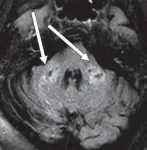
COVID-19 associated with leukoencephalopathy on brain MRI
COVID-19-related disseminated leukoencephalopathy represents an important differential consideration in patients with neurologic manifestations of coronavirus disease
2021-02-17
(Press-News.org) Leesburg, VA, February 17, 2021--According to an open-access article in ARRS' American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), COVID-19-related disseminated leukoencephalopathy (CRDL) represents an important--albeit uncommon--differential consideration in patients with neurologic manifestations of coronavirus disease (COVID-19).
"Increasingly," wrote Colbey W. Freeman and colleagues from the University of Pennsylvania, "effects of COVID-19 on the brain are being reported, including acute necrotizing encephalopathy, infarcts, microhemorrhage, acute disseminated encephalomyelitis, and leukoencephalopathy."
Among the 2,820 patients with COVID-19 admitted to the authors' institution between March 1 and June 18, 2020, 59 (2.1%) underwent brain MRI. Three (5.1%) had known white matter lesions from multiple sclerosis, 23 (39.0%) had white matter lesions of small vessel ischemic disease, six (10.2%) had acute infarcts, four (6.8%) had subacute infarcts, four (6.8%) had chronic infarcts, one (1.7%) had abnormal basal ganglia signal from hypoxemia, two (3.4%) had microhemorrhage in association with chronic infarcts, and two (3.4%) had microhemorrhage associated with acute or subacute infarcts.
Six patients (10.2%; four women, two men; age range, 41-86 years) had neuroimaging findings suggestive of CRDL--"characterized by extensive confluent or multifocal white matter lesions (with characteristics and locations atypical for other causes), microhemorrhages, diffusion restriction, and enhancement," Freeman et al. explained. Hypertension (4/6, 66.7%) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (3/6, 50.0%) were common comorbidities.
Reiterating that no established criteria exist for defining CRDL, "our patients had white matter lesions atypical for other causes," as well as "involvement of the bilateral middle cerebellar peduncles and corpus callosum," the authors of this AJR article concluded.
INFORMATION:
Founded in 1900, the American Roentgen Ray Society (ARRS) is the first and oldest radiological society in North America, dedicated to the advancement of medicine through the profession of radiology and its allied sciences. An international forum for progress in medical imaging since the discovery of the x-ray, ARRS maintains its mission of improving health through a community committed to advancing knowledge and skills with an annual scientific meeting, monthly publication of the peer-reviewed American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), quarterly issues of InPractice magazine, AJR Live Webinars and Podcasts, topical symposia, print and online educational materials, as well as awarding scholarships via The Roentgen Fund®.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-17
When materials reach extremely small size scales, strange things begin to happen. One of those phenomena is the formation of mesocrystals.
Despite being composed of separate individual crystals, mesocrystals come together to form a larger, fused structure that behaves as a pure, single crystal. However, these processes happen at scales far too small for the human eye to see and their creation is extremely challenging to observe.
Because of these challenges, scientists had not been able to confirm exactly how mesocrystals form.
Now new research by a Pacific ...
2021-02-17
A considerable portion of the efforts to realize a sustainable world has gone into developing hydrogen fuel cells so that a hydrogen economy can be achieved. Fuel cells have distinctive advantages: high energy-conversion efficiencies (up to 70%) and a clean by-product, water. In the past decade, anion exchange membrane fuel cells (AEMFC), which convert chemical energy to electrical energy via the transport of negatively charged ions (anions) through a membrane, have received attention due to their low-cost and relative environment friendliness compared ...
2021-02-17
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. -- Researchers who focus on fat know that some adipose tissue is more prone to inflammation-related comorbidities than others, but the reasons why are not well understood. Thanks to a new analytical technique, scientists are getting a clearer view of the microenvironments found within adipose tissue associated with obesity. This advance may illuminate why some adipose tissues are more prone to inflammation - leading to diseases like type 2 diabetes, cancer and cardiovascular disorders - and help direct future drug therapies to treat obesity.
In a new study, University of Illinois ...
