To help keep cats from killing wildlife, add more meat and play to their day
2021-02-11
(Press-News.org) Domestic cats are a major threat to wild species, including birds and small mammals. But researchers reporting in the journal Current Biology on February 11 now have evidence that some simple strategies can help to reduce cats' environmental impact without restricting their freedom. Their studies show that domestic cats hunt less when owners feed them a diet including plenty of meat proteins. Equally, it helps to play with them each day in ways that allow cats to mimic hunting.
"While keeping cats indoors is the only sure-fire way to prevent hunting, some owners are worried about the welfare implications of restricting their cat's outdoor access," said Robbie McDonald from the University of Exeter's Environment and Sustainability Institute. "Our study shows that--using entirely non-invasive, non-restrictive methods--owners can change what the cats themselves want to do."
Most cat owners don't actually want their cats killing wild animals. In addition to keeping cats indoors, methods such as putting cats in brightly colored collars can help protect birds from hunting cats. But these products don't protect mammals, and some cats find them uncomfortable or tend to lose them. So, in the new study, McDonald and his colleagues decided to try some new strategies, including puzzle feeders, meaty diets, and play, all of which have potential to reduce predation while enriching cats' lives in other ways.
The researchers enrolled 219 households in southwest England in the 12-week trial to test the effect of such strategies on hunting by cats. Altogether, the study included 355 cats. The evidence shows that diets where proteins were derived from meat reduced the number of prey animals brought home to cat owners by 36 percent.
"Some cat foods contain protein from plant sources such as soy, and it is possible that despite forming a 'complete diet' these foods leave some cats deficient in one or more micronutrients--prompting them to hunt," said Martina Cecchetti, the PhD student who conducted the experiments.
In the "play" group, cats could stalk, chase, and pounce on a feather toy dangled by their owner on a string and wand. Owners also gave cats a mouse-like toy to play with after each "hunt," mimicking a real kill. As little as five to ten minutes a day of such play reduced predation by 25 percent, the study reports.
Use of puzzle feeders didn't have the desired effect. In fact, owners found that their cats brought home even more prey animals than before. The reasons for that aren't yet clear. It's possible that in a short trial, cats and owners struggled to use the puzzle feeders and that the cats simply may have been hungrier, the researchers say.
Nevertheless, the new findings show that limiting predation by cats depends as much on what owners do with their cats as it does on the cats themselves. In future studies, the researchers hope to find ways to reduce cat predation even more. They're interested in exploring whether particular micronutrients could be added to cat foods to reduce hunting without as much meat.
"We also plan to investigate whether different kinds of play have different effects and whether combining strategies can reduce hunting even further," Cechetti said.
INFORMATION:
This work was supported by SongBird Survival and the University of Exeter.
Current Biology, Cecchetti et al.: "Provision of high-meat-content food and object play reduce predation of wild animals by domestic cats Felis catus" https://www.cell.com/current-biology/fulltext/S0960-9822(20)31896-0
Current Biology (CurrentBiology), published by Cell Press, is a bimonthly journal that features papers across all areas of biology. Current Biology strives to foster communication across fields of biology, both by publishing important findings of general interest and through highly accessible front matter for non-specialists. Visit: http://www.cell.com/current-biology. To receive Cell Press media alerts, contact press@cell.com.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-11
Domestic cats hunt wildlife less if owners play with them daily and feed them a meat-rich food, new research shows.
Hunting by cats is a conservation and welfare concern, but methods to reduce this are controversial and often rely on restricting cat behaviour in ways many owners find unacceptable.
The new study - by the University of Exeter - found that introducing a premium commercial food where proteins came from meat reduced the number of prey animals cats brought home by 36%, and also that five to ten minutes of daily play with an owner resulted ...
2021-02-11
Cambridge, MA - February 11, 2020 - Dyno Therapeutics, a biotech company applying artificial intelligence (AI) to gene therapy, today announced a publication in Nature Biotechnology that demonstrates the use of artificial intelligence to generate an unprecedented diversity of adeno-associated virus (AAV) capsids towards identifying functional variants capable of evading the immune system, a factor that is critical to enabling all patients to benefit from gene therapies. The research was conducted in collaboration with Google Research, Harvard's Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering and the Harvard Medical School laboratory of George M. Church, Ph.D., a Dyno scientific co-founder. The publication is entitled "Deep diversification ...
