(Press-News.org) Its muscular body shape and large pectoral fins are perfect for long-distance travel, yet movement patterns of the whitespotted eagle ray (Aetobatus narinari) remain a mystery. Researchers from Florida Atlantic University's Harbor Branch Oceanographic Institute in collaboration with Mote Marine Laboratory & Aquarium, the University of Florida and the Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission, are the first to conduct a multiyear study examining large-scale movements of whitespotted eagle rays in United States waters.
Between 2016 and 2018, scientists fitted 54 rays with acoustic transmitters and tracked them using collaborative acoustic telemetry networks. The rays were tagged along both the Gulf of Mexico and Atlantic coasts of Florida, which differ in environmental characteristics. Scientists compared rays' movement patterns between the Atlantic and Gulf coasts and gathered data on migratory routes, seasonality and habitat use. Their findings suggest that potential sub-population structuring may be occurring within Florida more than previously thought and have significant conservation and adaptive management implications for this protected species.
Results of the study, published in the journal Marine Biology, reveal striking differences in travel patterns on the Atlantic coast compared to the Gulf coast. The majority of Gulf coast whitespotted eagle rays preferred to "spread their wings," exhibiting migratory and transient behaviors, while most Atlantic coast tagged rays were "homebodies" and remained a resident within the Indian River Lagoon. Atlantic coast rays spent greater than five times the amount of time inshore, regardless of maturity or sex, than Gulf coast rays.
"Although tagged at similar latitudes, whitespotted eagle rays exhibited coastline-specific movements. The rays on the Gulf coast conduct repetitive annual migration patterns, heading south from Sarasota starting in fall and returning to the area in early spring," said Breanna DeGroot, M.S., first author and research coordinator, FAU Harbor Branch.
DeGroot worked on the study with co-author Matt Ajemian, Ph.D., principal investigator, an assistant research professor at FAU Harbor Branch and head of the Fisheries Ecology and Conservation (FEC) Lab, who supervised the study.
"This behavior is likely driven by a combination of environmental factors, but most notably temperature. In addition, the expansive, shallow shelf on the Gulf coast may provide additional habitat, enabling rays to move over larger distances along nearshore migratory corridors and lessen their reliance on inshore estuaries," said Ajemian.
On both coastlines, water temperatures during times when rays were present were significantly warmer (at least 27.8 degrees Celsius) compared to temperatures when rays were absent (below 24.9 degrees Celsius), suggesting it may be a major abiotic factor influencing migration patterns. Ontogenetic shifts in habitat use were evident along the Atlantic coast in the Indian River Lagoon, but not along the Gulf coast. Immature rays spent significantly more time (about 91.5 percent) inside the Indian River Lagoon compared to mature counterparts (about 60.2 percent).
"Most of the rays we tagged on Florida's Atlantic coast resided in the same area where they were originally tagged, which increases their susceptibility to local stressors like persistent environmental impacts in the Indian River Lagoon," said DeGroot. "Moreover, immature rays spent a significantly larger proportion of time inside the confines of the lagoon. This is especially disconcerting because we found no evidence of neonate or young-of-the-year rays leaving the lagoon throughout the entire three-year study."
The consistent presence of rays in the Indian River Lagoon throughout the study suggests that it serves as parturition grounds and nursery habitat for rays. As males and females were equally resident to the Sebastian portion of the Indian River Lagoon, this area is likely an important feeding ground, nursery habitat, mating location, pupping ground, or serves a combination of these roles.
"This information about year-round or seasonal residency and longer distance migrations would not be possible without the collaborative data sharing of the acoustic telemetry networks such as iTAG and the FACT Network," said Kim Bassos-Hull, M.Sc., co-author and senior biologist with Mote Marine Lab's Sharks & Rays Conservation Research Program.
According to Ajemian, there is a need for a better understanding of how extreme weather events such as hurricanes and fluctuations in environmental factors such as red tide and harmful algal blooms may impact ecologically important large-bodied mesopredators like the whitespotted eagle ray, because the frequency of these events is predicted to increase yet the potential alterations on the ecosystem remain unknown.
