Monoclonal antibodies against MERS coronavirus show promise in phase 1 NIH-sponsored trial
2021-02-23
(Press-News.org) WHAT:
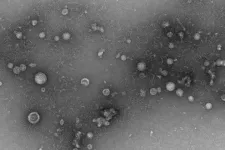
A randomized, placebo-controlled Phase 1 clinical trial of two monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) directed against the coronavirus that causes Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS) found that they were well tolerated and generally safe when administered simultaneously to healthy adults. The experimental mAbs, REGN3048 and REGN3051, target the MERS coronavirus (MERS CoV) spike protein used by the virus to attach to and infect target cells. The mAbs were discovered and developed by scientists at the biopharmaceutical company Regeneron, located in Tarrytown, New York. The trial was sponsored by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health.
The trial was the first to test the experimental antibodies
Hyperlink Code in people. Conducted at WCCT Global, a clinical trial site in California, the study enrolled 48 healthy adults, 36 of whom received the mAbs. All volunteers were followed for 121 days after receiving mAbs (or placebo) by intravenous infusion. No serious adverse events occurred.
In preclinical studies, investigators at Regeneron and the University of Maryland, College Park, also administered REGN3048 and REGN3051 sequentially and in combination to genetically modified mice that, unlike wild-type mice, can be infected with MERS CoV. When administered one day prior to coronavirus exposure, both REGN3048 and REGN3051 reduced the levels of virus later detected in the lungs, with co-administration providing more potent protective effects than either mAb alone. Similarly, co-administering the mAbs one day after MERS CoV exposure provided a therapeutic benefit in mice by lowering viral levels and lessening tissue damage in the lungs as compared to mice that received placebo.
Together, the findings from the clinical trial and the preclinical mouse studies "demonstrate the potential efficacy and utility of monoclonal antibody therapy for the prevention or treatment of MERS-CoV and lays the groundwork for the development of spike-targeted mAb therapies for other infectious disease threats, including SARS-CoV-2," which causes COVID-19, the authors conclude.
INFORMATION:
Additional information about the trial is available at clinicaltrials.gov using the identifier NCT03301090. The trial is funded through contract HHSN272201500005I.
ARTICLE:
S Sivapalasingam et al. Human monoclonal antibody cocktail for the treatment or prophylaxis of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV).
The Journal of Infectious Diseases DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jiab036 (2021).
WHO:
John Beigel, M.D., associate director for clinical research, Division of Microbiology and Infectious Diseases, NIAID, is available to discuss this study.
CONTACT:
To schedule interviews, please contact Anne A. Oplinger, (301) 402-1663, niaidnews@niaid.nih.gov.
NIAID conducts and supports research--at NIH, throughout the United States, and worldwide--to study the causes of infectious and immune-mediated diseases, and to develop better means of preventing, diagnosing and treating these illnesses. News releases, fact sheets and other NIAID-related materials are available on the NIAID website.
About the National Institutes of Health (NIH): NIH, the nation's medical research agency, includes 27 Institutes and Centers and is a component of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. NIH is the primary federal agency conducting and supporting basic, clinical, and translational medical research, and is investigating the causes, treatments, and cures for both common and rare diseases. For more information about NIH and its programs, visit http://www.nih.gov/.
NIH...Turning Discovery Into Health®
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-23
Inflammatory lung diseases such as asthma, COPD and, most recently, COVID-19, have proven difficult to treat. Current therapies reduce symptoms and do little to stop such diseases from continuing to damage the lungs. Much research into treating chronic inflammatory diseases has focused on blocking chemicals called cytokines, which trigger cascades of molecular events that fuel damaging inflammation.
Now, scientists at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have found that such cytokines can drive inflammation in more ways than previously understood, perhaps revealing new routes ...
2021-02-23
Using the symmetries of the systems, people can define various topological invariants to describe different topological states. The topological materials can be accurately discovered by calculating the topological invariants. Recently, researchers found that irreducible representations and compatibility relationships can be used to determine whether a material is topological nontrivial/trivial insulator (satisfying the compatibility relations) or topological semimetal (violating the compatibility relations), which leads to a large number of topological materials predicted by theoretical calculations. However, Weyl semimetals go beyond this paradigm because the existence of Weyl fermions does not need any symmetry protections (except for lattice translation symmetries). At present, ...
