(Press-News.org) EAST LANSING, Mich. - The 1918 influenza pandemic provides a cautionary tale for what the future may hold for COVID-19, says a Michigan State University researcher.
After a decade studying a flu virus that killed approximately 15,000 Michigan residents, Siddharth Chandra, a professor in MSU's James Madison College, saw his research come to life as he watched the spread of the COVID-19 pandemic.
"It was so surreal," said Chandra, who has a courtesy appointment in epidemiology and biostatistics. "All of a sudden, I was living my research."
Chandra's research is published in the American Journal of Public Health with co-authors Julia Christensen, a graduate of James Madison College; Madhur Chandra, Senior Community Epidemiologist with the Ingham County Health Department and graduate of the Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics at MSU; and Nigel Paneth, professor of epidemiology and biostatistics and pediatrics at MSU.
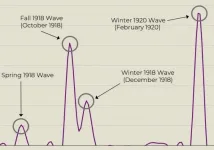
Using influenza infection and mortality data on Michigan from 1918-1920, Chandra identified four distinct waves. The first large peak was in March 1918. "After a second spike in cases in October 1918, the governor instituted a statewide ban on public gatherings," Chandra said. "Much like the restrictions that were put in place during the COVID-19 pandemic."
After three weeks, the number of cases decreased and the ban was lifted, which led to another peak in December 1918. "The ban didn't stop the spread of the flu. It just delayed the spike in cases," he said.
Chandra mapped the data showing the peaks and spikes in cases from October 1918 and December 1918 and tracked flu virus case growth by county over time. In October, counties in the southern part of the state and near the Mackinac Straits had the highest numbers but by December, the highest numbers of cases were in the heart of the state.
The most surprising piece of data came 18 months later in February 1920, when a statewide explosion of cases created a massive spike even larger than the one in October 1918. For Chandra, it is an educated guess as to the reasons for this delayed increase.
"Assuming it's the same influenza virus, World War I ended in 1918 and the men were coming home to their families," he said. "We had a mobile agent that brought the virus home to infect family members, which would explain the increase in cases among children and the elderly."
Unfortunately, there is not a way to confirm this, Chandra noted. "We would need samples from patients in 1920 from across the state. Then, we would need to compare those with samples from patients in 1918 from across the state, and that's not likely to happen."
The weather may have also been a factor since cool temperatures with low humidity likely provided optimal conditions for the virus to live and spread. Another factor that played a role was the absence of a vaccine.
"In 1918, there was no hope for a vaccine. In 2021, we have a vaccine available," he said.
One of the key insights from the 1918 pandemic that can inform the public health response to the 2020 COVID-19 pandemic is the number of people who are susceptible to the virus. Which means that it is possible that a spike like the February 1920 one will occur in late 2021 or early 2022.
"So many people will remain susceptible until they get vaccinated," Chandra said. "Bad things can still happen a year or two from now even if we see a decrease in the number of cases now. We still have over 200 million people walking around who are susceptible to the virus, including myself."
INFORMATION:
(Note for media: Please include the following link to the study in all online media coverage: https://ajph.aphapublications.org/doi/10.2105/AJPH.2020.305969)
Michigan State University has been working to advance the common good in uncommon ways for more than 165 years. One of the top research universities in the world, MSU focuses its vast resources on creating solutions to some of the world's most pressing challenges, while providing life-changing opportunities to a diverse and inclusive academic community through more than 200 programs of study in 17 degree-granting colleges.
For MSU news on the Web, go to MSUToday. Follow MSU News on Twitter at twitter.com/MSUnews
A team of astronomers, including associate professor Chad Trujillo of Northern Arizona University's Department of Astronomy and Planetary Science, have confirmed a planetoid that is almost four times farther from the Sun than Pluto, making it the most distant object ever observed in our solar system. The planetoid, which has been nicknamed "Farfarout," was first detected in 2018, and the team has now collected enough observations to pin down its orbit. The Minor Planet Center has now given it the official designation of 2018 AG37.
Farfarout's nickname distinguished it from the previous record holder "Farout," found by the same team of astronomers ...
Orange, Calif. - The mutually beneficial relationship between legumes and rhizobia, the nitrogen-fixing soil bacteria that make their home in legume root nodules and create nutrient-rich fertilizer for them, is one of the most well-known and agronomically important examples of symbiosis. New research from END ...
