(Press-News.org) A new study finds that California's commuters are likely inhaling chemicals at levels that increase the risk for cancer and birth defects.
As with most chemicals, the poison is in the amount. Under a certain threshold of exposure, even known carcinogens are not likely to cause cancer. Once you cross that threshold, the risk for disease increases.
Governmental agencies tend to regulate that threshold in workplaces. However, private spaces such as the interior of our cars and living rooms are less studied and less regulated.
Benzene and formaldehyde -- both used in automobile manufacturing -- are known to cause cancer at or above certain levels of exposure and are Prop. 65-listed chemicals.
New UC Riverside research shows that the average commuter in California is exceeding the threshold for exposure, breathing in unsustainably high levels of both chemicals.
Both benzene and formaldehyde are carcinogens, and benzene carries the additional risk of reproductive and developmental toxicity.
"These chemicals are very volatile, moving easily from plastics and textiles to the air that you breathe," said David Volz, UCR professor of environmental toxicology.
The study, published in the journal END
Commuters are inhaling unacceptably high levels of carcinogens
Twenty minutes or longer in the car also raises risk of birth defects
2021-02-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Strange creatures accidentally discovered beneath Antarctica's ice shelves
2021-02-15
Far underneath the ice shelves of the Antarctic, there's more life than expected, finds a recent study in the journal Frontiers in Marine Science.
During an exploratory survey, researchers drilled through 900 meters of ice in the Filchner-Ronne Ice Shelf, situated on the south eastern Weddell Sea. At a distance of 260km away from the open ocean, under complete darkness and with temperatures of -2.2°C, very few animals have ever been observed in these conditions.
But this study is the first to discover the existence of stationary animals - similar to sponges and potentially several previously unknown species - attached to a boulder on the sea floor.
"This discovery is one of those ...
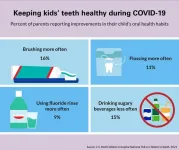
Parents Say COVID-19 has disrupted children's dental care
2021-02-15
ANN ARBOR, Mich. - A third of parents say the COVID-19 pandemic has made it difficult to get dental care for their children, a new national poll suggests.
But some families may face greater challenges than others. Inability to get a dentist appointment during the pandemic was three times as common for children with Medicaid versus those with private dental coverage, according to the C.S. Mott Children's Hospital National Poll on Children's Health at Michigan Medicine.
"Regular preventive dental care helps keep children's teeth healthy and allows providers to address any tooth decay ...
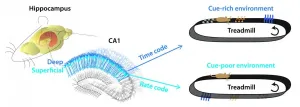
Peeking at the pathfinding strategies of the hippocampus in the brain
2021-02-15
We find routes to destination and remember special places because there is an area somewhere in the brain that functions like a GPS and navigation system. When taking a new path for the first time, we pay attention to the landmarks along the way. Owing to such navigation system, it becomes easier to find destinations along the path after having already used the path. Over the years, scientists have learned, based on a variety of animal experiments, that cells in the brain region called hippocampus are responsible for spatial perception and are activated in discrete positions ...
Membrane building blocks play decisive role in controlling cell growth
2021-02-15
Lipids are the building blocks of a cell's envelope - the cell membrane. In addition to their structural function, some lipids also play a regulatory role and decisively influence cell growth. This has been investigated in a new study by scientists at Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg (MLU). The impact of the lipids depends on how they are distributed over the plasma membrane. The study was published in "The Plant Cell".
If plant cells want to move, they need to grow. One notable example of this is the pollen tube. When pollen lands on a flower, the pollen tube grows directionally into the female reproductive organs. This allows the male gametes to be delivered, so fertilisation can occur. The pollen tube is special ...
Capuchin monkey genome reveals clues to its long life and large brain
2021-02-15
An international team of scientists has sequenced the genome of a capuchin monkey for the first time, uncovering new genetic clues about the evolution of their long lifespan and large brains.
Published in PNAS, the work was led by the University of Calgary in Canada and involved researchers at the University of Liverpool.
"Capuchins have the largest relative brain size of any monkey and can live past the age of 50, despite their small size, but their genetic underpinnings had remained unexplored until now," explains Professor Joao Pedro De Magalhaes, who researches ageing at the University of Liverpool.
The researchers developed and annotated a reference assembly for white-faced ...
