Bacterial degradation of the MYC oncogene -- a new cancer treatment strategy?
2021-02-12
(Press-News.org) Scientists at Lund University have discovered how E. coli bacteria target and degrade the well-known oncogene MYC, which is involved in many forms of cancer. The study is now published in Nature Biotechnology.
Cancer cells grow too fast, outcompete normal cells and spread to distant sites, where they cause metastases. Understanding what makes cancer cells so efficient and threatening is critically important and stopping them has always been the goal of cancer research. Early studies identified so-called ''oncogenes''; genes that that normally control cell growth but when mutated may be responsible for the creation of cancer cells and explain their competitive advantage.
The pleiotropic transcription factor MYC has been named ''the quintessential oncogene'' and is hyperactive in the majority of human cancers. Targeting MYC is therefore highly desirable. Still, finding c-MYC inhibitors for therapeutic use has been problematic and MYC itself has long been viewed as "undruggable".
Researchers at Lund University have made the surprising discovery that uropathogenic E. coli deplete c-MYC protein from infected cells and tissues as a result of accelerated c-MYC protein degradation and attenuated MYC expression.
The discovery was made after observing that children with acute pyelonephritis have decreased MYC expression. By screening molecules released by the bacteria, Lon protease was identified as the main effector of MYC degradation, with selectivity for MYC. The bacterial strategy was then translated into cancer therapy, showing prominent effects of Lon treatment in two different cancer models. Potent treatment effects on tumor growth and increased survival support the therapeutic potential of this molecule.. Surprisingly, the Lon protease was shown to mainly affect cells where MYC is overactive, suggesting limited toxicity. These findings have now been published in Nature Biotechnology
''The next step is to understand this "magical molecule" in more detail and to develop the project for future clinical trials''
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-12
(BOSTON) -- Many life-threatening medical conditions, such as sepsis, which is triggered by blood-borne pathogens, cannot be detected accurately and quickly enough to initiate the right course of treatment. In patients that have been infected by an unknown pathogen and progress to overt sepsis, every additional hour that an effective antibiotic cannot be administered significantly increases the mortality rate, so time is of utmost essence.
The challenge with rapidly diagnosing sepsis stems from the fact that measuring only one biomarker often does not allow a clear-cut diagnosis. Engineers have struggled for decades to simultaneously quantify multiple biomarkers in whole blood with high ...
2021-02-12
The drug thalidomide was sold as a sedative under the trade name Contergan in the 1950s and 1960s. At the time, its side-effects triggered one of the largest pharmaceutical scandals in history: The medication was taken from the market after it became known that the use of Contergan during pregnancy had resulted in over 10,000 cases of severe birth defects.
Currently, the successor preparations lenalidomide and pomalidomide are prescribed under strict supervision by experienced oncologists - the active ingredients are a cornerstone of modern cancer therapies. The use of lenalidomide and pomalidomide has considerably improved the success ...
2021-02-12
EL PASO, Texas - Science is a step closer to a new response to obesity, thanks in part to a study conducted by a team that included Sergio Iñiguez, Ph.D., associate professor of psychology at The University of Texas at El Paso.
The 10-member team led by Brandon Warren, Ph.D., assistant professor of pharmacodynamics at the University of Florida, made discoveries about a specific area of the brain tied to recollection and the desire to seek and consume food. It could lead to a way to inhibit the desire to overeat.
Iñiguez, who directs UTEP's Iñiguez Behavioral Neuroscience Lab and helped design novel experimental techniques for the research, said that people tend to overeat when exposed to cues or environments that remind them of treats, which is one reason ...
2021-02-12
BUFFALO, N.Y. - Humpback and bowhead whales are the only mammals other than humans thought to progressively change the songs they sing through a process of cultural learning.
But maybe the humpbacks are no longer part of that trio. Humpbacks might be singing songs that are not as "cultured" as once assumed.
A new study by a University at Buffalo researcher is directly contradicting the widely accepted cultural transmission hypothesis suggesting that whales learn their songs from other whales.
"It seems like that is not correct," says Eduardo Mercado, a professor of psychology in UB's College of Arts and Sciences. "Our findings indicate that neither cultural transmission nor social learning contributes significantly to how humpback whales ...
2021-02-12
Scientists have accepted natural selection as a driver of evolution for more than 160 years, thanks to Charles Darwin.
But University of Cincinnati biologist Michal Polak says Darwin's book "The Descent of Man" only tells part of the story. Sometimes when the victor vanquishes his sexual rival, the quest to pass genes to the next generation is just beginning.
According to a new UC study published in the journal Current Biology, male fruit flies with the most impressive sexual ornamentation also have super sperm that can outcompete that of rivals in the post-mating fertilization game.
UC studied Drosophila bipectinata, a tiny red-eyed fruit fly ...
2021-02-12
Researchers of the Research Programme on Biomedical Informatics (GRIB) from UPF and Hospital del Mar Medical Research Institute (IMIM) in Barcelona, Spain, have identified behavioural and linguistic changes in tweets in Spanish published by users suffering from depression and who are taking medication to treat this disease.
Their work has been published in Journal of Medical Internet Research and was led by Ferran Sanz; with Angela Leis and Francesco Ronzano as first authors, who conducted the work together with Miguel Angel Mayer and Laura I Furlong, all from the Integrative Biomedical Informatics research ...
2021-02-12
Fast and energy-efficient future data processing technologies are on the horizon after an international team of scientists successfully manipulated magnets at the atomic level.
Physicist Dr Rostislav Mikhaylovskiy from Lancaster University said: "With stalling efficiency trends of current technology, new scientific approaches are especially valuable. Our discovery of the atomically-driven ultrafast control of magnetism opens broad avenues for fast and energy-efficient future data processing technologies essential to keep up with our data hunger."
Magnetic materials are heavily used in modern life with applications ranging from fridge magnets to Google and Amazon's ...
2021-02-12
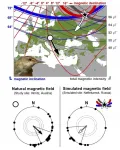
Birdwatchers get very excited when a 'rare' migratory bird makes landfall having been blown off-course and flown beyond its normal range. But these are rare for a reason; most birds that have made the journey before are able to correct for large displacements and find their final destination.
Now, new research by an international team shows for the first time, how birds displaced in this way are able to navigate back to their migratory route and gives us an insight into how they accomplish this feat.
Writing in Current Biology, the team from Bangor and Keele Universities describe how reed warblers can navigate from a 'magnetic position' beyond what they have ...
2021-02-12
What The Study Did: These findings suggest that treatment with zinc, ascorbic acid or both doesn't affect SARS-CoV-2 symptoms.
Authors: Milind Y. Desai, M.D., M.B.A., of the Cleveland Clinic in Ohio, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.0369)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media advisory: The full study is linked to ...
2021-02-12
What The Study Did: Pediatric admissions to U.S. hospitals decreased last year across an array of pediatric conditions and some may represent unmet needs in pediatric care during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Authors: Christopher M. Horvat, M.D., M.H.A., of UPMC Children's Hospital of Pittsburgh, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.37227)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media advisory: ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Bacterial degradation of the MYC oncogene -- a new cancer treatment strategy?