Changing livestock in ancient Europe reflect political shifts
Archaeology shows that politics and economics played a major impact in choosing livestock
2021-02-17
(Press-News.org) In ancient European settlements, livestock use was likely primarily determined by political structure and market demands, according to a study published February 17, 2021 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Ariadna Nieto-Espinet and colleagues of the Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas, Barcelona.
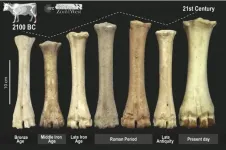
Zooarchaeology - the study of animal remains from archaeological sites - has great potential to provide information on past human communities. Livestock preferences are known to have changed over time in Europe, but little is known about how much these changes are influenced by environmental, economic, or political conditions of ancient settlements.
In this study, Nieto-Espinet and colleagues gathered data from 101 archaeological sites across the northeastern Iberian Peninsula, ranging from the Late Bronze Age to Late Antiquity, a span of around 1700 years during which European cultural and agricultural practices underwent significant changes. At each site, they compared livestock remains with data on the local environment (including plant and climate data) and the economic and political conditions of the settlement.
These data show that political and economic factors were most important in determining the species distribution and body size of ancient livestock. During the Late Bronze Age and Late Antiquity, when political systems were more fragmented and food production was focused more on local markets, livestock choice was more dependent upon local environmental conditions. But during the later Iron Age and the time of the Roman Empire, the demands of a pan-Mediterranean market economy favored more changes in livestock use independent of environmental factors. Zooarchaeology is thus a vital source of information for understanding political and economic changes through time.
The authors add: "Archaeology reveals the influence of political systems on livestock practices over time."
INFORMATION:
Citation: Nieto Espinet A, Huet T, Trentacoste A, Guimarães S, Orengo H, Valenzuela-Lamas S (2021) Resilience and livestock adaptations to demographic growth and technological change: A diachronic perspective from the Late Bronze Age to Late Antiquity in NE Iberia. PLoS ONE 16(2): e0246201. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0246201
Funding: This work was financially supported by the ERC-Starting Grant ZooMWest - Zooarchaeology and Mobility in the Western Mediterranean: Husbandry production from the Late Bronze Age to the Late Antiquity (award number 716298), funded by the European Research Council Agency (ERCEA) under the direction of Sílvia Valenzuela-Lamas. In cooperation with PID2019-110022GB -100 MOBICEX (Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación, ES); 2017 SGR 995-GRC-Archaeology of Social Dynamics (ASD)-CSIC (Generalitat de Catalunya, ES). The funders had no role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
In your coverage please use this URL to provide access to the freely available article in PLOS ONE: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0246201
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-17
The new method works without extremely high temperatures, is therefore more energy-efficient and has a significantly higher recovery rate (approx. 96 per cent of the starting material) than established processes. These findings will be published on 17 February 2021 in the scientific journal Nature.
Mechanical recycling vs. chemical recycling
"The direct re-utilization of plastics is often hampered by the fact that, in practice, mechanical recycling only functions to a limited degree - because the plastics are contaminated and mixed with additives, which impairs the properties ...
2021-02-17
Engineers at the University of California San Diego have created a four-legged soft robot that doesn't need any electronics to work. The robot only needs a constant source of pressurized air for all its functions, including its controls and locomotion systems.
The team, led by Michael T. Tolley, a professor of mechanical engineering at the Jacobs School of Engineering at UC San Diego, details its findings in the Feb. 17, 2021 issue of the journal Science Robotics.
"This work represents a fundamental yet significant step towards fully-autonomous, electronics-free walking robots," said Dylan Drotman, a Ph.D. student in Tolley's research group and the paper's first author.
Applications include low-cost robotics for entertainment, such ...
2021-02-17
The unprecedented and deadly blazes that engulfed the American West in 2020 attest to the increasing number, size and severity of wildfires in the region. And while scientists predict the climate crisis will exacerbate this situation, there's still much discussion around its contributing factors.
