New targets for the development of a drug treatment for obesity and type 2 diabetes
The hormone GIP regulates body weight and food intake via a receptor in the brain
2021-02-10
(Press-News.org) The GIP receptor in the central nervous system plays a crucial role in the regulation of body weight and food intake. This is shown by a recent study by Helmholtz Zentrum München, ETH Zurich and the German Center for Diabetes Research (DZD). The study, which has now been published in 'Cell Metabolism', identifies new targets for the development of a drug treatment for obesity and type 2 diabetes.
Dual-agonists targeting the receptors for Glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) are promising novel drug candidates for the treatment of obesity and diabetes. The new study shows how GIP decreases body weight. GIP is a hormone produced by the digestive tract. After food intake, GIP stimulates the release of insulin and thus lowers blood glucose levels. The hormone also has an effect on appetite regulation. However, the mechanisms and organs through which GIP affects body weight are unknown. Until now, it was unclear whether the GIP receptor should be activated or inhibited for body weight reduction and what role the brain plays in the effect of GIP. "The aim of our studies was to find out whether the GIP receptor in the brain plays a special role in the action of GIP," said first author Qian Zhang of the Institute for Diabetes and Obesity at Helmholtz Zentrum München.
GIP lowers body weight through brain-mediated inhibition of food intake
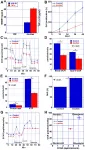
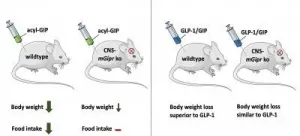
The researchers were able to show that the administration of GIP reduces body weight and food intake in wild-type mice, but not in mice that lack the GIP receptor in the central nervous system.
Does the hormone act on specific areas in the brain? To answer this question, the researchers investigated the brain activity of mice with diet-induced obesity after they had been treated with GIP. "This revealed increased neuronal activity in areas of the hypothalamus associated with appetite control," said Professor Christian Wolfrum of ETH Zurich. The authors conclude that the central regulation of food intake via GIP also includes the activation of important neurons in the hypothalamus.
New targets for the development of a drug treatment for obesity and type 2 diabetes
The new findings are also important for the development of drug treatment for obesity and type-2 diabetes. Researchers at Helmholtz Zentrum München, together with Indiana University, have developed a new therapeutic approach for type-2 diabetes. They combined hormones in a single molecule that act equally at the receptors of the insulin-stimulating hormones GLP-1 and GIP. The dual agonist lowers body weight and improves blood glucose levels1. GLP-1/GIP dual-agonists are already in phase 3 clinical trials. Clinical studies showed that GLP-1/GIP reduces body weight to a greater extent than treatment with GLP-1 alone.
However, these marked differences in weight loss were not observed in mice lacking the GIP receptor in the CNS, says Dr. Timo Müller, last author of the new study and acting Director of the Institute for Diabetes and Obesity. Here, the GLP-1/GIP dual-agonist and the administration of GLP-1 equally reduce body weight. "Our research shows for the first time that the GLP-1/GIP dual-agonist requires the GIP receptor in the brain to reduce body weight and food intake," said DZD-Researcher Dr. Müller. "These findings may aid in the development of novel drug targets that improve the signaling and effect of the GIP receptor. This could help to further increase the metabolic benefits of treatment with GIP and GLP-1/GIP."
INFORMATION:
Scientific Contact:
Dr. Timo Müller
Helmholtz Zentrum München
German Research Center for Environmental Health (GmbH)
Institute for Diabetes and Obesity
Ingolstädter Landstraße 1
D-85764 Neuherberg
Phone: +49 89 3187-43278
Original publication:
Qian Zhang et al.: The glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) regulates body weight and food intake via CNS-GIPR signaling. Cell Metabolism. DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2021.01.015
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-10
With the recent development of foldable mobile phone screens, research on foldable electronics has never been so intensive. One particularly useful application of the foldable technology is in solar panels.
Current solar cells are restricted to rigid, flat panels, which are difficult to store in large numbers and integrate into everyday appliances, including phones, windows, vehicles, or indoor devices. But, one problem prevents this formidable technology from breaking through: to be integrated into these items, solar cells need to be foldable, to bend at will repeatedly without breaking. Traditional conducting materials used in ...
2021-02-10
MAX-phases are the new promising class of artificially created compounds that started to be extensively studied in the last two decades. They are a family of ternary layered compounds with the general formula Mn+1AXn (n = 1, 2, 3 ...), where M is an early transition metal (Sc, Ti, V, Cr, et cetera; elements from the left side of the d-block of the periodic table from group III to group VII); A -- an element from group IIIA or IVA (the most common are Al, Ga, Si, Ge); X is carbon or nitrogen, that is, the MAX phase is carbide or nitride, respectively.
