Role of diet in risk of colorectal cancer
2021-02-16
(Press-News.org) What The Study Did: Researchers examined the strength of the evidence from published meta-analyses of observational studies that looked at the association between diet and the risk of colorectal cancer.
Authors: Nathorn Chaiyakunapruk, Pharm.D., Ph.D., of the University of Utah in Salt Lake City, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.37341)
Editor's Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media advisory: The full study is linked to this news release.
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time http://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.37341?utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_term=021621
About JAMA Network Open: JAMA Network Open is the new online-only open access general medical journal from the JAMA Network. On weekdays, the journal publishes peer-reviewed clinical research and commentary in more than 40 medical and health subject areas. Every article is free online from the day of publication.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-16
WASHINGTON, February 16, 2021 -- The widespread use of high-speed and high-energy weapons in modern warfare has led to an increasing incidence of explosive injuries. For such wounds as well as those incurred in disasters and accidents, severe hemorrhage is the leading cause of death.
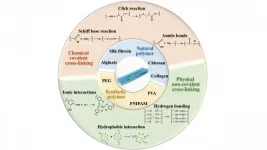
In APL Bioengineering, by AIP Publishing, researchers from the Southern University of Science and Technology in China examine the advances in hydrogel dressings in recent years, which are good at promoting wound healing and can better meet the demands of different situations.
"With the rapid developments of material science, there are numerous highly ...
2021-02-16
CHICAGO --- A mother's heart health while she is pregnant may have a significant impact on her child's cardiovascular health in early adolescence (ages 10 to 14), according to a new study from Northwestern Medicine and the Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children's Hospital of Chicago.
The study will be published Feb. 16 in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA). It is the first study to examine the implications of a mother's cardiovascular health during pregnancy for offspring health in the longer term.
The findings are troubling, as they build upon previous Northwestern Medicine and Lurie Children's Hospital research that found ...
2021-02-16
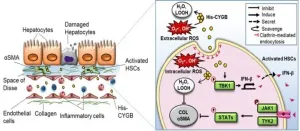
Researchers have discovered that the use of Cytoglobin (CYGB) as an intravenous drug could delay liver fibrosis progression in mice.
CYGB, discovered in 2001 by Professor Norifumi Kawada, is present in hepatic stellate cells, the cells that produce fibrotic molecules such as collagens when the liver has acute or chronic inflammation induced by different etiologies. The enhancement of CYGB on these cells or the injection of recombinant CYGB has the effect of suppressing liver damage and cirrhosis. These findings published in the February 2021 issue of the journal Hepatology.
Anti-fibrotic therapy remains an unmet medical need in human chronic liver diseases. A research team led by Professor Norifumi Kawada, Osaka City University ...
2021-02-16
Dry and cloudless weather was mainly responsible for the unusually high solar irradiance in western Europe during the spring of 2020, not the reduction in aerosol emissions due to the first lockdown. This was the result of an international meteorological study, in which scientists from the University of Cologne participated. The results have been published in the current issue of Nature Communications Earth & Environment.
A large part of western Europe experienced exceptionally sunny and dry weather from March 23 to the end of May 2020. New sunshine extremes were reported in the United Kingdom, Belgium, Germany, and the Netherlands, coupled with exceptionally deep blue skies. At the same time, these countries had gone into lockdown in response ...
2021-02-16
Historically, most electric transmission system operators have used heuristics (rules based on experience) to hold sufficient reserves to guard against unforeseen large outages and maintain system reliability. However, the expansion of competitive wholesale electricity markets has led to efforts to translate reserve heuristics into competitively procured services. A common approach constructs an administrative demand curve for valuing and procuring least cost reserve supply offers. The technical term for this is the operating reserve demand curve (ORDC). A new paper quantifies how better accounting for the temperature-dependent probability of large generator contingencies with time-varying dynamic ORDC construction improves reserve procurement.
The paper, "Dynamic Operating Reserve Procurement ...
2021-02-16
Between January 2012 and March 2018, there were an average of 1,000 failures each year at large North American gas power plants due to unscheduled fuel shortages and fuel conservation interruptions. This is a problem as the power grid depends on reliable natural gas delivery from these power plants in order to function. More than a third of all U.S. electricity is generated from natural gas. New research now indicates that these fuel shortages are not due to failures of pipelines and that in certain areas of the country a change in how gas is purchased ...
2021-02-16
DALLAS - Feb. 16, 2021 - A study that identifies how a coronavirus protein called Nsp1 blocks the activity of genes that promote viral replication provides hope for new COVID-19 treatments.
Since the start of the pandemic, scientists have worked endlessly to understand SARS-CoV-2, the coronavirus that causes COVID-19. Even with the arrival of vaccines, the virus is still spreading and there is a need to develop alternative therapies. Scientists hope to achieve this by studying how SARS-CoV-2 infects cells and propagates itself while avoiding the body's natural immune system.
Now researchers at UT Southwestern have added another piece to this puzzle with their END ...
2021-02-16
TUCSON, Ariz. -- The ongoing pandemic has had a significant and alarming trend of increased alcohol use and abuse - especially among younger adults, males and those who have lost their jobs - according to a new study by University of Arizona Health Sciences researchers.
Research led by William "Scott" Killgore, PhD, professor of psychiatry in the UArizona College of Medicine - Tucson and director of the Social, Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience Lab, found that hazardous alcohol use and likely dependence increased every month for those under lockdowns compared to those not under restrictions.
"Being under lockdown during a worldwide pandemic has been hard on everyone, and many people are relying on greater quantities of alcohol to ease their distress," said Dr. ...
2021-02-16
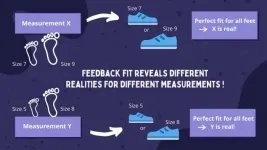
Shoe shops sell a variety of shoe sizes to accommodate a variety of foot sizes -- but what if both the shoe and foot size depended on how it was measured? Recent developments in quantum theory suggest that the available values of a physical quantity, such as a foot size, can depend on the type of measurement used to determine them. If feet were governed by the laws of quantum mechanics, foot size would depend on the markings on a foot measure to find the best fit -- at the time of measurement -- and even if the markings were changed, the measurement could still be precise.
In quantum mechanics, the "size" of a physical ...
2021-02-16
Because cancers in children are rare, many details about their biology remain unknown. In the field of cancer genetics, there's a limited understanding of how inherited genetic changes may contribute to the formation and growth of tumors. Making connections between particular gene mutations and disease requires a lot of data, which until recently has been largely unavailable for pediatric cancers.
Now, tests like MSK-IMPACTTM can screen tumors for mutations in more than 500 genes as well as analyze patients' normal (germline) cells. In the largest study of its kind so far, researchers from Memorial Sloan Kettering's pediatric program, MSK Kids, are reporting germline genomic sequencing details for 751 pediatric patients treated for solid tumors.
The paper, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Role of diet in risk of colorectal cancer