Aspirin preferred to prevent blood clots in kids after heart surgery
2021-02-14
Aspirin should be favoured over warfarin to prevent blood clotting in children who undergo a surgery that replumbs their hearts, according to a new study.
The research, led by the Murdoch Children's Research Institute (MCRI) and published in The Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, will have implications for clinicians when prescribing blood thinning medications after Fontan surgery, a complex congenital heart disease operation redirecting blood flow from the lower body to the lungs.
The Fontan procedure is offered to children born with severe heart defects, allowing the child to live with just one pumping heart chamber ...
Cabozantinib most effective treatment for metastatic papillary kidney cancer
2021-02-13
In a SWOG Cancer Research Network trial that put three targeted drugs to the test, the small molecule inhibitor cabozantinib was found most effective in treating patients with metastatic papillary kidney cancer - findings expected to change medical practice.
These findings will be presented at ASCO's virtual 2021 Genitourinary Cancers Symposium on Feb. 13, 2021 at 1 p.m. ET. The findings will be simultaneously published in The Lancet.
There are currently no effective treatments for metastatic papillary kidney cancer, or metastatic pRCC, a rare subtype of kidney cancer. One study of 38 patients found that the average survival ...
Immunotherapy -- targeted drug combination improves survival in advanced kidney cancer
2021-02-13
Lenvatinib plus pembrolizumab yields better overall survival than single-agent sunitinib when given as first-line therapy in untreated patients with metastatic kidney cancer
The combination also improved progression-free survival and overall response rate
BOSTON - Patients with advanced kidney cancer, who received a targeted drug combined with a checkpoint-blocker immunotherapy agent had longer survival than patients treated with the standard targeted drug, said an investigator from Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, reporting results from a phase 3 clinical trial.
The survival benefit demonstrates that an immune checkpoint inhibitor together with a targeted kinase inhibitor drug "is important ...
Gene-based blood test for melanoma spread evaluates treatment progress
2021-02-13
A test that monitors blood levels of DNA fragments released by dying tumor cells may serve as an accurate early indicator of treatment success in people in late stages of one of the most aggressive forms of skin cancer, a new study finds.
Led by NYU Grossman School of Medicine and Perlmutter Cancer Center researchers, the investigation looked at adults with undetectable levels of freely circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) four weeks into drug treatment for metastatic melanoma tumors that cannot be removed surgically (unresectable). The study showed that these patients, all of whom had common genetic changes (BRAFV600 mutations) linked to cancer, were living ...
The Lancet: COVID-19 vaccination potential will not be achieved without increased production, affordable pricing, global availability, and successful rollout
2021-02-13
Peer-reviewed / Review, Survey and Opinion piece
To ensure an effective global immunisation strategy against COVID-19, vaccines need to be produced at scale, priced affordably, and allocated globally so that they are available where needed, and successfully rolled out.
Review of evidence includes a comparison of 26 leading vaccines on their potential contribution to achieving global vaccine immunity, and a new survey of COVID-19 vaccine confidence in 32 countries.
Having new COVID-19 vaccines will mean little if people around the world are unable to get vaccinated in a timely manner. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Simple test could transform time to endometriosis diagnosis
Why ‘being squeezed’ helps breast cancer cells to thrive
Mpox immune test validated during Rwandan outbreak
Scientists pinpoint protein shapes that track Alzheimer’s progression
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
Moisture powered materials could make cleaning CO₂ from air more efficient
Scientists identify the gatekeeper of retinal progenitor cell identity
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
In the ocean’s marine ‘snow,’ a scientist seeks clues to future climate
Understanding how “marine snow” acts as a carbon sink
In search of the room temperature superconductor: international team formulates research agenda
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
New robotic microfluidic platform brings ai to lipid nanoparticle design
COSMOS trial results show daily multivitamin use may slow biological aging
Immune cells play key role in regulating eye pressure linked to glaucoma
National policy to remedy harms of race-based kidney function estimation associated with increased transplants for Black patients
Study finds teens spend nearly one-third of the school day on smartphones, with frequent checking linked to poorer attention
Team simulates a living cell that grows and divides
Study illuminates the experiences of people needing to seek abortion care out of state
Digital media use and child health and development
Seeking abortion care across state lines after the Dobbs decision
[Press-News.org] Commuters are inhaling unacceptably high levels of carcinogensTwenty minutes or longer in the car also raises risk of birth defects