(Press-News.org) People with attention-deficit / hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) combined with disruptive behaviour disorders (DBDs) share about the 80% of genetic variants associated with aggressive and antisocial behaviours.
This is one of the conclusions of a study published in the journal Nature Communications which counts on the participation of professor Bru Cormand, from the Faculty of Biology and the Institute of Biomedicine of the University of Barcelona (IBUB), Sant Joan de Déu Research Institute (IRSJD) and the Rare Diseases Networking Biomedical Research Centre (CIBERER), and researchers Marta Ribasés and Josep Antoni Ramos Quiroga, from Vall d'Hebron Research Institute (VHIR) and the Mental Health Networking Biomedical Research Centre (CIBERSAM).
The study -the most ambitious one published to date on risk genetic factors shared between people with ADHD and DBDs- is based on the study conducted to about 4,000 affected people by these pathologies and 30,000 control individuals, within the frame of the European project Aggressotype, from the Horizon 2020 program, aimed at doing research on the neurobiological basis of the aggressive behaviour. The study is led by Ditte Demontis and Anders D. Børglum (Aarhus University, Denmark) and Stephen V. Faraone (State University of New York, United States).
ADHD: a psychiatric disorder that does not always come alone
ADHD is a common behaviour disorder -it affects about 5% of children and 2.5% adult people- and features hyperactivity, impulsiveness and attention deficit. This disorder usually comes with other psychiatric alterations, mainly disruptive behaviour disorders (DBDs), which can be associated with antisocial and aggressive behaviours.
"ADHD and DBD are caused by genetic and environmental factors. Regarding ADHD, it is estimated that genetics account for a 75%, while in DBDs, it would oscillate between 40 and 70%. These clinical pictures are more frequent in boys than girls, and when they come together, people are more likely to fall into risky behaviours, addictive substance use, and premature death", notes Bru Cormand, professor at the Department of Genetics, Microbiology and Statistics and head of the Research Group on Neurogenetics of the UB.
"Certain people feature two or more psychiatric disorders, and this coexistence continues, in many cases, in a chronological axis, in which suffering from a psychiatric disorder such as ADHD involves opening the door to other comorbid pathologies that aggravate the life quality of those who suffer from the disorder", notes Marta Ribasés, head of the Laboratory of Genetic Psychiatry of Vall d'Hebrón Research Institute (VHIR).
Through genome-wide association studies (GWAS), researchers analyzed the genetic contribution of changes in a single DNA nucleotide (SNP) -the most abundant ones in the human genome- to these psychiatric disorders. As part of the study, VHIR and UB experts brought samples of patients with ADHD diagnosed at Hospital Vall d'Hebron and took part in the analysis of genetic data.
More risk genetic variants in patients with ADHD and DBDs
The research team identified a genomic segment in the chromosome 11 which increases the risk of having ADHD combined with DBD. "This region has the STIM1 gen, which is involved in the regulation of calcium cell levels, neuronal plasticity and learning memory", notes Bru Cormand, who coordinated the international working group on genetics in the Aggressotype project.
"Our study shows that genetics are more determining in people with ADHD and DBD than those who only suffer from ADHD", highlights Bru Cormand. "If we compare the genome of patients with ADHD and DBD to that of those patients with only ADHD, we see that people affected by both disorders have a higher genetic correlation with risk genetic variants. These extra correlations of ADHD and DBD patients would probably correspond to alterations other authors had related to aggressive-related behaviours", notes Cormand.
"If we consider ADHD to be an open door to a negative trajectory, using genetic information to identify those individuals who are more vulnerable will have a strong impact on prevention, early detection and treatment, and will shed light on new research studies to find efficient therapies that can be specific for the disorder or shared between several disorders", notes Marta Ribasés.
The study, published in the journal Nature Communications, is a new science advance that will contribute to broaden the genetic landscape of ADHD comorbidities (that is, the series of pathologies that are correlated with this disorder). From a clinical perspective, knowing the psychiatric alterations that share genetics is a step forward, because it will enable the prediction of potential secondary complications over the life of those individuals with ADHD.
"These results allow us to better understand the origins of DBDs associated with ADHD and provide better information to the family members about this disorder", concludes Josep Antoni Ramos Quiroga, head of the Psychiatry Service of Hospital Vall d'Hebron and the Research Group on Mental Health Psychiatry and Addictions at VHIR.
INFORMATION:
Since Wilhelm Röntgen discovered them in 1895, X-rays have become a staple of medical imaging. In fact, barely a month after Röntgen's famous paper was published, doctors in Connecticut took the first ever radiograph of a boy's broken wrist.
There has been a lot of progress since. Aside from radiographs, which most people have taken at least once in their lives, today's X-ray medical uses includes fluoroscopy, radiotherapy for cancer, and computer tomography (CT), which takes multiple X-ray scans of the body from different angles and then combines them in a computer to generate ...
