Scientists of Kemerovo State University have developed a technology for creating in vitro root
Scientists of Kemerovo State University have developed a technology for creating in vitro root cultures with a high content of biologically active substances
2021-02-16
(Press-News.org) Scientists of Kemerovo State University, within the framework of the Russian Scientific Foundation grant "Cultivation of isolated cells and organs of rare and endemic medicinal plants of Siberia and the Far East in vitro as a biotechnological method for obtaining biologically active substances", are investigating the fundamental principles of in vitro cultivation of isolated cells and organs of rare medicinal plants - producers of biologically active substances with cytotoxic, antioxidant and antimicrobial properties. One of the urgent problems of medicine and biology is the search and use of plant objects as medicines. The unfavorable environmental situation and the increasing need for medicinal raw materials create its shortage. A new solution was the use of an alternative source of raw materials - cultures of cells and organs of higher plants. The main advantages of this approach are the ecological purity of biomass production by biotechnological method, the possibility of obtaining plant biomass with specified characteristics regardless of the season, climate and weather conditions, high rates of biomass production, guaranteed purity of biomass from pesticides, herbicides, radioactive compounds and other pollutants. The presence of an effective industrial super-producer strain guarantees a higher content of the target product than in an intact plant.
Under the scope of the project, it has been possible to obtain the collection of callus, suspension cells and in vitro root cultures of medicinal plants of Siberia and the Far East since 2018. These cultures have cytotoxic, antioxidant and antimicrobial properties. Their growth characteristics have been successfully studied. Furthermore, scientists developed in vitro crops cultivation systems, as well as methodology for obtaining target biologically active substances by extraction.
Currently, the work is underway to optimize the secretion conditions and purification of biologically active substance from the callus extracts, suspension cultures of cells and root cultures in vitro. Scientists also selected the conditions for drying isolated BAS. On the completion of the research project, they plan to passport the received biotechnological objects of medicinal plants in Siberia and the Far East. Based on the results of the research project, a technology for creating root cultures in vitro will be presented. These cultivated plants are distinguished by higher content of biologically active substance, which remains the base of high-quality herbal raw materials for medicine and pharmaceutical industries.
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-16
In our ongoing struggle to reduce the usage of fossil fuel, technology to directly convert the world's waste heat into electricity stands out as very promising. Thermoelectric materials, which carry out this energy conversion process, have, thus, recently become the focus of intense research worldwide. Of the various potential candidates applicable at a broad range of temperatures, between 30 and 630 °C, lead telluride (PbTe) offers the best thermoelectric performance. Unfortunately, the outstanding qualities of PbTe are eclipsed by the toxic nature of lead, driving researchers to look into safer thermoelectric semiconductors.
Tin telluride (SnTe) could be an ...
2021-02-16
Ben-Gurion University Researchers Uncover a Catch-22 When It Comes to Social Media Online Support Groups and Privacy Concerns
BEER-SHEVA, Israel...February 16, 2021- People who seek support online social media groups may end up not getting the help they need due to privacy concerns, according to a new study by Ben-Gurion University of the Negev (BGU) and Gutenberg University in Sweden.
The new research, published in END ...
2021-02-16
Could long-distance interactions between individual molecules forge a new way to compute?
Interactions between individual molecules on a metal surface extend for surprisingly large distances - up to several nanometers.
A new study, just published, of the changing shape of electronic states induced by these interactions, has potential future application in the use of molecules as individually addressable units.
For example, in a future computer based on this technology, the state of each individual molecule could be controlled, mirroring binary operation of transistors in current computing.
MEASURING SOCIALLY-DISTANT MOLECULAR INTERACTIONS ON A METAL SURFACE
The Monash-University of Melbourne collaboration studied the electronic properties of ...
2021-02-16
The placement of a wet cotton pellet against Mineral Trioxide Aggregate (MTA) is often recommended to ensure the completion of its setting reaction. This study aimed to evaluate the setting behaviour of MTA Angelus and NeoMTA by comparing their hardness after placing them in dry and moist conditions.