"This is a critical issue that requires increased tracking infrastructure and new analytical approaches," said Susan Lowerre-Barbieri, Ph.D., co-author, University of Florida and Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission, who led an iTAG workshop on this topic.
Study co-authors are Krystan A. Wilkinson, Ph.D., Mote Marine Lab's Sharks & Rays Conservation Research Program and the Chicago Zoological Society's Sarasota Dolphin Research Program; and Gregg R. Poulakis, Ph.D., Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission.
"I'm looking forward to adding more pieces to the eagle ray puzzle in the coming years as these animals get detected for years to come along both coasts of the state and beyond," said Poulakis.
INFORMATION:
Rays were tagged using handling permits: Gulf coast, FWC SAL-16-1140-SRP; Atlantic coast, FWC SAL-16-1785-SRP.
This work was funded by the Guy Harvey Ocean Foundation, Vero Beach Rotary Club, Indian River Graduate Research Fellowship (2017, 2018), "3-min Thesis Award," Specialty License Plate (Save Our Seas) fund administered by the Harbor Branch Oceanographic Institute Foundation, Mote Scientific Foundation, Georgia Aquarium, and the NOAA-NMFS Species Recovery Grants to States (Section 6 Program).
- FAU -
About Harbor Branch Oceanographic Institute:
Founded in 1971, Harbor Branch Oceanographic Institute at Florida Atlantic University is a research community of marine scientists, engineers, educators and other professionals focused on Ocean Science for a Better World. The institute drives innovation in ocean engineering, at-sea operations, drug discovery and biotechnology from the oceans, coastal ecology and conservation, marine mammal research and conservation, aquaculture, ocean observing systems and marine education. For more information, visit http://www.fau.edu/hboi.
About Florida Atlantic University:
Florida Atlantic University, established in 1961, officially opened its doors in 1964 as the fifth public university in Florida. Today, the University serves more than 30,000 undergraduate and graduate students across six campuses located along the southeast Florida coast. In recent years, the University has doubled its research expenditures and outpaced its peers in student achievement rates. Through the coexistence of access and excellence, FAU embodies an innovative model where traditional achievement gaps vanish. FAU is designated a Hispanic-serving institution, ranked as a top public university by U.S. News & World Report and a High Research Activity institution by the Carnegie Foundation for the Advancement of Teaching. For more information, visit http://www.fau.edu.
Doha, Qatar - (February 23, 2021) - A group of researchers at Qatar Foundation have reported the first and largest genetic association study in the Middle East, that has been published online in Nature Communications - a leading a peer-reviewed, open access, scientific journal published by Nature Research.
The study titled "Whole genome sequencing in the Middle Eastern Qatari population identifies genetic associations with 45 clinically relevant traits" highlights a vital piece of information wherein now there is a better understanding of the genetic risk factors that are specific to the Arab population, including those that are shared with other ethnicities.
Qatar was among the first countries to launch its own large-scale, national genome project. Qatar Genome ...
A recent genetic study at the University of Helsinki provides new information on the occurrence of a DVL2 gene defect associated with a screw tail and its relevance to canine constitution and health. The variant was found in several Bulldog and Pit Bull type breeds, and it was shown to result in caudal vertebral anomalies and shortening of the muzzle. The DLV2 variant may also affect the development of the heart.
Dog breeding is often focused on appearance. In some breeds, the ideal body shape is bulky, with a broad head and short muzzle, short legs and a very short and kinked tail, also known as a "screw tail". In a previous study in the United States, screw tail was linked to a variant in the DVL2 gene. The variant has become enriched ...
According to recent estimates, there will be roughly 10 billion people to feed in 2050. Agricultural production will need to increase by almost 56% to guarantee food security globally, without converting more land for agriculture (in line with environmental and climate targets). This unprecedented challenge has ushered in the era of "smart agriculture," which promises to revolutionize food production by combining agricultural techniques with information technology, automation, and artificial intelligence. This new era, called "Agriculture 4.0," could ensure sustainable food production for the entire world. However, as communities gradually embrace smart agriculture, it is important to understand how to manage the security and privacy risks associated with the integration of ...
