Regular caffeine consumption affects brain structure
2021-02-16
(Press-News.org) Coffee, cola or an energy drink: caffeine is the world's most widely consumed psychoactive substance. Researchers from the University of Basel have now shown in a study that regular caffeine intake can change the gray matter of the brain. However, the effect appears to be temporary.
No question - caffeine helps most of us to feel more alert. However, it can disrupt our sleep if consumed in the evening. Sleep deprivation can in turn affect the gray matter of the brain, as previous studies have shown. So can regular caffeine consumption affect brain structure due to poor sleep? A research team led by Dr. Carolin Reichert and Professor Christian Cajochen of the University of Basel and UPK (the Psychiatric Hospital of the University of Basel) investigated this question in a study.
The result was surprising: the caffeine consumed as part of the study did not result in poor sleep. However, the researchers observed changes in the gray matter, as they report in the journal Cerebral Cortex. Gray matter refers to the parts of the central nervous system made up primarily of the cell bodies of nerve cells, while white matter mainly comprises the neural pathways, the long extensions of the nerve cells.
A group of 20 healthy young individuals, all of whom regularly drink coffee on a daily basis, took part in the study. They were given tablets to take over two 10-day periods, and were asked not to consume any other caffeine during this time. During one study period, they received tablets with caffeine; in the other, tablets with no active ingredient (placebo). At the end of each 10-day period, the researchers examined the volume of the subjects' gray matter by means of brain scans. They also investigated the participants' sleep quality in the sleep laboratory by recording the electrical activity of the brain (EEG).
Sleep unaffected, but not gray matter
Data comparison revealed that the participants' depth of sleep was equal, regardless of whether they had taken the caffeine or the placebo capsules. But they saw a significant difference in the gray matter, depending on whether the subject had received caffeine or the placebo. After 10 days of placebo - i.e. "caffeine abstinence" - the volume of gray matter was greater than following the same period of time with caffeine capsules.
The difference was particularly striking in the right medial temporal lobe, including the hippocampus, a region of the brain that is essential to memory consolidation. "Our results do not necessarily mean that caffeine consumption has a negative impact on the brain," emphasizes Reichert. "But daily caffeine consumption evidently affects our cognitive hardware, which in itself should give rise to further studies." She adds that in the past, the health effects of caffeine have been investigated primarily in patients, but there is also a need for research on healthy subjects.
Although caffeine appears to reduce the volume of gray matter, after just 10 days of coffee abstinence it had significantly regenerated in the test subjects. "The changes in brain morphology seem to be temporary, but systematic comparisons between coffee drinkers and those who usually consume little or no caffeine have so far been lacking," says Reichert.
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-16
Here is a link to watch a video interview with Dr. Beatrice Aramini about this topic on the Oncotarget YouTube Channel
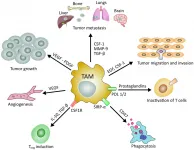
Oncotarget published "Cancer stem cells and macrophages: molecular connections and future perspectives against cancer" which reported that Cancer stem cells have been considered the key drivers of cancer initiation and progression due to their unlimited self-renewal capacity and their ability to induce tumor formation.
Macrophages, particularly tumor-associated macrophages, establish a tumor microenvironment to protect and induce CSCs development and dissemination.
Many studies in the past decade have been performed to understand the molecular ...
2021-02-16
For the first time, physicists from the University of Basel have produced a graphene compound consisting of carbon atoms and a small number of nitrogen atoms in a regular grid of hexagons and triangles. This honeycomb-structured "kagome lattice" behaves as a semiconductor and may also have unusual electrical properties. In the future, it could potentially be used in electronic sensors or quantum computers.
Researchers around the world are searching for new synthetic materials with special properties such as superconductivity -- that is, the conduction of electric current without resistance. These new substances are an important step in the development ...
2021-02-16
Climate change is rapid in the Arctic. As the climate warms, shrubs expand towards higher latitudes and altitudes. Researcher Julia Kemppinen together with her colleagues investigated the impacts of dwarf shrubs on tundra soils in the sub-Arctic Fennoscandia.
The study revealed that the dominance of dwarf shrubs impacts soil microclimate and carbon stocks. Microclimate describes the moisture and temperature conditions close to ground surface. Shrubs are the largest plant life form in the Arctic, and in comparison, to other arctic plants, shrubs use more water and cast more shade.
