(Press-News.org) In the paper, 'Tracking Reactions of Asymmetric Organo-Osmium Transfer Hydrogenation Catalysts in Cancer Cells', published in the journal Angewandte Chemie, researchers from the University of Warwick have, for the first time, used the new 185 m beamline to track Osmium in a single cancer cell at a scale of 100 nanometers.
They used two techniques to track potential treatments in cancer cells, the first, ICP-MS, which stands for Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry, can quantify a wide range of natural and drug elements in millions of cells. However, to investigate a single cancer cell, researchers used synchrotron X-ray Fluorescence (XRF) imaging.
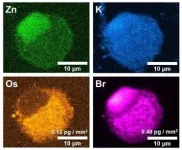
Using a hard-x-ray nanoprobe beamline, researchers from the University of Warwick observed how Osmium reacted in a single lung cancer cell. However, the reactivity of Osmium is determined by its coating (its ligands), so they monitored the ligands too in the same XRF experiment by labelling them with Bromine.
Once the Osmium was in the cell researchers observed that Osmium stays in the cytoplasm, whereas the ligands entered the nucleus, potentially indicative of dual attack on the cancer cell.Caption: Detection of an anticancer compound in a cancer cell, the pink is the Bromine and orange in Osmium Credit: University of Warwick
Professor Peter Sadler, from the Department of Chemistry at the University of Warwick comments:
"With one in two people getting cancer in their lifetime, the need to find new drugs has never been more urgent. Part of drug discovery is seeing exactly how they react and work in cells."
"Osmium is a rare precious metal, however, since it can act as a catalyst, a very little amount is needed for reactions in the cancer cell, therefore it could be a sustainable treatment going forward. We wanted to see how exactly it worked in a single cancer cell, which involved a variety of novel techniques, including taking water molecules out of the cell and rapidly flash-freezing it. Whereas usually cells are chemically altered to see the reactions, in our method they are close to their natural state, making our results more authentic."
Dr Elizabeth Bolitho, from the Department of Chemistry and Diamond adds:
"We worked 24 hours a day, 5 days a week to collect these exciting data, allowing us to see inside cancer cells to a nanoscale resolution. This has provided crucial insights into potential cellular targets of such Osmium catalysts.
"Not only were we able to track the Osmium in a lung cancer cell, but more widely in breast cancer, ovarian and prostate cancer cells, for example, which provides hope that in the future Osmium could be used to treat a range of different cancers."
Professor Sadler added: "Our team hopes to progress their discoveries through pre-clinical development towards new Osmium drugs for cancer treatment, although this typically takes several years. If we succeed, then the days and sleepless nights spent collecting XRF data at the Diamond synchrotron will certainly have been worthwhile."
Paul Quinn, Imaging group leader at Diamond Light Source added:
"The collaboration between Warwick and the I14 beamline is very exciting. Our research has exploited the advanced nano-imaging methods we've developed and built at Diamond to neatly image the location of these drugs within cancer cells and gain significant insights into how they interact."
INFORMATION:
Gravity might play a bigger role in the formation of elementary particles than scientists used to believe. A team of physicists from RUDN University obtained some solutions of semi-classical models that describe particle-like waves. They also calculated the ratio between the gravitational interaction of particles and the interaction of their charges. The results of the study were published in the Universe journal.
Due to their small size, the gravitational interaction between elementary particles (electrons, protons, and neutrons) is weak compared to Coulomb forces--attraction ...
Experts say English slang and regional dialect should not be banned from classrooms but when you're getting to grips with a second language how helpful is it to learn non-standard lingo?
Very, says Sascha Stollhans, of the Department of Languages and Cultures at Lancaster University, who argues that standardised language norms are artificial and language learners should learn about all aspects of language, even the controversial ones.
In his policy paper, just published in the Languages, Society & Policy Journal, he says:
There are concerns among professionals that introducing learners to 'non-standard' language could lead to ambiguity and confusion and that students might be penalised for using it in assessments.
Linguistic variation is a rich area of study that can appeal to language ...
