Graphene "nano-origami" creates tiniest microchips yet
Nanomaterial developments could lead to computers and phones running thousands of times faster
2021-02-16
(Press-News.org) The tiniest microchips yet can be made from graphene and other 2D-materials, using a form of 'nano-origami', physicists at the University of Sussex have found.
This is the first time any researchers have done this, and it is covered in a paper published in the ACS Nano journal.
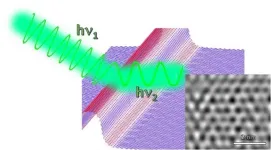
By creating kinks in the structure of graphene, researchers at the University of Sussex have made the nanomaterial behave like a transistor, and have shown that when a strip of graphene is crinkled in this way, it can behave like a microchip, which is around 100 times smaller than conventional microchips.
Prof Alan Dalton in the School of Mathematical and Physics Sciences at the University of Sussex, said:
"We're mechanically creating kinks in a layer of graphene. It's a bit like nano-origami.
"Using these nanomaterials will make our computer chips smaller and faster. It is absolutely critical that this happens as computer manufacturers are now at the limit of what they can do with traditional semiconducting technology. Ultimately, this will make our computers and phones thousands of times faster in the future.
"This kind of technology - "straintronics" using nanomaterials as opposed to electronics - allows space for more chips inside any device. Everything we want to do with computers - to speed them up - can be done by crinkling graphene like this."
Dr Manoj Tripathi, Research Fellow in Nano-structured Materials at the University of Sussex and lead author on the paper, said:
"Instead of having to add foreign materials into a device, we've shown we can create structures from graphene and other 2D materials simply by adding deliberate kinks into the structure. By making this sort of corrugation we can create a smart electronic component, like a transistor, or a logic gate."
The development is a greener, more sustainable technology. Because no additional materials need to be added, and because this process works at room temperature rather than high temperature, it uses less energy to create.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-16
A cloud simulation that captures the development and evolution of clouds based on atmospheric physical processes is more accurate than other models.
"Our model describes atmospheric conditions and thermodynamic processes as well as the fluid dynamics that govern the motion of air in the atmosphere," says Torsten Hädrich, a KAUST Ph.D. student in the international research team. "This allows us to simulate cloud phenomena more realistically than previous methods."
The model can take known atmospheric information at any time, such as temperature, humidity and wind, and simulate cloud formation, which is used for "nowcasting" of imminent cloud phenomena.
"For example, our model is able to simulate the formation of cumulonimbus clouds by considering ...
2021-02-16
Scientists at Cardiff University have discovered a unique way to target a common virus that affects one in 200 newborn babies in the UK but for which there is only limited treatments available.
Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) is a master at "hiding" from the body's immune system so antibodies and T-cells cannot attack it as they do in other viruses, like the current coronavirus.
The researchers have now discovered a new type of antibody in the lab which - instead of killing the virus directly - marks infected cells so the immune system can "see" them.
Once the immune system can see the infected cells it is able to kill the virus.
The team have submitted a patent for the unique immunotherapeutic and hope it can help to treat HCMV, which can leave newborn babies severely disabled or ...
2021-02-16
It does not happen often. But on rare occasions, physicians make mistakes and may make a wrong diagnosis. Patients may have many diseases all at once, where it can be difficult to distinguish the symptoms of one illness from the other, or there may be a lack of symptoms.
Errors in diagnosis may lead to incorrect treatment or a lack of treatment. Therefore, everyone in the healthcare system tries to minimise errors as much as possible.
Now, researchers at the University of Copenhagen have developed an algorithm that can help with just that.
'Our new algorithm can find the patients who have such an unusual disease trajectory that they may indeed not suffer from the disease ...
2021-02-16
Scientists have discovered that pollution concentration varies between seasons. A new study, conducted in the North China Plain, determined where volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are distributed within the vertical layers of the atmosphere, and found notable changes from winter to summer.
"The concentration of VOCs in the vertical direction was much higher in winter than that in summer and their emission sources showed different contributions in both seasons," said Guiqian Tang, associate professor in the Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, and the corresponding author of a study just published in Advances in Atmospheric Sciences .
The researchers conducted a field campaign from June 8 to July 3, 2019. They focused ...
2021-02-16
Researchers have used the zebrafish (Danio rerio) to identify the role of a gene involved in cardiac rhythm, which could help explain the fundamentals of what it takes to make a human heartbeat.
The University of Melbourne study also found that mutation of the gene, Tmem161b, causes potentially fatal cardiac arrhythmia. 2.5 per cent of Australians are living with cardiac arrhythmia ( END ...
2021-02-16
Almost half of people testing positive for coronavirus have reported symptoms of depression, according to a new study published in the International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.
Researchers from Bangladesh, the United States and Anglia Ruskin University (ARU) in the UK carried out a cross-sectional survey of more than 1,000 Bangladeshi adult coronavirus patients over the course of one month.
A total of 48% of respondents were categorised as having moderate to severe depression, with a higher prevalence in those with persistent symptoms, low family income ...
2021-02-16
Brain tumours are the most common solid tumours in childhood and the largest cause of death from cancer in this age group
Being able to classify a brain tumour's type, without the use of biopsy, is hard to do; however diffusion weighted imaging, an advanced imaging technique, when combined with machine learning, can help a UK-based multi-centre study, including WMG, University of Warwick has found.
Being able to characterise the tumour(s) faster and more accurately means they can be treated more efficiently
Diffusion weighted imaging and machine learning can successfully classify the diagnosis and characteristics of common types of paediatric brain tumours a UK-based multi-centre study, including WMG at the University of Warwick ...
2021-02-16
Researchers from North Carolina State University, Boston University and Kraton Corporation have demonstrated a family of self-sterilizing polymers that are effective at inactivating coronaviruses, including SARS-CoV-2 - the virus that causes COVID-19. The work opens the door to a suite of applications that could help to reduce the transmission of COVID-19 and other diseases.
"Our work here provides conclusive evidence that these materials, anionic polymers, can inactivate human coronaviruses quickly and efficiently," says Richard Spontak, co-author of a paper on the work accepted for publication in Advanced Science. Spontak is a Distinguished Professor of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering and ...
2021-02-16
A team of soil scientists developed a new approach to the automatic generation and updating of soil maps. Having applied machine learning technologies to a set of rules traditionally used by experts in manual mapping, the team obtained a highly accurate model that provides easy-to-interpret results. The study was published in ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information.
Many software solutions for digital soil mapping are based on statistical models. The accuracy of such programs is limited because statistical models depend on the quality and quantity of field data and can ignore local irregularities in soil properties. It is difficult to obtain accurate and useful information from ...
2021-02-16
TAMPA, Fla. - One of the most challenging issues in cancer therapy is the development of drug resistance and subsequent disease progression. In a new article featured on this month's cover of Cancer Research, Moffitt Cancer Center researchers, in collaboration with Oxford University, report results from their study using mathematical modeling to show that cell turnover impacts drug resistance and is an important factor that governs the success of adaptive therapy.
Cancer treatment options have increased substantially over the past few decades; however, many patients eventually develop drug resistance. Physicians strive to overcome resistance by either trying to target cancer cells through an alternative approach or targeting the resistance mechanism itself, but success with ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Graphene "nano-origami" creates tiniest microchips yet
Nanomaterial developments could lead to computers and phones running thousands of times faster