The international research collaboration involving the research team led by evolutionary biologist Professor Axel Meyer at the University of Konstanz and researchers from China and Singapore was able to identify factors that led to the success of the seahorse from a developmental biology perspective: its quickness to adapt by, for example, repeatedly evolving spines in the skin and its fast genetic rates of evolution. The results will be published on 17 February 2021 in Nature Communications.
Seahorses of the genus Hippocampus emerged about 25 million years ago in the Indo-Pacific region from pipefish, ...
COLUMBUS, Ohio - Though Ohio never formally enacted a so-called "heartbeat bill" banning abortions after six weeks of gestation, legislative and legal actions appear to have fueled beliefs that abortion is illegal in the state, a new study has found.
One in 10 Ohio women surveyed for the study thought abortion was prohibited. The percentage with that belief increased from 5% to 16% during the study period, corresponding to sustained activity to limit abortions from fall of 2018 through summer of 2019. The study appears in the American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology.
Maria Gallo, the study's lead author and a professor of epidemiology at The Ohio State University, said repeated legislative attempts at extreme restrictions on abortion, the veto by ...
In Switzerland and other European countries, drug prices are regulated to ensure affordable access to drugs. In the last few years, many European countries have introduced rebate schemes for drugs. In most cases, however, the rebates negotiated with the manufacturer are confidential. This means that a country basically has two prices for a drug: an official, higher price and an actual, lower price. Price comparisons of drugs between countries is frequently based on the higher price. Switzerland too has introduced such rebates, which are often confidential, and plans to anchor this practice in the regulation. The Federal Social ...
Scientists have little understanding of the role fishes play in the global carbon cycle linked to climate change, but a Rutgers-led study found that carbon in feces, respiration and other excretions from fishes - roughly 1.65 billion tons annually - make up about 16 percent of the total carbon that sinks below the ocean's upper layers.
Better data on this key part of the Earth's biological pump will help scientists understand the impact of climate change and seafood harvesting on the role of fishes in carbon flux, according to the study - the first of its kind - in the journal Limnology and Oceanography. Carbon flux means the movement of carbon in the ocean, including from the surface to the deep sea - the focus of this study.
"Our study is the first to review ...
Robotic clothing that is entirely soft and could help people to move more easily is a step closer to reality thanks to the development of a new flexible and lightweight power system for soft robotics.
The discovery by a team at the University of Bristol could pave the way for wearable assist devices for people with disabilities and people suffering from age-related muscle degeneration. The study is published today [17 February] in Science Robotics.
Soft robots are made from compliant materials that can stretch and twist. These materials can be made into artificial muscles that contract when air is pumped into them. The softness of these muscles makes then suited to powering assistive clothing. Until now, however, these ...
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. -- Scientists used accelerometers to track daily activity levels for a week in 89 adults with obesity or overweight and, in a series of tests, measured their ability to multitask and maintain their attention despite distractions. The study revealed that individuals who spent more sedentary time in bouts lasting 20 minutes or more were less able to overcome distractions.
Reported in the International Journal of Obesity, the research adds to the evidence linking sedentary behaviors and cognition, said University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign kinesiology and ...
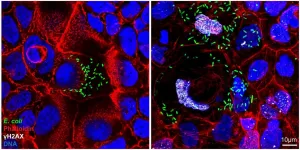
Escherichia coli bacteria are constitutive members of the human gut microbiota. However, some strains produce a genotoxin called colibactin, which is implicated in the development of colorectal cancer. While it has been shown that colibactin leaves very specific changes in the DNA of host cells that can be detected in colorectal cancer cells, such cancers take many years to develop, leaving the actual process by which a normal cell becomes cancerous obscure. The group of Thomas F. Meyer at the Max Planck Institute for Infection Biology in Berlin together with their collaborators have now been able to "catch colibactin in the act" of inducing genetic changes that are characteristic of colorectal cancer cells and cause a transformed ...
Scientists at Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health developed a method using a DNA biomarker to easily screen pregnant women for harmful prenatal environmental contaminants like air pollution linked to childhood illness and developmental disorders. This approach has the potential to prevent childhood developmental disorders and chronic illness through the early identification of children at risk.
While environmental factors--including air pollutants--have previously been associated with DNA markers, no studies to date have used DNA markers to flag environmental exposures in children. Study results are published ...
Women who received physical therapy after undergoing a cesarean section had significantly improved outcomes compared to those who did not according to a new study from University of Missouri Health Care.
"C-section is one of the most commonly performed inpatient procedures, and women who require C-section instead of a spontaneous vaginal delivery are at least twice as likely to suffer low back and pelvic pain," said study author Jennifer Stone, DPT, of MU Health Care's Mizzou Therapy Services. "Our goal was to evaluate the impact of comprehensive physical therapy on recovery following a cesarean birth."
Stone's study recruited 72 women who delivered by cesarean section ...