Washington, DC / New Delhi, India - Researchers at CDDEP, in collaboration with leading experts in the field, have produced the "Infectious Diseases in the South-East Asia Region" report, which examines cross-boundary challenges in communicable disease control in countries in the South-and South-East Asia region. The report emphasizes infectious diseases related to other sources of disease burden in the region and communicates overall trends in the health and economic burden they impose.
Despite substantial progress in recent years, which has seen reductions in deaths from HIV and malaria and an increase ...
Researchers of the University of Helsinki have resolved for the first time, how the ultrafine particles of atmosphere effect on the climate and health.
Atmospheric air pollution kills more than 10,000 people every day. The biggest threat to human health has been assumed to be the mass accumulation of atmospheric particles with diameter smaller 2.5 μm: the higher the mass and loss of visibility, the bigger the threat.
The researchers of the Institute for Atmospheric and Earth System Research (INAR) at the University of Helsinki together with collaborators in China discovered that if we want to solve the accumulation of the biggest particles, we need to start with the smallest.
Until recent ...
A new study has for the first time explored the rate at which the world's largest fish, the endangered whale shark, can recover from its injuries. The findings reveal that lacerations and abrasions, increasingly caused through collisions with boats, can heal in a matter of weeks and researchers found evidence of partially removed dorsal fins re-growing.
This work, published in the journal Conservation Physiology, comes at a critical time for these large sharks, that can reach lengths of up to 18 metres. Other recent studies have shown that as their popularity within the wildlife tourism sector increases, so do interactions with humans and boat traffic. As a result, these ...
Huntington's disease is caused by a mutation in the Huntingtin gene (HTT), which appears in adults and features motor, cognitive and psychiatric alterations. The origin of this disease has been associated with the anomalous functioning of the mutated protein: mHTT, but recent data showed the involvement of other molecular mechanisms.
A new study conducted by the University of Barcelona has identified a type of ribonucleic acid (RNA) as a potential therapeutic target for the treatment of the disease. These are the small RNA, or sRNAs, molecules that do not code proteins but have important functions in the regulation of gene expression. According to the study, sRNAs would ...
X-ray scans revolutionised medical treatments by allowing us to see inside humans without surgery. Similarly, terahertz spectroscopy penetrates graphene films allowing scientists to make detailed maps of their electrical quality, without damaging or contaminating the material. The Graphene Flagship brought together researchers from academia and industry to develop and mature this analytical technique, and now a novel measurement tool for graphene characterisation is ready.
The effort was possible thanks to the collaborative environment enabled by the Graphene Flagship European consortium, with participation by scientists from Graphene Flagship partners DTU, Denmark, IIT, Italy, Aalto University, Finland, AIXTRON, UK, imec, Belgium, Graphenea, Spain, Warsaw ...
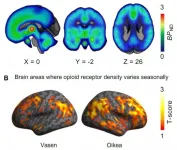
Seasons have an impact on our emotions and social life. Negative emotions are more subdued in the summer, whereas seasonal affective disorder rates peak during the darker winter months. Opioids regulate both mood and sociability in the brain.
In the study conducted at the Turku PET Centre, Finland, researchers compared how the length of daylight hours affected the opioid receptors in humans and rats.
"In the study, we observed that the number of opioid receptors was dependent on the time of the year the brain was imaged. The changes were most prominent in the brain regions that control emotions and sociability. The changes in the opioid receptors caused by the variation in the amount of daylight could be an important factor in seasonal affective disorder," ...
WASHINGTON -- Researchers have developed a new sensor that could allow practical and low-cost detection of low concentrations of methane gas. Measuring methane emissions and leaks is important to a variety of industries because the gas contributes to global warming and air pollution.
"Agricultural and waste industries emit significant amounts of methane," said Mark Zondlo, leader of the Princeton University research team that developed the sensor. "Detecting methane leaks is also critical to the oil and gas industry for both environmental and economic reasons because natural gas is mainly composed of methane."
In ...