"The results indicate ...
2021-02-16
WASHINGTON -- When people pause before replying to a question, even for just a few seconds, their answers are perceived to be less sincere and credible than if they had replied immediately, according to research published by the American Psychological Association.
And the longer the hesitation, the less sincere the response appears.
"Evaluating other people's sincerity is a ubiquitous and important part of social interactions," said lead author Ignazio Ziano, PhD, of Grenoble Ecole de Management. "Our research shows that response speed is an important cue on which people base their sincerity inferences."
The research was published in the Journal of Personality and Social Psychology.
Researchers ...
2021-02-16
Cancer is one of the most thought-provoking healthcare problems throughout the world. The development of therapeutic agents with highly selective anti-cancer activities is increasingly attractive due to the lack of tumor selectivity of conventional treatments.
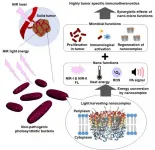
Scientists at Japan Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (JAIST) have created a photosynthetic bacteria-based cancer optotheranostics (Figure 1).
Discovered by Associate Professor Eijiro Miyako and his team from JAIST, natural purple photosynthetic bacteria (PPSB) can play a key role as a highly active cancer immunotheranostics agent that uses the bio-optical-window I and II near-infrared (NIR) light thanks to the light harvesting nanocomplexes in microbial ...
2021-02-16
There is no coat colour that distinguishes dingoes from dingo-dog hybrids, a study involving UNSW Sydney has found.
The Centre for Ecosystem Science research suggests that animals assumed to be dingo-dog hybrids based on their coat colour and culled may have been pure dingoes.
"We actually found pure dingoes that had a brindle, black and tan, patchy or sable coat colour," Dr Kylie Cairns, a conservation biologist from UNSW Sydney and co-author of the study said.
"So that's showing that really dingoes are much more variable than we think and seeing an animal with an odd coat colour doesn't immediately mean that it's a hybrid.
"Using coat colour to decide what animals should be culled is not a very good idea."
The study follows 2019 research by UNSW and collaborators which found ...
2021-02-16
San Antonio, Texas (February 15, 2020) - Researchers at the Southwest National Primate Research Center (SNPRC) at Texas Biomedical Research Institute (Texas Biomed) may have found a new pathway to treat and control tuberculosis (TB), the disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb). Using single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNAseq), a next-generation sequencing technology, scientists were able to further define the mechanisms that lead to TB infection and latency. Co-led by Deepak Kaushal, Ph.D., Director of the SNPRC, this is the first study that used scRNAseq to study TB in macaques in depth. Results from the study were published ...
2021-02-16
Scientists of Kemerovo State University, within the framework of the Russian Scientific Foundation grant "Cultivation of isolated cells and organs of rare and endemic medicinal plants of Siberia and the Far East in vitro as a biotechnological method for obtaining biologically active substances", are investigating the fundamental principles of in vitro cultivation of isolated cells and organs of rare medicinal plants - producers of biologically active substances with cytotoxic, antioxidant and antimicrobial properties. One of the urgent problems of medicine and biology is the search and use of plant objects as medicines. The unfavorable environmental situation and the increasing need for medicinal raw materials create its shortage. A new solution ...
2021-02-16
In our ongoing struggle to reduce the usage of fossil fuel, technology to directly convert the world's waste heat into electricity stands out as very promising. Thermoelectric materials, which carry out this energy conversion process, have, thus, recently become the focus of intense research worldwide. Of the various potential candidates applicable at a broad range of temperatures, between 30 and 630 °C, lead telluride (PbTe) offers the best thermoelectric performance. Unfortunately, the outstanding qualities of PbTe are eclipsed by the toxic nature of lead, driving researchers to look into safer thermoelectric semiconductors.
Tin telluride (SnTe) could be an ...
2021-02-16
Ben-Gurion University Researchers Uncover a Catch-22 When It Comes to Social Media Online Support Groups and Privacy Concerns
BEER-SHEVA, Israel...February 16, 2021- People who seek support online social media groups may end up not getting the help they need due to privacy concerns, according to a new study by Ben-Gurion University of the Negev (BGU) and Gutenberg University in Sweden.
The new research, published in END ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Regular caffeine consumption affects brain structure