Due to their structure and composition, ternary layered carbides and nitrides of d- and p-elements have a unique combination of physical properties. These compounds have high electrical and heat conductivity ...
2021-02-10
One of the many mysteries still surrounding COVID-19 is why some people experience only mild, flu-like symptoms, whereas others suffer life-threatening respiratory problems, vascular dysfunction and tissue damage. Now, researchers reporting in ACS' Analytical Chemistry have used a combination of metabolomics and machine learning to identify possible biomarkers that could both help diagnose COVID-19 and assess the risk of developing severe illness.
Although some pre-existing conditions, such as diabetes or obesity, can increase the risk of hospitalization and death from COVID-19, some otherwise healthy people have also experienced ...
2021-02-10
If you watch the leaves of a plant long enough, you may see them shift and turn toward the sunlight through the day. It happens slowly, but surely.
Some man-made materials can mimic this slow but steady reaction to light energy, usually triggered by lasers or focused ambient light. New research from the University of Pittsburgh and Carnegie Mellon University has discovered a way to speed up this effect enough that its performance can compete against electrical and pneumatic systems.
"We wanted to create machines where light is the only source of energy and direction," explained M. Ravi Shankar, professor of industrial engineering and senior author of the paper. "The challenge is that while we could get some movement and actuation with light-driven polymers, ...
2021-02-10
CORVALLIS, Ore. - The Columbia River basin will see an increase in flooding over the next 50 years as a result of climate change, new modeling from Oregon State University indicates.
The magnitude of flooding - the term used to describe flooding severity - is expected to increase throughout the basin, which includes the Columbia, Willamette and Snake rivers and hundreds of tributaries. In some areas, the flooding season will expand, as well.
"The flood you're used to seeing out your window once every 10 years will likely be larger than it has been in the past," said the study's lead author, Laura Queen, a research assistant at OSU's Oregon Climate Change Research Institute. ...
2021-02-10
A team of scientists from Immanuel Kant Baltic Federal University with their colleagues from the Institute of Ecology and Genetics of Microorganisms of the Ural Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences (Perm) studied the effect of trophoblastic β1-glycoprotein in the blood of pregnant women on pro-inflammatory immune cells. Thanks to trophoblastic β1-glycoprotein, a woman's body does not adversely react to the fetus and supports its normal development until birth. It turned out that trophoblastic β1-glycoproteins also suppressed the development of pro-inflammatory lymphocytes ...
2021-02-10
Exposure to some odorless, colorless and tasteless gases, such as nerve agents, can be toxic or even lethal. And having the ability to detect other types of vapors could save people from eating spoiled or rotten food. Easy-to-use portable devices could, therefore, go a long way toward protecting the public. Now researchers reporting in ACS Materials Letters have created a pen-like sensor that changes color when exposed to harmful gases.
Humans can't detect many toxic vapors, such as poisonous nerve agents or volatile amines released from spoiled foods, so a sensor that can notice these gases' very minute concentrations would be useful. Fluorescence-based sensors are a potential solution because they are inexpensive and can reveal trace amounts of compounds. However, some fluorescing ...
2021-02-10
CHICAGO --- Northwestern University's Noshir Contractor will discuss team problem-solving and human systems integration for Mars exploration at the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) annual meeting.
At a AAAS press briefing at 12 p.m. ET, Wednesday, Feb. 10, Contractor will discuss recent findings and opportunities for social science research on astronauts as exploration advances into deep space. The embargo will lift at the time of the press briefing.
In addition, he will present "Pairing Teams for, and (Re)pairing Teams During, Long-Duration Space Exploration" at 1 p.m. ET on Thursday, Feb. 11 ...
2021-02-10
Political polarization is having far-reaching impacts on American life, harming consumer welfare and creating challenges for people ranging from elected officials and policymakers to corporate executives and marketers.
That's one of the conclusions of a new scholarly paper by researchers from the University of Wyoming and five other universities across the country. The paper appears in the Journal of Public Policy & Marketing of the American Marketing Association.
"I think we're all aware of how political polarization has affected our elections and system of government, but the impacts go far beyond the political arena," ...
2021-02-10
Oncotarget recently published "Evaluation of cancer-derived myocardial impairments using a mouse model" which reported that Myocardial damage in cancer patients is emphasized as a cause of death; however, there are not many murine cachexia models to evaluate cancer-derived heart disorder.
Using the mouse cachexia model that they established previously, the authors investigated myocardial damage in tumor-bearing mice.
When rat cardiomyoblasts were treated with mouse cachexia model ascites and subjected to flux analysis, both oxidative phosphorylation and glycolysis were suppressed, and the cells were in a quiescent state.
These results are in good agreement with those previously reported on cancerous myocardial damage.
The established mouse cachexia ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New targets for the development of a drug treatment for obesity and type 2 diabetes
The hormone GIP regulates body weight and food intake via a receptor in the brain