(Press-News.org) Dogs are generally considered the first domesticated animal, while its ancestor is generally considered to be the wolf, but where the Australian dingo fits into this framework is still debated, according to a retired Penn State anthropologist.
"Indigenous Australians understood that there was something different about the dingoes and the colonial dogs," said Pat Shipman, retired adjunct professor of anthropology, Penn State. "They really are, I think, different animals. They react differently to humans. A lot of genetic and behavioral work has been done with wolves, dogs and dingoes. Dingoes come out somewhere in between."
Wolves, dogs and dingoes are all species of the canidae family and are called canids. In most animals, hybridization between closely related species does not happen, or like female horses and male donkeys, produce mules -- usually non-fertile offspring. However, many canid species, including wolves, dingoes and dogs, can interbreed and produce fertile offspring. Defining species boundaries in canids becomes more difficult.
Domestic dogs came to the Australian continent in 1788 with the first 11 ships of convicts, but dingoes were already there, as were aboriginal Australians who arrived on the continent about 65,000 years ago. A large portion of dingoes in Australia today have domestic dog in their ancestry, but dingoes came to Australia at least 4,000 years ago according to fossil evidence. Shipman believes that date may be even earlier, but no fossils have yet been found.
"Part of the reason I'm so fascinated with dingoes is that if you see a dingo through American eyes you say, 'that's a dog,'" said Shipman. "In evolutionary terms, dingoes give us a glimpse of what started the domestication process."
Shipman reports her analysis of wolves, dogs and dingoes in a January 2021 special issue of the Anatomical Record.
Dingoes, and the closely related New Guinea singing dogs, look like the default definition of dog, but they are not dogs.
"There is a basic doggy look to dingoes," said Shipman.
Genetically and behaviorally they differ from dogs and are more like wolves in their inability to digest starches and their relationships with humans.
Most domestic dogs evolved along with humans as humans became agriculturalists and moved to a diet containing large amounts of starch, whether from maize, rice, potatoes or wheat. Their genome changed to allow the digestion of these starches. Dingoes, like wolves, have very few of the genes for starch digestion.
While indigenous Australians stole dingo puppies from their dens and raised them, these puppies generally left human homes at maturity and went off to breed and raise offspring. The ability to closely bond with humans is limited in dingoes, although present in dogs. Native Australians also did not manipulate dingo breeding, which is a hallmark of domestication.
Dingoes are also well-adapted to the Australian outback and fare well in that environment. Domestic dogs that become feral do not survive well in the outback.
"Aboriginal Australians were not well-regarded as holders of knowledge or special skill when Europeans came to the continent," said Shipman. "So, no one thought to ask them about dingoes. Even recently, asking aboriginals for their scientific or behavioral knowledge really was not common."
However, aboriginal Australians have a long history of living with dingoes in their lives. Many people argue that dingoes are just dogs -- strange dogs, but just dogs, said Shipman. But, according to aboriginals, dingoes are not dogs.
With dingoes showing behaviors somewhere between wolves and dogs and exhibiting only slight genetic ability to consume starchy foods or tolerate captivity, Shipman concluded that "A dingo is a wolf on its way to becoming a dog, that never got there."
INFORMATION:
Scientists from the Skoltech Center for Computational and Data-Intensive Science and Engineering (CDISE) and the Skoltech Digital Agriculture Laboratory and their collaborators from the German Aerospace Center (DLR) have developed an artificial intelligence (AI) system that enables processing images from autonomous greenhouses, monitoring plant growth and automating the cultivation process. Their research was published in the journal IEEE Sensors.
Modern technology has long become a fixture in all spheres of human life on Earth. Reaching out to other planets is a new challenge for humankind. Since greenhouses are likely to be the only source ...
BOSTON - Use of a cosmetic laser invented at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) may improve the effectiveness of certain anti-tumor therapies and extend their use to more diverse forms of cancer. The strategy was tested and validated in mice, as described in a study published in Science Translational Medicine.
Immune checkpoint inhibitors are important medications that boost the immune system's response against various cancers, but only certain patients seem to benefit from the drugs. The cancer cells of these patients often have multiple mutations that can be recognized as foreign by the immune system, thereby inducing an inflammatory response.
In an attempt to expand the benefits of immune checkpoint inhibitors ...
