sc, Ti, V, Cr, et cetera; elements from the left side of the d-block of the periodic table from group III to group VII); A -- an element from group IIIA or IVA (the most common are Al, Ga, Si, Ge); X is carbon or nitrogen, that is, the MAX phase is carbide or nitride, respectively.
Due to their structure and composition, ternary layered carbides and nitrides of d- and p-elements have a unique combination of physical properties. These compounds have high electrical and heat conductivity ...
2021-02-10
One of the many mysteries still surrounding COVID-19 is why some people experience only mild, flu-like symptoms, whereas others suffer life-threatening respiratory problems, vascular dysfunction and tissue damage. Now, researchers reporting in ACS' Analytical Chemistry have used a combination of metabolomics and machine learning to identify possible biomarkers that could both help diagnose COVID-19 and assess the risk of developing severe illness.
Although some pre-existing conditions, such as diabetes or obesity, can increase the risk of hospitalization and death from COVID-19, some otherwise healthy people have also experienced ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] CWRU researchers uncover biochemical rules between RNA-protein interactions and expr
Work has potential implications for new therapies to treat cancer and neurodegenerative disorders