(Press-News.org) In response to the increase in opioid overdose deaths in the United States, many states have implemented supply-controlling and harm-reduction policy measures aimed at reducing those deaths. But a recent study from Indiana University found the policies may have had the unintended consequence of motivating those with opioid use disorders to switch to alternative illicit substances, leading to higher overdose mortality.
"Literature from public health to social sciences has presented mixed and contradictory findings on the impact of opioid policies on various opioid adverse outcomes," said Byungkyu Lee, assistant professor of sociology at IU and co-author of the study. "Our findings suggest that the so-called opioid paradox -- the rise of opioid-related deaths despite declines in opioid prescriptions -- may arise from the success, not the failure, of state interventions to control opioid prescriptions."
Researchers used the National Vital Statics System and Optum Clinformatics DataMart to look at drug overdose mortality data from 50 states and claims data from 23 million commercially insured patients in the U.S. between 2007 and 2018. They then evaluated the prevalence of indicators of prescription opioid abuse, opioid use disorder and overdose diagnosis, and the prescription of medications-assisted treatment and drug overdose deaths before and after implementation of six state-level policies targeting the opioid epidemic.
Policies included prescription drug monitoring program access, mandatory prescription drug monitoring programs, pain clinic laws, prescription limit laws, naloxone access laws and Good Samaritan laws.
The study, published in the JAMA Network Open, found that supply-controlling policies were associated a lower proportion of patients who take opioids, have overlapping claims, receive higher opioid doses and visit multiple providers and pharmacies. They also found that harm-reduction policies were associated with modest increases in the proportion of patients with overdose and opioid use disorder. Additionally, the proportion of patients receiving medications-assisted treatment drugs increased following the implementation of supply-controlling policies.
Brea Perry, professor of sociology at IU and co-author of the study, said these findings demonstrate the power of big data to provide insights into the opioid epidemic and how to best reverse it.
"Our work reveals the unintended and negative consequences of policies designed to reduce the supply of opioids in the population for overdose," Perry said. "We believe that policy goals should be shifted from easy solutions such as dose reduction to more difficult fundamental ones, focusing on improving social conditions that create demand for opioids and other illicit drugs."
In terms of overdose mortality, the study found that all overdose deaths increased following the implementation of naloxone access laws, especially deaths attributable to heroin, synthetic opioids and cocaine. Good Samaritan laws were also associated with increases in overall overdose deaths.
Furthermore, mandatory prescription drug monitoring programs were associated with a reduction in overdose deaths from natural opioids and methadone, and the implementation of pain clinic laws was associated with an increase in the number of overdose deaths from heroin and cocaine. However, having a prescription limit law was associated with a decrease in overdose deaths from synthetic opioids.
"Our work demonstrates that there is no easy policy solution to reverse the epidemic of opioid dependence and mortality in the U.S.," Lee said. "To resolve the opioid paradox, it is imperative to design policies to address the fundamental causes of overdose deaths, such as lack of economic opportunity, persistent physical, and mental pain, and enhance treatment for drug dependence and overdose rather than focusing on opioid analgesic agents as the cause of harm."
INFORMATION:
Other co-authors of the study are Wanying Zhao, Kai-Cheng Yang and YY Ahn, all from the IU Luddy School of Informatics. This work was supported by a National Institute on Drug Abuse grant.
IU Research
Indiana University's world-class researchers have driven innovation and creative initiatives that matter for 200 years. From curing testicular cancer to collaborating with NASA to search for life on Mars, IU has earned its reputation as a world-class research institution. Supported by $854 million last year from our partners, IU researchers are building collaborations and uncovering new solutions that improve lives in Indiana and around the globe.
INFORMS Journal on Applied Analytics Key Takeaways:
Although waiting times in walk-up clinics are shorter, people preferred the convenience of drive-through clinics.
People believe drive-through clinics are safer, more convenient and less contagious.
You can vaccinate a large number of people without a lot of waiting and confusion using a drive-through clinic.
CATONSVILLE, MD, February 17, 2021 - Policymakers at all levels of government are racing to vaccinate hundreds of millions of people to save lives and blunt the deadly COVID-19 pandemic. New research published ...
Researchers have developed a new tool for addressing disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) - a blood disorder that proves fatal in many patients. The technology has not yet entered clinical trials, but in vivo studies using rat models and in vitro models using blood from DIC patients highlight the tech's potential.
