The effects of picking up primary school pupils on surrounding street's traffic
The article by Dr. Dinh Hiep and colleagues was published in The Open Transportation Journal
2021-02-16
(Press-News.org) The schools in Vietnam observe a phenomenon that almost all parents send their children to school using private vehicles, mostly motorcycles. The parents usually park their vehicle on streets outside the school gates which can cause serious congestion and chances of of traffic accidents.
This study aims to identify the factors affecting the picking up of pupils at primary school by analysing typical primary schools in Hanoi city. The researchers used the binary logistic regression model to determine the factors that influence the decision of picking up pupils and the waiting duration of parents. The behaviour of motorcyclists during the process was identified and studied in detail using the Kinovea software. Through the results the researchers found that, on the way back home, almost all the parents use motorbikes (89.15%) to pick up their children. During their waiting time (8.48 minutes on average), the parents did a lot of illegal parking activities on the streets which caused a lot of trouble, testing the other commuters, and created chances for potential accidents in front of the primary school entrance gate. Risky picking-up behaviours were observed in the research.
Based on the results, several traffic management measures have been proposed by the researchers to improve traffic safety and to reduce traffic congestion in front of school gates. In addition, the results of the study is expected to provide a useful reference for policymakers and authorities.
INFORMATION:
Read the Full-text article here: https://benthamopen.com/ABSTRACT/TOTJ-14-237
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-16
If B is better than A, and C is better than B, it follows by the transitive property that C is better than A. And, yet, this is not always the case. Every kid is familiar with the Rock-Paper-Scissors game--the epitome of nontransitivity in which there is no clear hierarchy among the three choices, despite each two-way interaction having a clear winner: Paper beats Rock, Scissors beats Paper, and Rock beats Scissors.
Evolution may be teeming with nontransitive interactions as well. While natural selection - the process by which organisms better adapted to their environments are more likely ...
2021-02-16
A new USC study puts ocean microbes in a new light with important implications for global warming.
The study, published Tuesday in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, provides a universal accounting method to measure how carbon-based matter accumulates and cycles in the ocean. While competing theories have often been debated, the new computational framework reconciles the differences and explains how oceans regulate organic carbon across time.
Surprisingly, most of the action involving carbon occurs not in the sky but underfoot and undersea. The Earth's plants, ...
2021-02-16
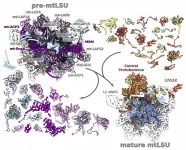
The mitochondrial ribosome is an intricate machine that translates the organellar genome into functional proteins. The formation of the mitochondrial ribosome is a hierarchical process involving dozens of different components. The newly published cryo-EM study by Tobiasson et al in the EMBO Journal characterized a key step in this process.
A complex of 2.2 MegaDalton representing a rare state of assembly of the large subunit was isolated from a model organism Trypanosoma brucei. Since the state was identified in only 3.5 % of the complexes, five cryo-EM datasets had to be collected at the SciLifeLab facility and ESRF in Grenoble and combined together.
The resulting structure revealed ...
2021-02-16
A new study published in Nature Communications suggests that the extinction of North America's largest mammals was not driven by overhunting by rapidly expanding human populations following their entrance into the Americas. Instead, the findings, based on a new statistical modelling approach, suggest that populations of large mammals fluctuated in response to climate change, with drastic decreases of temperatures around 13,000 years ago initiating the decline and extinction of these massive creatures. Still, humans may have been involved in more complex and indirect ways than simple models of overhunting suggest.
Before around 10,000 years ago, North America was ...
2021-02-16
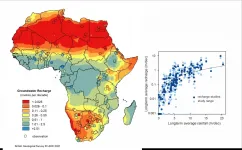
Effective governance and investment decisions need to be informed by reliable data, not only about where groundwater exists, but also the rate at which groundwater is replenished. For the first time using ground measurements, a recent study has quantified groundwater recharge rates across the whole of Africa - averaged over a fifty-year period - which will help to identify the sustainability of water resources for African nations.
The study, led by the British Geological Survey and involving an international team from the UK, South Africa, France, Nigeria, and America, developed a dataset of 134 existing recharge studies ...
2021-02-16
Gender equity and racial diversity in medicine can promote creative solutions to complex health problems and improve the delivery of high-quality care, argue authors in an analysis in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal).
"[T]here is no excuse for not working to change the climate and environment of the medical profession so that it is welcoming of diversity," writes lead author Dr. Andrea Tricco, Knowledge Translation Program, Unity Health, and the University of Toronto, with coauthors. "The medical profession should be professional, be collegial, show mutual respect, and facilitate the full potential and contribution of all genders, races, ethnicities, religions and nationalities for the benefit of patient ...
2021-02-16
NASA, in collaboration with other leading space agencies, aims to send its first human missions to Mars in the early 2030s, while companies like SpaceX may do so even earlier. Astronauts on Mars will need oxygen, water, food, and other consumables. These will need to be sourced from Mars, because importing them from Earth would be impractical in the long term. In Frontiers in Microbiology, scientists show for the first time that Anabaena cyanobacteria can be grown with only local gases, water, and other nutrients and at low pressure. This makes it much easier to develop sustainable biological life support systems.
"Here we show that cyanobacteria can use gases available in the Martian atmosphere, at a low total pressure, as their source of carbon and nitrogen. Under these conditions, ...
2021-02-16
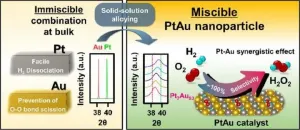
Hydrogen peroxide is used as a disinfectant, after dilution in water, to treat wounds. It is widely used across the industry as an eco-friendly oxidizing agent for impurity removal from semiconductors, waste treatment, etc. Currently, it is mainly produced by the sequential hydrogenation and oxidation of anthraquinone (AQ). However, this process is not only energy intensive and requires large-scale facilities, but AQ is also toxic.
As an alternative to the AQ process, hydrogen peroxide direct synthesis from hydrogen (H2) and oxygen (O2) using a palladium (Pd) catalyst was proposed. However, the commercialization of the technology ...
2021-02-16
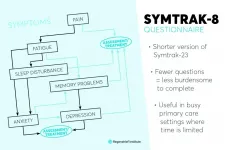
INDIANAPOLIS -- Researchers from Regenstrief Institute and Indiana University School of Medicine have developed and validated a short questionnaire to help patients report symptoms and assist healthcare providers in assessing the severity of symptoms, and in monitoring and adjusting treatment accordingly.
The tool, called SymTrak-8, is a shorter version of the SymTrak-23. The questionnaire tracks symptoms such as pain, fatigue, sleep disturbance, memory problems, anxiety and depression in older adults, enabling clinicians to provide better care for the diseases causing the symptoms.
"These symptoms are commonly reported in primary care, but they can be a sign of a variety of different diseases, so tracking them is important," said Kurt ...
2021-02-16
Teens may be more likely to use marijuana after legalization for adult recreational use
PISCATAWAY, NJ - Adolescents who live in California may be more likely to use marijuana since adult recreational marijuana use was legalized in 2016, according to a new report in the Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs.
"The apparent increase in marijuana use among California adolescents after recreational marijuana legalization for adult use in 2016 is surprising given the steady downward trend in marijuana use during years before legalization," says lead researcher Mallie J. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] The effects of picking up primary school pupils on surrounding street's traffic
The article by Dr. Dinh Hiep and colleagues was published in The Open Transportation Journal