2021-02-23
Urban areas are on the rise and changing rapidly in form and function, with spillover effects on virtually all areas of the Earth. The UN estimates that by 2050, 68% of the world's population will reside in urban areas. In the inaugural issue of npj Urban Sustainability, a new Nature Partner Journal out today, a team of leading urban ecologists outlines a practical checklist to guide interventions, strategies, and research that better position urban systems to meet urgent sustainability goals.
Co-author Steward Pickett of Cary Institute of Ecosystem Studies explains, "Urban areas shape demographics, ...
2021-02-23
By Maria Fernanda Ziegler | Agência FAPESP – Yellow fever was the first human disease to have a licensed vaccine and has long been considered important to an understanding of how epidemics happen and should be combated. It was introduced to the Americas in the seventeenth century, and high death rates have resulted from successive outbreaks since then. Epidemics of yellow fever were associated with the slave trade, the US gold rush and settlement of the Old West, the Haitian Revolution, and construction of the Panama Canal, to cite only a few examples.
Centuries after the disease was first reported in the Americas, an international team of researchers will embark on a groundbreaking study to develop ...
2021-02-23
What should researchers do if they encounter a study participant who reports suicidal thoughts?
UIC College of Nursing associate professor Susan Dunn explores this question as lead author of "Suicide Risk Management Protocol for a Randomized Controlled Trial of Cardiac Patients Reporting Hopelessness," a paper published in the January/February edition of Nursing Research.
Suicide is ranked as the 10th leading cause of death for all ages in the U.S. and can be identified through clinical research, according to the paper.
Although suicide screening tools are widely available for patients in emergency, hospital and primary care settings and ...
2021-02-23
The environmental impacts of removing dingoes from the landscape are visible from space, a new UNSW Sydney study shows.
The study, recently published in Landscape Ecology, pairs 32 years' worth of satellite imagery with site-based field research on both sides of the Dingo Fence in the Strzelecki Desert.
The researchers found that vegetation inside the fence - that is, areas without dingoes - had poorer long-term growth than vegetation in areas with dingoes.
"Dingoes indirectly affect vegetation by controlling numbers of kangaroos and small mammals," says Professor Mike Letnic, senior author of the study and researcher at UNSW's Centre ...
2021-02-23
Since astronomers captured the bright explosion of a star on February 24, 1987, researchers have been searching for the squashed stellar core that should have been left behind. A group of astronomers using data from NASA space missions and ground-based telescopes may have finally found it.
As the first supernova visible with the naked eye in about 400 years, Supernova 1987A (or SN 1987A for short) sparked great excitement among scientists and soon became one of the most studied objects in the sky. The supernova is located in the Large Magellanic Cloud, a small companion galaxy to our own Milky Way, only about 170,000 light-years from Earth.
While astronomers watched debris ...
2021-02-23
Unlike the Higgs boson, discovered at CERN's Large Hadron Collider in 2012 after a 40-year quest, the new particle proposed by these researchers is so heavy that it could not be produced directly even in this collider
The University of Granada is among the participants in this major scientific advancement in Theoretical Physics, which could help unravel the mysteries of dark matter
Scientists from the University of Granada (UGR) and the Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (Germany) have recently published a study in which they endeavour to extend the Standard Model of particle physics (the equivalent of 'the periodic table' for particle physics) and answer some of the questions that this model is unable to answer. Such puzzles include: What ...
2021-02-23
This study, published recently in the international journal Insects, was conducted by researchers from the University of Granada, the Doñana Biological Station, and the Biomedical Research Networking Centre for Epidemiology and Public Health (CIBERESP)
Researchers from the University of Granada (UGR), the Doñana Biological Station (EBD-CSIC), and the Biomedical Research Networking Centre for Epidemiology and Public Health (CIBERESP) have carried out the most comprehensive study to date of the eating patterns of the tiger mosquito (Aedes albopictus) and other invasive species of the same genus in Europe. The results of the study were recently published in the international journal Insects.
This research, which reviews ...
2021-02-23
With a survival rate of only five years, the most common and aggressive form of primary brain tumor, glioblastoma multiforme, is notoriously hard to treat using current regimens that rely on surgery, radiation, chemotherapy and their combinations.
"Two of the major challenges in the treatment of gliomas include poor transport of chemotherapeutics across the blood brain barrier and undesired side effects of these therapeutics on healthy tissues," said Sheereen Majd, assistant professor of biomedical engineering at the University of Houston. "To get enough medicine across the blood brain barrier, a high dosage ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Monoclonal antibodies against MERS coronavirus show promise in phase 1 NIH-sponsored trial