"DIC basically causes too much clotting and too much bleeding at the same time," says Ashley Brown, corresponding author of a paper on the work. "Small blood clots can form throughout the circulatory system, often causing organ damage. And because this taxes the body's supply of clotting factors, patients also experience excess bleeding. Depending on ...
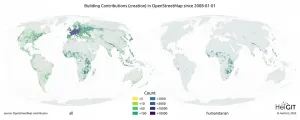
In recent years, free digital world maps like OpenStreetMap (OSM) have become a vital instrument to support humanitarian missions over the entire world. In disaster management as well as the implementation of the United Nations Sustainability Development Goals (SDGs), geodata compiled by the volunteer mapper community open up new possibilities to coordinate aid interventions and carry out sustainability projects. The mapping data are collected either locally using a smartphone and GPS device or on the basis of satellite images. An international team of researchers led by geoinformation ...
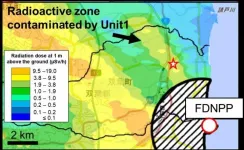
The 10 year anniversary of the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear accident occurs in March. Work just published in the Journal 'Science of the Total Environment' documents new, large (> 300 micrometers), highly radioactive particles that were released from one of the damaged Fukushima reactors.
Particles containing radioactive cesium (134+137Cs) were released from the damaged reactors at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (FDNPP) during the 2011 nuclear disaster. Small (micrometer-sized) particles (known as CsMPs) were widely distributed, reaching as far as Tokyo. CsMPs have been the subject of many studies in recent years. However, it recently became apparent that larger (>300 micrometers) Cs-containing particles, with much higher levels of activity (~ 105 Bq), were also ...
The brain's neural activity is irregular, changing from one moment to the next. To date, this apparent "noise" has been thought to be due to random natural variations or measurement error. However, researchers at the Max Planck Institute for Human Development have shown that this neural variability may provide a unique window into brain function. In a new Perspective article out now in the journal Neuron, the authors argue that researchers need to focus more on neural variability to fully understand how behavior emerges from the brain.
When neuroscientists investigate the brain, its activity seems to vary all the time. Sometimes activity is higher or lower, rhythmic or irregular. Whereas averaging brain activity ...
The researchers analysed how Spanish children and adolescents get to school, based on studies examining the commuting patterns of 36,781 individuals over a 7-year period (2010-2017)
Researchers from the University of Granada (UGR) have conducted the most comprehensive study to date on how Spanish children and young people get to school each day, to determine the active commuting rate.
The results showed that, between 2010 and 2017, in the region of 60% of Spanish children and adolescents actively commuted to school, with no significant variations being observed during this period.
The study, which was recently ...
Our brains are complicated webs of billions of neurons, constantly transmitting information across synapses, and this communication underlies our every thought and movement.
But what happens to the circuit when a neuron dies? Can other neurons around it pick up the slack to maintain the same level of function?
Indeed they can, but not all neurons have this capacity, according to new research from the University of Chicago. By studying several neuron pairs that innervate distinct muscles in a fruit fly model, researchers found that some neurons compensate for ...
Scientists have used cutting-edge research in quantum computation and quantum technology to pioneer a radical new approach to determining how our Universe works at its most fundamental level.
An international team of experts, led by the University of Nottingham, have demonstrated that only quantum and not classical gravity could be used to create a certain informatic ingredient that is needed for quantum computation. Their research "Non-Gaussianity as a signature of a quantum theory of gravity" has been published today in PRX Quantum.
Dr Richard Howl led the research during his time at the University of Nottingham's School of Mathematics, he said: "For ...
One early feature of reporting on the coronavirus pandemic was the perception that sub-Saharan Africa was largely being spared the skyrocketing infection and death rates that were disrupting nations around the world.
While still seemingly mild, the true toll of the novel coronavirus, SARS-CoV-2, on the countries of sub-Saharan Africa may be obscured by a tremendous variability in risk factors combined with surveillance challenges, according to a study published in the journal Nature Medicine by an international team led by Princeton University researchers and supported by Princeton's High Meadows Environmental Institute (HMEI).
"Although ...
Adequate spacing between births can help to alleviate the likelihood of stunting in children, according to a new study from the Tata-Cornell Institute for Agriculture and Nutrition (TCI).
In an article published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, TCI postdoctoral associate Sunaina Dhingra and Director Prabhu Pingali find that differences in height between firstborn and later-born children may be due to inadequate time between births. When children are born at least three years after their older siblings, the height gap between them disappears.
India's family planning policies have focused on lowering population growth and postponing pregnancy to improve maternal health outcomes. But while the overall fertility rate has fallen as low ...