UMass Amherst team helps demonstrate spontaneous quantum error correction
New research tackles a central challenge of powerful quantum computing
2021-02-11
(Press-News.org) To build a universal quantum computer from fragile quantum components, effective implementation of quantum error correction (QEC) is an essential requirement and a central challenge. QEC is used in quantum computing, which has the potential to solve scientific problems beyond the scope of supercomputers, to protect quantum information from errors due to various noise.
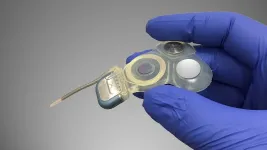
Published by the journal Nature, research co-authored by University of Massachusetts Amherst physicist Chen Wang, graduate students Jeffrey Gertler and Shruti Shirol, and postdoctoral researcher Juliang Li takes a step toward building a fault-tolerant quantum computer. They have realized a novel type of QEC where the quantum errors are spontaneously corrected.
Today's computers are built with transistors representing classical bits (0's or 1's). Quantum computing is an exciting new paradigm of computation using quantum bits (qubits) where quantum superposition can be exploited for exponential gains in processing power. Fault-tolerant quantum computing may immensely advance new materials discovery, artificial intelligence, biochemical engineering and many other disciplines.
Since qubits are intrinsically fragile, the most outstanding challenge of building such powerful quantum computers is efficient implementation of quantum error correction. Existing demonstrations of QEC are active, meaning that they require periodically checking for errors and immediately fixing them, which is very demanding in hardware resources and hence hinders the scaling of quantum computers.
In contrast, the researchers' experiment achieves passive QEC by tailoring the friction (or dissipation) experienced by the qubit. Because friction is commonly considered the nemesis of quantum coherence, this result may appear quite surprising. The trick is that the dissipation has to be designed specifically in a quantum manner. This general strategy has been known in theory for about two decades, but a practical way to obtain such dissipation and put it in use for QEC has been a challenge.
"Although our experiment is still a rather rudimentary demonstration, we have finally fulfilled this counterintuitive theoretical possibility of dissipative QEC," says Chen. "Looking forward, the implication is that there may be more avenues to protect our qubits from errors and do so less expensively. Therefore, this experiment raises the outlook of potentially building a useful fault-tolerant quantum computer in the mid to long run."
Chen describes in layman's terms how strange the quantum world can be. "As in German physicist Erwin Schrödinger's famous (or infamous) example, a cat packed in a closed box can be dead or alive at the same time. Each logical qubit in our quantum processor is very much like a mini-Schrödinger's cat. In fact, we quite literally call it a `cat qubit.' Having lots of such cats can help us solve some of the world's most difficult problems.
"Unfortunately, it is very difficult to keep a cat staying that way since any gas, light, or anything leaking into box will destroy the magic: The cat will become either dead or just a regular live cat," explains Chen. "The most straightforward strategy to protect a Schrodinger's cat is to make the box as tight as possible, but that also makes it harder to use it for computation. What we just demonstrated was akin to painting the inside of the box in a special way and that somehow helps the cat better survive the inevitable harm of the outside world."
INFORMATION:
Co-authors also include Brian Baker and Jens Koch from Northwestern University.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-11
New research from the Indiana University Kelley School of Business shows first evidence that watching and learning from others can help reduce bias and improve decision-making.
The research, published END ...
2021-02-11
MUSC Hollings Cancer Center researcher Yongxia Wu, Ph.D., identified a new target molecule in the fight against graft-versus-host disease (GVHD). Bone marrow transplant, a treatment for certain blood cancers, is accompanied by potentially life-threatening GVHD in nearly 50% of patients. A January 2021 paper published in Cellular and Molecular Immunology revealed that activating a molecule called STING may be a new approach to reduce GVHD.
Xue-Zhong Yu, M.D., professor in the Department of Microbiology and Immunology, focuses on understanding the intricate immune mechanisms that regulate GVHD development and anti-tumor activity.
Recently, STING (stimulator of interferon genes) has been highly studied in the context of cancer. Data from other groups has shown that STING activation ...
2021-02-11
Irvine, CA - February 11, 2021 - Subconsciously, our bodies keep time for us through an ancient means - the circadian clock. A new University of California, Irvine-led article reviews how the clock controls various aspects of homeostasis, and how organs coordinate their function over the course of a day.