Individual choices in medicine carry a certain amount of uncertainty.
An innovative partnership at The University of Texas at Austin takes aim at medicine down to the individual level by applying state-of-the-art computation to medical care.
"Medicine in its essence is decision-making under uncertainty, decisions about tests and treatments," said Radek Bukowski, MD, PhD, professor and associate chair of Investigation and Discovery in the Department of Women's Health at Dell Medical School at UT Austin.
"The human body and the healthcare system are complex systems made of ...
Firefighters and emergency medical services workers are at high risk of exposure to COVID-19 while on the job and pose an additional risk of transmitting the virus to others. Although vaccines are a promising public health tool for reducing COVID-19 transmission, little has been known about the perceptions of the COVID-19 vaccine among first responders.
To provide insight, a University of Miami Miller School of Medicine-led study queried a national sample of U.S. firefighters and emergency medical services workers through an anonymous online survey. The study results, published online Feb. 1 in the Journal of Occupational ...
Ten years ago, researchers at Aarhus University, Denmark, reported the discovery of centimeter-long cable bacteria, that live by conducting an electric current from one end to the other. Now the researchers document that a few cells operate with extremely high oxygen consumption while the rest of the cells process food and grow without oxygen. An outstanding way of life.
We humans need food and oxygen to live.
Now, imagine if oxygen was to be found only at the mountain top and food only in the valley. That's how the world looks like for cable bacteria, which live in the bottom of seas and lakes. For them, ...
In far too many cases over the years, scientists have discovered promising new cancer treatments, only to report later that the tumor cells found ways to become resistant. These disappointing results have made overcoming drug resistance a major goal in cancer research.
Now, experts at Cincinnati Children's report success at averting drug resistance in a subtype of brain tumors called glioblastomas. Importantly, the research indicates that the approach may also work in other cancers, such as melanoma, that exhibit a similar pathway of drug resistance.
The method involves inhibiting a protein called SCD and reducing the ...
A potent ozone-depleting chemical whose emissions unexpectedly spiked in recent years has quickly dropped back to much lower levels, putting the recovery of the stratospheric ozone layer back on track, according to a new study by scientists at MIT, the University of Bristol, and other institutions in South Korea, the U.S., Japan, Australia, and Switzerland.
The chemical in question is CFC-11, a chlorofluorocarbon that was once commonly used for refrigeration, insulation, and other purposes. When emitted to the atmosphere, CFC-11 can loft into the stratosphere, where the sun's ultraviolet radiation breaks the chemical down to release chlorine -- a noxious chemical that then eats ...
In the face of a changing climate and crop diseases, manufacturers of products containing natural flavors and fragrances are pivoting to a new way to source ingredients. Companies have been partnering with biotechnology firms to manufacture scents and flavors using fermented microbes, which experts say are more sustainable. A new story in Chemical & Engineering News (C&EN), the weekly newsmagazine of the American Chemical Society, details how the industry is brewing up new fragrances.
Although the availability of natural fragrances and flavors like citrus and vanilla is dwindling, the demand for them has increased, writes Senior Business Editor Melody Bomgardner. In recent years, flavor and fragrance companies have been working with the biotech industry to shore ...
Rates of overweight and obesity in children are rising around the world, with serious long-term consequences for health and health care costs. In prior research, video and mobile games have helped children eat healthier and exercise more. A new study examined how Indian 10- and 11-year-olds' food choices were affected by playing a pediatric dietary mobile game that uses implicit learning--educating players without making them aware of the lessons through innovations in neurocognitive training and immersive technology. The study found that the game significantly improved children's food choices immediately after play.
The study was conducted by researchers at Carnegie Mellon University (CMU), Hofstra University, Johns Hopkins University Center for Communication Programs (CCP), ...
The visibility of scientific articles and conference papers is conditional upon being easily found in academic search engines, especially Google Scholar. To enhance this visibility, search engine optimization (SEO) has been applied in recent years to academic search engines in order to optimize documents and, thereby, ensure they are better ranked in search pages (i.e., academic search engine optimization or ASEO).
Recent research, published in Future Internet, has found out whether the language of the document is a factor involved in the sorting algorithm of search results on Google Scholar. The study authors are Cristòfol Rovira, Lluís Codina and ...