With this in mind, scientists at five western universities, including UC Santa Barbara, investigated the effects of human-driven climate change and more than a century of fire suppression, which has produced dense forests primed to burn. Their research, published in the journal Environmental ...
2021-02-17
In the search for planets capable of sustaining life, an international research team with members from ETH has taken a significant step forward. As the researchers reported recently in the journal Nature Communications, they found signs of a Neptune-sized planet in the Alpha Centauri star system, a mere 4.4 light years away from Earth. This exoplanet is located in a zone that may offer suitable conditions for life. The team was able to collect data with unprecedented sensitivity, thus registering even very weak signals.
Earth is a disruptive factor
Thanks to the new process, the researchers have advanced one step closer to ...
2021-02-17
In the paper, 'Tracking Reactions of Asymmetric Organo-Osmium Transfer Hydrogenation Catalysts in Cancer Cells', published in the journal Angewandte Chemie, researchers from the University of Warwick have, for the first time, used the new 185 m beamline to track Osmium in a single cancer cell at a scale of 100 nanometers.
They used two techniques to track potential treatments in cancer cells, the first, ICP-MS, which stands for Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry, can quantify a wide range of natural and drug elements in millions of cells. However, to investigate a single cancer cell, researchers used synchrotron X-ray Fluorescence ...
2021-02-17
Gravity might play a bigger role in the formation of elementary particles than scientists used to believe. A team of physicists from RUDN University obtained some solutions of semi-classical models that describe particle-like waves. They also calculated the ratio between the gravitational interaction of particles and the interaction of their charges. The results of the study were published in the Universe journal.
Due to their small size, the gravitational interaction between elementary particles (electrons, protons, and neutrons) is weak compared to Coulomb forces--attraction ...
2021-02-17
Experts say English slang and regional dialect should not be banned from classrooms but when you're getting to grips with a second language how helpful is it to learn non-standard lingo?
Very, says Sascha Stollhans, of the Department of Languages and Cultures at Lancaster University, who argues that standardised language norms are artificial and language learners should learn about all aspects of language, even the controversial ones.
In his policy paper, just published in the Languages, Society & Policy Journal, he says:
There are concerns among professionals that introducing learners to 'non-standard' language could lead to ambiguity and confusion and that students might be penalised for using it in assessments.
Linguistic variation is a rich area of study that can appeal to language ...
2021-02-17
Researchers from the University of Granada warn that an accumulation of fatty tissue in the neck (both the double chin and the deeper deposits, located between muscles and around the cervical vertebrae) is a predictor of central and overall adiposity, cardiometabolic risk, and a pro-inflammatory profile in sedentary young adults.
A study conducted by researchers from the University of Granada (UGR) has revealed that an accumulation of fatty tissue in the neck is a predictor of central and overall adiposity, cardiometabolic risk (heart problems), and a pro-inflammatory profile in sedentary young adults.
Traditionally, the accumulation of visceral adipose tissue has been considered one of the factors most strongly ...
2021-02-17
Research teams from Ruhr-Universität Bochum (RUB) and the University of Copenhagen have therefore developed an approach that can predict the optimal composition and confirm its accuracy with high-throughput experiments. They report in the journal Angewandte Chemie International Edition of 28. December 2020.
Much less expensive elements than previous catalysts
Many electrochemical reactions go through several steps. Each should be optimized on a catalyst surface if possible, but different requirements apply to each step. "Since previous catalysts usually had only one optimized ...
2021-02-17
Blockchain is a decentralized technology used to protect the security and privacy of online transactions and is usually associated with cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin. However, it is a mechanism that can be applied to all kinds of digital exchanges. In a new study, researchers from the K-riptography and Information Security for Open Networks (KISON) group at the Internet Interdisciplinary Institute (IN3) Amna Qureshi and professor David Megías (who is also the director of the IN3) analysed existing blockchain-based multimedia content protection systems and established a taxonomy to classify them according ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Changing livestock in ancient Europe reflect political shifts
Archaeology shows that politics and economics played a major impact in choosing livestock