(Press-News.org) Scientists have discovered that pollution concentration varies between seasons. A new study, conducted in the North China Plain, determined where volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are distributed within the vertical layers of the atmosphere, and found notable changes from winter to summer.
"The concentration of VOCs in the vertical direction was much higher in winter than that in summer and their emission sources showed different contributions in both seasons," said Guiqian Tang, associate professor in the Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, and the corresponding author of a study just published in Advances in Atmospheric Sciences .
The researchers conducted a field campaign from June 8 to July 3, 2019. They focused on VOCs, which react with nitrogen oxides and carbon monoxide to produce excess ozone (O3), a notable greenhouse gas. The most serious photochemical and VOC pollution in the North China Plain is concentrated near the city of Shijiazhuang, where the team chose to conduct their research.
"Photochemical pollution in summer over the North China Plain is a serious problem, but the mechanisms are not fully understood," said Dr. Tang. He also cited the importance of analyzing the vertical layers of the atmosphere to understand how VOCs evolve vertically and contribute to O3 formation.
Researchers used a tethered balloon, which was better suited than tower, aircraft, and unmanned aerial vehicles for low altitude observations below 1000 m. The balloon explored the vertical evolution of VOCs in the atmospheric boundary layer near the surface.
"Our findings in this campaign were compared with the results of our winter observations from January 2019. It showed that the VOC concentrations and proportions in winter and summer exhibited significant differences vertically," Dr. Tang said.
The total VOC concentration was relatively uniform through the year below 600 m, slightly increasing from 600 m to 1000 m through summer. Alkanes were the largest chemical species in both winter and summer, according to the researchers. These VOCs result from gasoline combustion in vehicles and industrial sources, and accounted for the largest proportion of VOCs that gradually increased at each sampling height.
"We should take measures to improve oil quality to limit exhaust emissions of motor vehicles to reduce VOC pollution," said Dr. Tang. He and his collaborators showed that gasoline emissions from vehicles should be controlled at the surface. Meanwhile, the effects of reducing VOC-based industrial pollution is most impactful at high altitudes.
Soon, researchers also plan to observe the vertical evolution of nitrogen oxides to further explore the formation mechanisms of O3. Nitrogen oxides and carbon monoxide present in the atmosphere are critical components in the reaction that produces ozone in the lower atmosphere.
INFORMATION:
Researchers have used the zebrafish (Danio rerio) to identify the role of a gene involved in cardiac rhythm, which could help explain the fundamentals of what it takes to make a human heartbeat.
The University of Melbourne study also found that mutation of the gene, Tmem161b, causes potentially fatal cardiac arrhythmia. 2.5 per cent of Australians are living with cardiac arrhythmia ( END ...
Almost half of people testing positive for coronavirus have reported symptoms of depression, according to a new study published in the International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.
Researchers from Bangladesh, the United States and Anglia Ruskin University (ARU) in the UK carried out a cross-sectional survey of more than 1,000 Bangladeshi adult coronavirus patients over the course of one month.
A total of 48% of respondents were categorised as having moderate to severe depression, with a higher prevalence in those with persistent symptoms, low family income ...
Brain tumours are the most common solid tumours in childhood and the largest cause of death from cancer in this age group
Being able to classify a brain tumour's type, without the use of biopsy, is hard to do; however diffusion weighted imaging, an advanced imaging technique, when combined with machine learning, can help a UK-based multi-centre study, including WMG, University of Warwick has found.
Being able to characterise the tumour(s) faster and more accurately means they can be treated more efficiently
Diffusion weighted imaging and machine learning can successfully classify the diagnosis and characteristics of common types of paediatric brain tumours a UK-based multi-centre study, including WMG at the University of Warwick ...
Researchers from North Carolina State University, Boston University and Kraton Corporation have demonstrated a family of self-sterilizing polymers that are effective at inactivating coronaviruses, including SARS-CoV-2 - the virus that causes COVID-19. The work opens the door to a suite of applications that could help to reduce the transmission of COVID-19 and other diseases.