Researchers from the University of Granada warn that an accumulation of fatty tissue in the neck (both the double chin and the deeper deposits, located between muscles and around the cervical vertebrae) is a predictor of central and overall adiposity, cardiometabolic risk, and a pro-inflammatory profile in sedentary young adults.
A study conducted by researchers from the University of Granada (UGR) has revealed that an accumulation of fatty tissue in the neck is a predictor of central and overall adiposity, cardiometabolic risk (heart problems), and a pro-inflammatory profile in sedentary young adults.
Traditionally, the accumulation of visceral adipose tissue has been considered one of the factors most strongly ...
Research teams from Ruhr-Universität Bochum (RUB) and the University of Copenhagen have therefore developed an approach that can predict the optimal composition and confirm its accuracy with high-throughput experiments. They report in the journal Angewandte Chemie International Edition of 28. December 2020.
Much less expensive elements than previous catalysts
Many electrochemical reactions go through several steps. Each should be optimized on a catalyst surface if possible, but different requirements apply to each step. "Since previous catalysts usually had only one optimized ...
Blockchain is a decentralized technology used to protect the security and privacy of online transactions and is usually associated with cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin. However, it is a mechanism that can be applied to all kinds of digital exchanges. In a new study, researchers from the K-riptography and Information Security for Open Networks (KISON) group at the Internet Interdisciplinary Institute (IN3) Amna Qureshi and professor David Megías (who is also the director of the IN3) analysed existing blockchain-based multimedia content protection systems and established a taxonomy to classify them according ...
Research has found fidaxomicin, an antibiotic usually used to treat bowel infections, prevents growth of resistant strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTb) in the lab.
Published in the Journal of Medical Microbiology, the research found that fidaxomicin was more effective than existing tuberculosis (TB) medication at preventing growth of the bacterium that causes TB.
Researchers compared the activity of fidaxomicin and rifampicin, an antibiotic currently used to treat TB, against 72 different strains of MTb. Of these strains, 34 were resistant to multiple antibiotics. They found that fidaxomicin could prevent growth of all 72 strains at lower doses than rifampicin.
Both of the drugs tested work in a similar way and ...
Ground-breaking research led by University of Limerick has revealed for the first time that the immune system directly links personality to long-term risk of death.
The study sheds new light on why people who are more conscientious tend to live longer.
Results from the new international study published in the journal Brain, Behavior, and Immunity have found that the immune system plays a previously unknown role in the link between personality traits and long-term risk of death.
"Personality is known to be associated with long-term risk of death, it is a well replicated ...
Women who gave birth during the COVID-19 pandemic report having felt greater stress in the delivery process, and rate lower the quality of care received.
Furthermore, almost 15% more women developed symptoms of postpartum depression after giving birth during the pandemic
A study carried out by researchers from the University of Granada (UGR) indicates that psychological variables have contributed to more severe anxiety and depression among pregnant women since the COVID-19 pandemic began. These psychological variables include the general stress suffered, the concerns that women have about the pregnancy itself, personal resilience, insomnia, fear of catching the virus, or the feeling of loneliness.
This study, published in the journal Medicina Clínica, has revealed that feeling ...
Studies have shown that SARS-CoV-2 remains active on aerosols and surfaces for between several hours and several days, depending on the nature of the surface and environmental conditions. Presently, researchers from Tel Aviv University have demonstrated that ozone, which has already long been used as an antibacterial and antiviral agent in water treatment, effectively sanitizes surfaces against Coronavirus after short exposure to low concentrations of ozone. The research team was led by Dr. Ines Zucker from the School of Mechanical Engineering at the Ivy and Eldar Fleischman Faculty of Engineering and the Porter School of the ...
People with attention-deficit / hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) combined with disruptive behaviour disorders (DBDs) share about the 80% of genetic variants associated with aggressive and antisocial behaviours.
This is one of the conclusions of a study published in the journal Nature Communications which counts on the participation of professor Bru Cormand, from the Faculty of Biology and the Institute of Biomedicine of the University of Barcelona (IBUB), Sant Joan de Déu Research Institute (IRSJD) and the Rare Diseases Networking Biomedical Research Centre (CIBERER), and researchers Marta Ribasés and Josep Antoni ...