"What is fascinating is that nearly every cell that makes up our organs has its own clock, and thus timing is a crucial aspect of biology," said Kevin B. Koronowski, PhD, lead author and a postdoctoral fellow in Biological Chemistry at the UCI School of Medicine. "Understanding how daily timing is integrated with function ...
2021-02-11
A Russian physicist and his international colleagues studied a quantum point contact (QCP) between two conductors with external oscillating fields applied to the contact. They found that, for some types of contacts, an increase in the oscillation frequency above a critical value reduced the current to zero - a promising mechanism that can help create nanoelectronics components. This research supported by the Russian Science Foundation (RSF) was published in the Physical Review B journal.
A persistent trend in the modern electronics, miniaturization has spurred demand for new nano-sized devices that boast advanced performance and leverage quantum effects with electrons ...
2021-02-11
Getting around without the need to concentrate on every step is something most of us can take for granted because our inner ears drive reflexes that make maintaining balance automatic. However, for about 1.8 million adults worldwide with bilateral vestibular hypofunction (BVH) -- loss of the inner ears' sense of balance -- walking requires constant attention to avoid a fall. Now, Johns Hopkins Medicine researchers have shown that they can facilitate walking, relieve dizziness and improve quality of life in patients with BVH by surgically implanting a stimulator that electrically ...
2021-02-11
CORVALLIS, Ore. - The songs of fin whales can be used for seismic imaging of the oceanic crust, providing scientists a novel alternative to conventional surveying, a new study published this week in Science shows.
Fin whale songs contain signals that are reflected and refracted within the crust, including the sediment and the solid rock layers beneath. These signals, recorded on seismometers on the ocean bottom, can be used to determine the thickness of the layers as well as other information relevant to seismic research, said John Nabelek, a professor in Oregon State University's College of Earth, Ocean, and Atmospheric Sciences and a co-author of the paper.
"People in the past have used whale calls to track whales and study whale behavior. ...
2021-02-11
For some 15,000 years, dogs have been our hunting partners, workmates, helpers and companions. Could they also be our next allies in the fight against COVID-19?
According to UC Santa Barbara professor emeritus Tommy Dickey(link is external) and his collaborator, BioScent researcher Heather Junqueira, they can. And with a review paper(link is external) published in the Journal of Osteopathic Medicine they have added to a small but growing consensus that trained medical scent dogs can effectively be used for screening individuals who may be infected with the COVID-19 virus.
This follows a comprehensive survey of research ...
2021-02-11
DURHAM, N.C. - People who have a gene variant associated with an increased risk of developing Alzheimer's disease also tend to have changes in the fluid around their brain and spinal cord that are detectable years before symptoms arise, according to new research from Duke Health.
The work found that in people who carry the APOE4 gene variant, which is found in roughly 25 percent of the population, the cerebrospinal fluid contains lower levels of certain inflammatory molecules. This raises the possibility that these inflammatory molecules may be collecting in the brain where they may be damaging synapses, rather than floating freely in the cerebrospinal fluid.
The findings, which were published online last month in the Journal of Alzheimer's Disease, provide a potential ...
2021-02-11
A team of researchers from Russia and Israel applied a new algorithm to classify the severity of autistic personality traits by studying subjects' brain activity.
The article 'Brief Report: Classification of Autistic Traits According to Brain Activity Recoded by fNIRS Using ε-Complexity Coefficients' is published in the Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders.
When diagnosing autism and other mental disorders, physicians increasingly use neuroimaging methods in addition to traditional testing and observation. Such diagnostic methods are not only ...
2021-02-11
Using a dataset on daily patrols and enforcement activities of officers in the Chicago Police Department (CPD) - an agency that has undergone substantial diversification in recent decades - researchers report Black officers used force less often than white officers during the three-year period studied, and women used force less often than men. These and other findings provide insight into impacts of diversification in policing, a widely proposed policing reform. "The magnitude of the differences [here] provides strong evidence that--at least in some cities--the number of officers who identify with vulnerable groups can matter quite a bit in predicting police behavior," writes Philip Goff in a related Perspective. Racial disparities in police-civilian interactions ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] UMass Amherst team helps demonstrate spontaneous quantum error correction
New research tackles a central challenge of powerful quantum computing