2021-02-11
Natural compounds found in apples and other fruits may help stimulate the production of new brain cells, which may have implications for learning and memory, according to a END ...
2021-02-11
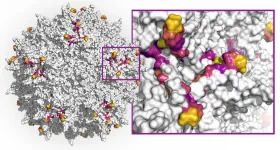
(Boston) -- Adeno-associated viruses (AAVs) have become promising vehicles for delivering gene therapies to defective tissues in the human body because they are non-pathogenic and can transfer therapeutic DNA into target cells. However, while the first gene therapy products approved by the Federal Drug Administration (FDA) use AAV vectors and others are likely to follow, AAV vectors still have not reached their full potential to meet gene therapeutic challenges.
First, currently used AAV capsids - the spherical protein structures enveloping the virus' single-stranded DNA genome which can be modified to encode therapeutic genes - are limited in their ability to specifically hone in on the tissue affected by a disease and their wider distribution throughout ...
2021-02-11
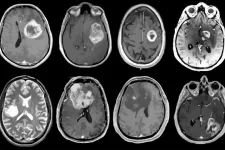
Glioblastoma is among the most aggressive and devastating of cancers. While rare compared with other cancers, it's the most common type of brain cancer. Even with intensive therapy, relatively few patients survive longer than two years after diagnosis, and fewer than 10% of patients survive beyond five years. Despite extensive studies focused on genomic features of glioblastoma, relatively little progress has been made in improving treatment for patients with this deadly disease.
Now, a new study led by Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, Case Western Reserve University and the National Cancer Institute (NCI) of the National Institutes of Health (NIH) has revealed a detailed map of the genes, ...
2021-02-11
What The Study Did: This observational study assessed CRISPR-based methods for screening to detect SARS-CoV-2 among asymptomatic college students.
Authors: Carolina Arias, Ph.D., of the University of California, Santa Barbara, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.37129)
Editor's Note: The article includes funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media advisory: ...
2021-02-11
What The Study Did: Changes in otolaryngology surgical volumes in the United States early on in the COVID-19 pandemic are described in this study.
Authors: Anirudh Saraswathula, M.D., M.S., of Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine in Baltimore, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaoto.2020.5472)
Editor's Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest ...
2021-02-11
What The Viewpoint Says: How pandemic-related disruptions may adversely impact progress toward a gender-balanced workforce in academic oncology is described in this article, which also offers possible solutions to mitigate the problem in this specialty.
Authors: Reshma Jagsi, M.D., D.Phil., of the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2020.7681)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflicts of interest disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media ...
2021-02-11
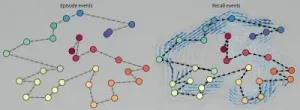
Your brain is constantly evaluating which aspects of your experiences to either remember for later, ignore, or forget. Dartmouth researchers have developed a new approach for studying these aspects of memory, by creating a computer program that turns sequences of events from a video into unique geometric shapes. These shapes can then be compared to the shapes of how people recounted the events. The study provides new insight into how experiences are committed to memory and recounted to others. The results are published in Nature Human Behavior and were based on how people remembered the experience of watching an episode of Sherlock, a BBC television show.
"When we represent experiences and memories as shapes, we can use the tools ...
2021-02-11
Considered the most lethal form of DNA damage, double-strand breaks must be repaired to prevent cell death. In developing therapies for hard-to-treat breast and ovarian cancers in patients with BRCA gene mutations, scientists aim to identify ways to keep cancer cells from using DNA break repair pathways. New findings demonstrate a previously-unknown capability for polymerase theta (pol theta) - a key enzyme in this repair function - that shows promise as a new avenue for treatment development.
The study results are published in Molecular Cell.
Researchers at the University of Vermont (UVM), The University of Texas MD Anderson ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] To help keep cats from killing wildlife, add more meat and play to their day