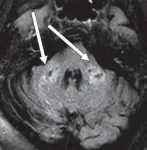
Leesburg, VA, February 17, 2021--According to an open-access article in ARRS' American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), COVID-19-related disseminated leukoencephalopathy (CRDL) represents an important--albeit uncommon--differential consideration in patients with neurologic manifestations of coronavirus disease (COVID-19).
"Increasingly," wrote Colbey W. Freeman and colleagues from the University of Pennsylvania, "effects of COVID-19 on the brain are being reported, including acute necrotizing encephalopathy, infarcts, microhemorrhage, acute disseminated encephalomyelitis, and leukoencephalopathy."
Among the 2,820 patients with COVID-19 admitted to the authors' institution between ...
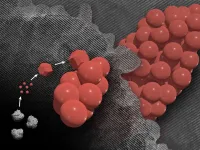
When materials reach extremely small size scales, strange things begin to happen. One of those phenomena is the formation of mesocrystals.
Despite being composed of separate individual crystals, mesocrystals come together to form a larger, fused structure that behaves as a pure, single crystal. However, these processes happen at scales far too small for the human eye to see and their creation is extremely challenging to observe.
Because of these challenges, scientists had not been able to confirm exactly how mesocrystals form.
Now new research by a Pacific ...
A considerable portion of the efforts to realize a sustainable world has gone into developing hydrogen fuel cells so that a hydrogen economy can be achieved. Fuel cells have distinctive advantages: high energy-conversion efficiencies (up to 70%) and a clean by-product, water. In the past decade, anion exchange membrane fuel cells (AEMFC), which convert chemical energy to electrical energy via the transport of negatively charged ions (anions) through a membrane, have received attention due to their low-cost and relative environment friendliness compared ...
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. -- Researchers who focus on fat know that some adipose tissue is more prone to inflammation-related comorbidities than others, but the reasons why are not well understood. Thanks to a new analytical technique, scientists are getting a clearer view of the microenvironments found within adipose tissue associated with obesity. This advance may illuminate why some adipose tissues are more prone to inflammation - leading to diseases like type 2 diabetes, cancer and cardiovascular disorders - and help direct future drug therapies to treat obesity.
In a new study, University of Illinois ...
A short-lived resurgence in the emission of ozone depleting pollutants in eastern China will not significantly delay the recovery of Earth's protective "sunscreen" layer, according to new research published Feb. 10 in Nature.
Stratospheric ozone, also known as Earth's ozone layer, helps shield us from the Sun's harmful Ultraviolet (UV) rays. Compounds like CFC-11 (Trichlorofluoromethane, also known as Freon-11), a chemical once considered safe and widely used as a refrigerant and in the production of insulation for buildings, rise to the stratosphere after emission on Earth's surface. Once in the atmosphere, CFC's are broken down by the UV light and result in the destruction of ozone molecules, both reducing stratospheric ozone concentrations globally ...
A neural network system that analyzes photographs can rank and distinguish suspicious, potentially precancerous skin lesions, which can turn into the deadly skin malignancy melanoma if not caught and removed early. The system accurately scoped out suspicious lesions from 68 patients in a manner that mostly matched tried-and-true evaluations from dermatologists. The results suggest the platform could help clinicians spot suspicious lesions during clinical visits faster and on a larger scale, potentially allowing for earlier diagnosis and treatment. Melanoma is ...
Understanding the molecular biology of brain tumors is key to prognosis and treatment said Le Bonheur Neuroscience Institute Co-Director Frederick Boop, MD, in his presentation "How Molecular Biology Impacts Clinical Practice" at the International Society for Pediatric Neurosurgery (ISPN) 2020 Virtual Meeting.
"Historically we have depended on what we see under a microscope to differentiate tumor types and determine prognosis and therapy," said Boop. "We know now that what we see doesn't necessarily predict how these tumors are going to behave."
Physicians are able to send a piece of a child's tumor to FoundationOne, an FDA-approved tissue-based broad companion diagnostic (CDx) for solid tumors, which provides the genomic alterations of that particular tumor. ...
A new UBC Okanagan study finds children not only reap the benefits of working with therapy dogs-they enjoy it too.
"Dog lovers often have an assumption that canine-assisted interventions are going to be effective because other people are going to love dogs," says Nicole Harris, who conducted this research while a master's student in the School of Education. "While we do frequently see children improve in therapy dog programs, we didn't have data to support that they enjoyed the time as well."
Harris was the lead researcher in the study that explored how children reacted while participating in a social skill-training program with therapy dogs.
The research saw 22 children from the Okanagan Boys and Girls ...