Evolution of cereal spikes
Plant research: publication in PNAS
2021-02-16
(Press-News.org) In plants, the "meristem" refers to a type of tissue comprising undifferentiated cells from which various other plant organs can develop through cell division and differentiation. These "plant stem cells" give rise to shoots, leaves and roots, but also spikes and flowers.
The research team including members of the Cluster of Excellence on Plant Sciences CEPLAS investigated the function of a gene responsible for the different spike forms of wheat and barley. This gene controls the activity of the spike and floret meristems and thus the number of spikelet and kernels per spike.
The closely related cool-season cereals, barley and wheat, produce variable and defined number of spikelets on their spikes, respectively. It is from these spikelets, that florets and the grains develop. The plant researchers have identified two barley mutants named "intermedium-m" and "double seed 1", which form a wheat-like spike with a terminal floret that consumes the spike meristem thereby reducing the number of lateral spikelets per spike. The INT-M/DUB1 gene maintains meristem identity and suppresses meristem differentiation. The ability of spike meristem to form lateral spikelets thus remains intact.
Prof. Dr. Maria von Korff Schmising, Head of the HHU Institute for Plant Genetics, about possible applications of the research findings: "These key regulators can be used to extend meristem activities. This may allow barley, wheat and other cereals to be modified to produce a higher grain yield."
INFORMATION:
Original publication
Jinshun Zhong, G. Wilma van Esse, Xiaojing Bi, Tianyu LAN, Agatha Walla, Qing Sang, Rainer Franzen, and Maria von Korff, INTERMEDIUM-M encodes an HvAP2L-H5 ortholog and is required for inflorescence determinacy and spikelet determinacy in barley, PNAS 2021 Vol. 118
DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2011779118
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-16
The research team that developed a biosensor that first recorded that a distinct gradient of the plant growth hormone gibberellin correlated with plant cell size has now revealed how this distribution pattern is created in roots.
Starting when a plant embryo forms within a seed and continuing throughout the plant lifecycle, undifferentiated stem cells undergo radical transformations into specialised root, stem, leaf and reproductive organ cells. This transformation relies on a suite of molecules called phytohormones that, much like human hormones, can move between cells and tissues and trigger distinct biological processes across the bodyplan. While it was not known at the time, mutations involving the gibberellin class of ...
2021-02-16
PITTSBURGH, Feb. 15, 2021 - Why do patients who receive antipsychotic medications to manage schizophrenia and bipolar disorder quickly gain weight and develop prediabetes and hyperinsulemia? The question remained a mystery for decades, but in a paper published today in Translational Psychiatry, researchers from the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine finally cracked the enigma.
Antipsychotic drugs, scientists showed, not only block dopamine signaling in the brain but also in the pancreas, leading to uncontrolled production of blood glucose-regulating hormones and, eventually, obesity and diabetes.
"There are dopamine theories of schizophrenia, drug addiction, depression and neurodegenerative disorders, and we are presenting a dopamine theory of metabolism," said lead ...
2021-02-16
For more than a decade, governments in countries across the world have made significant progress to expand their protected areas network to conserve the planet's biodiversity. According to a new study published in the journal Global Change Biology, the locations of these protected areas do not take into account the potential long-term effects of climate change in these protected areas.
Creating and managing protected areas, such as national parks, is key for biodiversity conservation. As the climate changes, however, species will disperse in order to maintain their specific habitat needs. Species that were in protected areas ...
2021-02-16
Almost half the patients admitted to an intensive care unit (ICU) require invasive mechanical ventilation (IMV), a medical procedure that guarantees a sufficient supply of oxygen to their organs and tissues. The therapy involves connecting patients to a machine that substitutes their spontaneous breathing. In recent months it has been in general use in intensive-care patients affected by COVID-19.
Although it can often save a patient's life, invasive mechanical ventilation is not risk-free: there can be accidental injury during intubation or extubation or the muscles ...
2021-02-16
A NEW study from the University of Chichester has shed light on how people coped psychologically with the sudden and life-changing disruption caused by COVID-19.
This new publication, by Chichester's Professor Laura Ritchie and PhD candidate Benjamin Sharpe, in collaboration with Professor Daniel Cervone of the University of Illinois at Chicago, provides a unique snapshot into people's understanding of their goals and self-beliefs amidst a shared, unexpected alteration of the daily landscape during lockdown.
Ritchie and colleagues collected their ...
2021-02-16
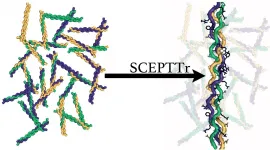
HOUSTON - (Feb. 15, 2021) - Collagen is the king of biological proteins, and now it has a SCEPTTr.
That's the handle of an algorithm developed by Rice University scientists who study natural and synthetic versions of collagen, which accounts for about a third of the body's proteins and forms the fibrous glue in skin, bones, muscles, tendons and ligaments.
The program -- full name, Scoring function for Collagen-Emulating-Peptides' Temperature of Transition -- accurately predicts the stability of collagen triple helices, the primary structure that forms fibrils.
The Rice team led by chemist and bioengineer Jeffrey ...
2021-02-16
According to some estimates, chronic pain affects up to 40% of Americans, and treating it frustrates both clinicians and patients--a frustration that's often compounded by a hesitation to prescribe opioids for pain.
A new study from the University of Michigan School of Dentistry confirms that a low dose of a drug called naltrexone is a good option for patients with orofacial and chronic pain, without the risk of addiction, said first author Elizabeth Hatfield, a clinical lecturer in the Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery and Hospital Dentistry.
Naltrexone is a semisynthetic opioid first developed in ...
2021-02-16
HOUSTON - (Feb. 15, 2021) - Rice University engineers have suggested a colorful solution to next-generation energy collection: Luminescent solar concentrators (LSCs) in your windows.
Led by Rafael Verduzco and postdoctoral researcher and lead author Yilin Li of Rice's Brown School of Engineering, the team designed and built foot-square "windows" that sandwich a conjugated polymer between two clear acrylic panels.
That thin middle layer is the secret sauce. It's designed to absorb light in a specific wavelength and guide it to panel edges lined with solar cells. Conjugated polymers are chemical compounds ...
2021-02-16
Researchers from the University of Southampton and Université Laval, Canada, have successfully measured for the first time back-reflection in cutting-edge hollow-core fibres that is around 10,000 times lower than conventional optical fibres.
This discovery, published this week in The Optical Society's flagship Optica journal, highlights yet another optical property in which hollow-core fibres are capable of outperforming standard optical fibres.
Research into improved optical fibres is key to enable progress in numerous photonic applications. Most notably, these would improve Internet performance ...
2021-02-16
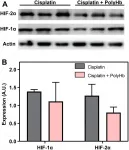
Oncotarget recently published "Polymerized human hemoglobin increases the effectiveness of cisplatin-based chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer" which reported that unfortunately, a significant portion of NSCLC patients relapse due to cisplatin chemoresistance.
Administration of hemoglobin-based oxygen carriers is a promising strategy to alleviate hypoxia in the tumor, which may make cisplatin more effective.
The R-state PolyHb administered in this study is unable to deliver O2 unless under severe hypoxia which significantly limits its oxygenation potential.
In vitro sensitivity studies indicate that the administration of PolyHb increases the effectiveness of cisplatin under ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Evolution of cereal spikes
Plant research: publication in PNAS