"Our work here provides conclusive evidence that these materials, anionic polymers, can inactivate human coronaviruses quickly and efficiently," says Richard Spontak, co-author of a paper on the work accepted for publication in Advanced Science. Spontak is a Distinguished Professor of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering and ...
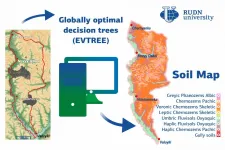
A team of soil scientists developed a new approach to the automatic generation and updating of soil maps. Having applied machine learning technologies to a set of rules traditionally used by experts in manual mapping, the team obtained a highly accurate model that provides easy-to-interpret results. The study was published in ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information.
Many software solutions for digital soil mapping are based on statistical models. The accuracy of such programs is limited because statistical models depend on the quality and quantity of field data and can ignore local irregularities in soil properties. It is difficult to obtain accurate and useful information from ...
TAMPA, Fla. - One of the most challenging issues in cancer therapy is the development of drug resistance and subsequent disease progression. In a new article featured on this month's cover of Cancer Research, Moffitt Cancer Center researchers, in collaboration with Oxford University, report results from their study using mathematical modeling to show that cell turnover impacts drug resistance and is an important factor that governs the success of adaptive therapy.
Cancer treatment options have increased substantially over the past few decades; however, many patients eventually develop drug resistance. Physicians strive to overcome resistance by either trying to target cancer cells through an alternative approach or targeting the resistance mechanism itself, but success with ...
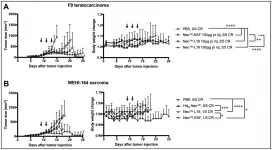
Oncotarget recently published "Targeting an engineered cytokine with interleukin-2 and interleukin-15 activity to the neovasculature of solid tumors" by Mortensen, et al. which reported that there is a growing interest in the antibody-based delivery of cytokines to the tumor environment as a means to boost the anti-cancer activity of tumor-resident T cells and NK cells.
Here, the authors described the expression and characterization of fusion proteins, featuring the L19 antibody and an engineered cytokine with interleukin-2 and interleukin-15 ...
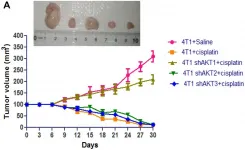
Oncotarget recently published "AKT isoforms have discrete expression in triple negative breast cancers and roles in cisplatin sensitivity" which reported that the authors investigated the expression and net effect of the individual isoforms in triple negative breast cancers and response to cisplatin treatment using cellular, mice models and clinical samples.
Interestingly, analysis of the expressions of AKT isoforms in clinical samples showed relatively higher expression of AKT1 in primary tissues; whereas lung and liver metastatic samples showed elevated ...
Coffee, cola or an energy drink: caffeine is the world's most widely consumed psychoactive substance. Researchers from the University of Basel have now shown in a study that regular caffeine intake can change the gray matter of the brain. However, the effect appears to be temporary.
No question - caffeine helps most of us to feel more alert. However, it can disrupt our sleep if consumed in the evening. Sleep deprivation can in turn affect the gray matter of the brain, as previous studies have shown. So can regular caffeine consumption affect brain structure due to poor sleep? A research team led by Dr. Carolin Reichert and Professor Christian Cajochen of the University of Basel ...
Here is a link to watch a video interview with Dr. Beatrice Aramini about this topic on the Oncotarget YouTube Channel
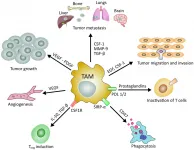
Oncotarget published "Cancer stem cells and macrophages: molecular connections and future perspectives against cancer" which reported that Cancer stem cells have been considered the key drivers of cancer initiation and progression due to their unlimited self-renewal capacity and their ability to induce tumor formation.
Macrophages, particularly tumor-associated macrophages, establish a tumor microenvironment to protect and induce CSCs development and dissemination.
Many studies in the past decade have been performed to understand the molecular ...