A simulated open apex was created on 40 polyvinyl tubes. The apical 4 mm of the tubes was filled with the two materials, NeoMTA Plus (Avalon Biomed Inc. Bradenton, FL, USA) and MTA Angelus (Angelus, Londrina, PR, Brazil) (n=20 per group). Both groups were subdivided into two subgroups based on the dry and wet conditions (n=10 per group). A wet cotton pellet was placed above the ...
2021-02-16
The schools in Vietnam observe a phenomenon that almost all parents send their children to school using private vehicles, mostly motorcycles. The parents usually park their vehicle on streets outside the school gates which can cause serious congestion and chances of of traffic accidents.
This study aims to identify the factors affecting the picking up of pupils at primary school by analysing typical primary schools in Hanoi city. The researchers used the binary logistic regression model to determine the factors that influence the decision of picking up pupils and the waiting duration of parents. The behaviour of motorcyclists during the process ...
2021-02-16
If B is better than A, and C is better than B, it follows by the transitive property that C is better than A. And, yet, this is not always the case. Every kid is familiar with the Rock-Paper-Scissors game--the epitome of nontransitivity in which there is no clear hierarchy among the three choices, despite each two-way interaction having a clear winner: Paper beats Rock, Scissors beats Paper, and Rock beats Scissors.
Evolution may be teeming with nontransitive interactions as well. While natural selection - the process by which organisms better adapted to their environments are more likely ...
2021-02-16
A new USC study puts ocean microbes in a new light with important implications for global warming.
The study, published Tuesday in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, provides a universal accounting method to measure how carbon-based matter accumulates and cycles in the ocean. While competing theories have often been debated, the new computational framework reconciles the differences and explains how oceans regulate organic carbon across time.
Surprisingly, most of the action involving carbon occurs not in the sky but underfoot and undersea. The Earth's plants, ...
2021-02-16
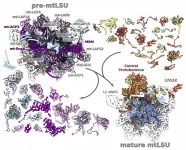
The mitochondrial ribosome is an intricate machine that translates the organellar genome into functional proteins. The formation of the mitochondrial ribosome is a hierarchical process involving dozens of different components. The newly published cryo-EM study by Tobiasson et al in the EMBO Journal characterized a key step in this process.
A complex of 2.2 MegaDalton representing a rare state of assembly of the large subunit was isolated from a model organism Trypanosoma brucei. Since the state was identified in only 3.5 % of the complexes, five cryo-EM datasets had to be collected at the SciLifeLab facility and ESRF in Grenoble and combined together.
The resulting structure revealed ...
2021-02-16
A new study published in Nature Communications suggests that the extinction of North America's largest mammals was not driven by overhunting by rapidly expanding human populations following their entrance into the Americas. Instead, the findings, based on a new statistical modelling approach, suggest that populations of large mammals fluctuated in response to climate change, with drastic decreases of temperatures around 13,000 years ago initiating the decline and extinction of these massive creatures. Still, humans may have been involved in more complex and indirect ways than simple models of overhunting suggest.
Before around 10,000 years ago, North America was ...
2021-02-16
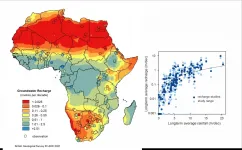
Effective governance and investment decisions need to be informed by reliable data, not only about where groundwater exists, but also the rate at which groundwater is replenished. For the first time using ground measurements, a recent study has quantified groundwater recharge rates across the whole of Africa - averaged over a fifty-year period - which will help to identify the sustainability of water resources for African nations.
The study, led by the British Geological Survey and involving an international team from the UK, South Africa, France, Nigeria, and America, developed a dataset of 134 existing recharge studies ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Scientists of Kemerovo State University have developed a technology for creating in vitro root
Scientists of Kemerovo State University have developed a technology for creating in vitro root cultures with a high content of biologically active substances