(Press-News.org) NASA, in collaboration with other leading space agencies, aims to send its first human missions to Mars in the early 2030s, while companies like SpaceX may do so even earlier. Astronauts on Mars will need oxygen, water, food, and other consumables. These will need to be sourced from Mars, because importing them from Earth would be impractical in the long term. In Frontiers in Microbiology, scientists show for the first time that Anabaena cyanobacteria can be grown with only local gases, water, and other nutrients and at low pressure. This makes it much easier to develop sustainable biological life support systems.
"Here we show that cyanobacteria can use gases available in the Martian atmosphere, at a low total pressure, as their source of carbon and nitrogen. Under these conditions, cyanobacteria kept their ability to grow in water containing only Mars-like dust and could still be used for feeding other microbes. This could help make long-term missions to Mars sustainable," says lead author Dr Cyprien Verseux, an astrobiologist who heads the Laboratory of Applied Space Microbiology at the Center of Applied Space Technology and Microgravity (ZARM) of the University of Bremen, Germany.
Low-pressure atmosphere
Cyanobacteria have long been targeted as candidates to drive biological life support on space missions, as all species produce oxygen through photosynthesis while some can fix atmospheric nitrogen into nutrients. A difficulty is that they cannot grow directly in the Martian atmosphere, where the total pressure is less than 1% of Earth's - 6 to 11 hPa, too low for the presence of liquid water - while the partial pressure of nitrogen gas - 0.2 to 0.3 hPa - is too low for their metabolism. But recreating an Earth-like atmosphere would be expensive: gases would need to be imported, while the culture system would need to be robust - hence, heavy to freight - to resist the pressure differences: "Think of a pressure cooker," Verseux says. So the researchers looked for a middle ground: an atmosphere close to Mars's which allows the cyanobacteria to grow well.
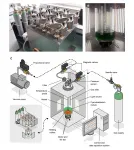
To find suitable atmospheric conditions, Verseux et al. developed a bioreactor called Atmos (for "Atmosphere Tester for Mars-bound Organic Systems"), in which cyanobacteria can be grown in artificial atmospheres at low pressure. Any input must come from the Red Planet itself: apart from nitrogen and carbon dioxide, gases abundant in the Martian atmosphere, and water which could be mined from ice, nutrients should come from "regolith", the dust covering Earth-like planets and moons. Martian regolith has been shown to be rich in nutrients such as phosphorus, sulphur, and calcium.
Anabaena: versatile cyanobacteria grown on Mars-like dust
Atmos has nine 1 L vessels made of glass and steel, each of which is sterile, heated, pressure-controlled, and digitally monitored, while the cultures inside are continuously stirred. The authors chose a strain of nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria called Anabaena sp. PCC 7938, because preliminary tests showed that it would be particularly good at using Martian resources and helping to grow other organisms. Closely related species have been shown to be edible, suitable for genetic engineering, and able to form specialized dormant cells to survive harsh conditions.
Verseux and his colleagues first grew Anabaena for 10 days under a mixture of 96% nitrogen and 4% carbon dioxide at a pressure of 100 hPa - ten times lower than on Earth. The cyanobacteria grew as well as under ambient air. Then they tested the combination of the modified atmosphere with regolith. Because no regolith has ever been brought from Mars, they used a substrate developed by the University of Central Florida (called "Mars Global Simulant") instead to create a growth medium. As controls, Anabaena were grown in standard medium, either at ambient air or under the same low-pressure artificial atmosphere.
The cyanobacteria grew well under all conditions, including in regolith under the nitrogen- and carbon dioxide-rich mixture at low pressure. As expected, they grew faster on standard medium optimized for cyanobacteria than on Mars Global Simulant, under either atmosphere. But this is still a major success: while standard medium would need to be imported from Earth, regolith is ubiquitous on Mars. "We want to use as nutrients resources available on Mars, and only those," says Verseux.
Dried Anabaena biomass was ground, suspended in sterile water, filtered, and successfully used as a substrate for growing of E. coli bacteria, proving that sugars, amino acids, and other nutrients can be extracted from them to feed other bacteria, which are less hardy but tried-and-tested tools for biotechnology. For example, E. coli could be engineered more easily than Anabaena to produce some food products and medicines on Mars that Anabaena cannot.
The researchers conclude that nitrogen-fixing, oxygen-producing cyanobacteria can be efficiently grown on Mars at low pressure under controlled conditions, with exclusively local ingredients.
Further refinements in the pipeline
These results are an important advance. But the authors caution that further studies are necessary: "We want to go from this proof-of-concept to a system that can be used on Mars efficiently," Verseux says. They suggest fine-tuning the combination of pressure, carbon dioxide, and nitrogen optimal for growth, while testing other genera of cyanobacteria, perhaps genetically tailored for space missions. A cultivation system for Mars also needs to be designed:
"Our bioreactor, Atmos, is not the cultivation system we would use on Mars: it is meant to test, on Earth, the conditions we would provide there. But our results will help guide the design of a Martian cultivation system. For example, the lower pressure means that we can develop a more lightweight structure that is more easily freighted, as it won't have to withstand great differences between inside and outside," concludes Verseux.
INFORMATION:
The project was funded by the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation.