2021-02-17
A short-lived resurgence in the emission of ozone depleting pollutants in eastern China will not significantly delay the recovery of Earth's protective "sunscreen" layer, according to new research published Feb. 10 in Nature.
Stratospheric ozone, also known as Earth's ozone layer, helps shield us from the Sun's harmful Ultraviolet (UV) rays. Compounds like CFC-11 (Trichlorofluoromethane, also known as Freon-11), a chemical once considered safe and widely used as a refrigerant and in the production of insulation for buildings, rise to the stratosphere after emission on Earth's surface. Once in the atmosphere, CFC's are broken down by the UV light and result in the destruction of ozone molecules, both reducing stratospheric ozone concentrations globally ...
2021-02-17
A neural network system that analyzes photographs can rank and distinguish suspicious, potentially precancerous skin lesions, which can turn into the deadly skin malignancy melanoma if not caught and removed early. The system accurately scoped out suspicious lesions from 68 patients in a manner that mostly matched tried-and-true evaluations from dermatologists. The results suggest the platform could help clinicians spot suspicious lesions during clinical visits faster and on a larger scale, potentially allowing for earlier diagnosis and treatment. Melanoma is ...
2021-02-17
Understanding the molecular biology of brain tumors is key to prognosis and treatment said Le Bonheur Neuroscience Institute Co-Director Frederick Boop, MD, in his presentation "How Molecular Biology Impacts Clinical Practice" at the International Society for Pediatric Neurosurgery (ISPN) 2020 Virtual Meeting.
"Historically we have depended on what we see under a microscope to differentiate tumor types and determine prognosis and therapy," said Boop. "We know now that what we see doesn't necessarily predict how these tumors are going to behave."
Physicians are able to send a piece of a child's tumor to FoundationOne, an FDA-approved tissue-based broad companion diagnostic (CDx) for solid tumors, which provides the genomic alterations of that particular tumor. ...
2021-02-17
A new UBC Okanagan study finds children not only reap the benefits of working with therapy dogs-they enjoy it too.
"Dog lovers often have an assumption that canine-assisted interventions are going to be effective because other people are going to love dogs," says Nicole Harris, who conducted this research while a master's student in the School of Education. "While we do frequently see children improve in therapy dog programs, we didn't have data to support that they enjoyed the time as well."
Harris was the lead researcher in the study that explored how children reacted while participating in a social skill-training program with therapy dogs.
The research saw 22 children from the Okanagan Boys and Girls ...
2021-02-17
Resistance to tangle formation may help preserve memory
SuperAgers have fewer tangles than normally aging individuals
Future research to see how SuperAgers are protected
CHICAGO - A new Northwestern Medicine study showed cognitive SuperAgers have resistance to the development of fibrous tangles in a brain region related to memory and which are known to be markers of Alzheimer's disease.
The tangles are made of the tau protein which forms structures that transport nutrients within the nerve cell. These tangles disrupt the cell's transport system, ...
2021-02-17
Nearly a half-million people a year die from sudden cardiac death (SCD) in the U.S. -- the result of malfunctions in the heart's electrical system.
A leading cause of SCD in young athletes is arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy (ACM), a genetic disease in which healthy heart muscle is replaced over time by scar tissue (fibrosis) and fat.
Stephen Chelko, an assistant professor of biomedical sciences at the Florida State University College of Medicine, has developed a better understanding of the pathological characteristics behind the disease, as well as promising avenues for ...
2021-02-17
The trial found that using sensor-based asthma inhalers may improve control of the condition and improve the quality of life for caregivers.
Greatest gains were among non-Hispanic Black participants, who experience more frequent and severe asthma than other groups.
Based on the study results, this asthma intervention should be considered for use by primary care, allergy and pulmonary care providers, to help engage diverse populations of pediatric asthma patients and their caregivers.
CHICAGO (February 17, 2021) -- Sensor-based inhalers integrated into health care providers' clinical workflows may help improve medication adherence and support children with asthma - and their families - to more effectively manage this condition, according ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] COVID-19 associated with leukoencephalopathy on brain MRI
COVID-19-related disseminated leukoencephalopathy represents an important differential consideration in patients with neurologic manifestations of coronavirus disease