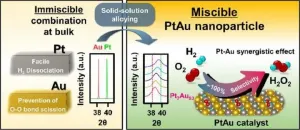
Hydrogen peroxide is used as a disinfectant, after dilution in water, to treat wounds. It is widely used across the industry as an eco-friendly oxidizing agent for impurity removal from semiconductors, waste treatment, etc. Currently, it is mainly produced by the sequential hydrogenation and oxidation of anthraquinone (AQ). However, this process is not only energy intensive and requires large-scale facilities, but AQ is also toxic.
As an alternative to the AQ process, hydrogen peroxide direct synthesis from hydrogen (H2) and oxygen (O2) using a palladium (Pd) catalyst was proposed. However, the commercialization of the technology ...
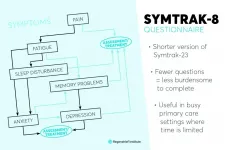
INDIANAPOLIS -- Researchers from Regenstrief Institute and Indiana University School of Medicine have developed and validated a short questionnaire to help patients report symptoms and assist healthcare providers in assessing the severity of symptoms, and in monitoring and adjusting treatment accordingly.
The tool, called SymTrak-8, is a shorter version of the SymTrak-23. The questionnaire tracks symptoms such as pain, fatigue, sleep disturbance, memory problems, anxiety and depression in older adults, enabling clinicians to provide better care for the diseases causing the symptoms.
"These symptoms are commonly reported in primary care, but they can be a sign of a variety of different diseases, so tracking them is important," said Kurt ...
Teens may be more likely to use marijuana after legalization for adult recreational use
PISCATAWAY, NJ - Adolescents who live in California may be more likely to use marijuana since adult recreational marijuana use was legalized in 2016, according to a new report in the Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs.
"The apparent increase in marijuana use among California adolescents after recreational marijuana legalization for adult use in 2016 is surprising given the steady downward trend in marijuana use during years before legalization," says lead researcher Mallie J. ...
A new first-of-its-kind study has questioned whether pub operators can effectively and consistently prevent COVID-19 transmission - after researchers observed risks arising in licensed premises last summer.
Led by the University of Stirling, the research was conducted in May to August last year in a wide range of licensed premises which re-opened after a nationwide lockdown, and were operating under detailed guidance from government intended to reduce transmission risks.
While observed venues had made physical and operational modifications on re-opening, ...
A technology that is widely used by commercial genetic testing companies is "extremely unreliable" in detecting very rare variants, meaning results suggesting individuals carry rare disease-causing genetic variants are usually wrong, according to new research published in the BMJ.
After hearing of cases where women had surgery scheduled after wrongly being told they had very rare genetic variations in the gene BRCA1 that could significantly increase risk of breast cancer, a team at the University of Exeter conducted a large-scale analysis of the technology using data from nearly 50,000 people. They found that the technology wrongly identified ...
Recreational drinking, smoking, and drug use is linked to premature heart disease in young people, particularly younger women, finds research published online in the journal Heart.
Those who regularly use 4 or more substances are 9 times as likely to be affected, the findings indicate.
The numbers of new cases of heart disease (atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease) have been increasing in young adults, but the potential role of recreational substance use isn't entirely clear.
To probe this further, the researchers explored whether the recreational use of tobacco, cannabis, alcohol, and illicit drugs, such as amphetamine and cocaine, might be linked to prematurely and extremely prematurely furred up arteries.
They drew on information supplied ...
Ageism, sexism, and Western ideals of the nuclear family have excluded grandmothers from national and international policy initiatives to save newborn lives in the Global South, suggests an analysis published in the online journal BMJ Global Health.
This is despite published research indicating that they are a valuable and influential resource for children's health and survival in many cultures, the study author points out.
Around three out of 4 newborn deaths in the Global South occur in the first week of life--40% of them on the first day, and most of them at home.
But ...
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also on behalf of the organization they represent.
1. Zika vaccine candidate shows promise in phase I trial
Abstract: https://www.acpjournals.org/doi/10.7326/M20-5306
Editorial: https://www.acpjournals.org/doi/10.7326/M21-0397
URL goes live when the embargo lifts
The Zika virus candidate, Ad26.ZIKV.001, a replication-incompetent human adenovirus serotype 26 (ad26) vector showed ...
A new paper refines estimates of when herbivorous dinosaurs must have traversed North America on a northerly trek to reach Greenland, and points out an intriguing climatic phenomenon that may have helped them along the journey.
The study, published today in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, is authored by Dennis Kent, adjunct research scientist at Columbia University's Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory, and Lars Clemmensen from the University of Copenhagen.
Previous estimates suggested that sauropodomorphs -- a group of long-necked, herbivorous dinosaurs that eventually included Brontosaurus and Brachiosaurus ...
Experts have devised a novel approach to selecting photos for police lineups that helps witnesses identify culprits more reliably.
In a paper published by the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, researchers - from the University of California San Diego and Duke University in the United States and the University of Birmingham in the U.K. - show for the first time that selecting fillers who match a basic description of the suspect but whose faces are less similar, rather than more, leads to better outcomes than traditional approaches in the field.
The counterintuitive technique improves eyewitness performance by about 10 percent.
"In ...