(Press-News.org) With the voice commands "Alexa Skills," users can load numerous extra functions onto their Amazon voice assistant. However, these Skills can often have security gaps and data protection problems, as a team of researchers from the Horst Görtz Institute for IT Security at Ruhr-Universität Bochum (RUB) and North Carolina State University discovered, together with a former PhD student who started to work for Google during the project. They will present their work at the "Network and Distributed System Security Symposium (NDSS)" conference on 24 February 2021.
More than 90,000 Skills analyzed
In their study, the researchers around Christopher Lentzsch and Dr. Martin Degeling studied first-time the ecosystem of Alexa Skills. These voice commands are developed not only by the U.S. tech company Amazon itself but also by external providers. Users can download them at a store operated by Amazon directly, and in some cases, they are also activated automatically by Amazon.
The researchers obtained and analyzed 90,194 Skills from the stores in seven country platforms. They found significant deficiencies for safe use. "A first problem is that Amazon has partially activated Skills automatically since 2017. Previously, users had to agree to the use of each Skill. Now they hardly have an overview of where the answer Alexa gives them comes from and who programmed it in the first place," explains Dr. Martin Degeling from the RUB Chair of System Security. Unfortunately, it is often unclear which Skill is activated at what time. For example, if you ask Alexa for a compliment, you can get a response from 31 different providers, but it's not immediately clear which one is automatically selected. Data that is needed for the technical implementation of the commands can be unintentionally forwarded to external providers.
Publishing new Skills under a false identity
"Furthermore, we were able to prove that Skills can be published under a false identity. Well-known automotive companies, for example, make voice commands available for their smart systems. Users download these believing that the company itself has provided these Skills. But that is not always the case," says Martin Degeling. Although Amazon checks all Skills offered in a certification process, this so-called Skill squatting, i.e., the adoption of already existing provider names and functions, is often not noticeable.
"In an experiment, we were able to publish Skills in the name of a large company. Valuable information from users can be tapped here," explains the researcher. So if an automotive supplier has not yet developed a Skill for its smart system in the car to turn up or turn down the music in the car, for example, attackers would be able to do so under the supplier's name. "They can exploit users' trust in the well-known name and in Amazon to tap into personal information such as location data or user behaviour," Degeling says. Criminals, however, could not directly tap encrypted data or change commands with malicious intent in this process to manipulate the smart car, for example to open the car doors.
Circumventing Amazon's security check
The researchers also identified another security risk: "Our study also showed that the Skills could be changed by the providers afterward," explains Christopher Lentzsch from the RUB Chair of Information and Technology Management. This vulnerability places the security of the previous certification process on the part of Amazon into another perspective. "Attackers could reprogram their voice command after a while to ask for users' credit card data, for example," Lentzsch says. Amazon's testing usually catches such prompts and does not allow them - the trick of changing the program afterward can bypass this control. By trusting the abused provider name and Amazon, numerous users could be fooled by this trick.
Unsufficient data protection declarations
In addition to these security risks, the research team also identified significant lacks in the general data protection declarations for the Skills. For example, only 24.2 percent of the Skills have a so-called Privacy Policy at all, and even fewer in the particularly sensitive areas of "Kids" and "Health and Fitness." "Especially here, there should be strong improvements," Degeling says.
Amazon has confirmed some of the problems to the research team and says it is working on countermeasures.
INFORMATION:
Technical details and the scientific paper are available from the researchers on the website http://www.alexa-skill-analysis.org.
Torino, February 24, 2021 - The eukaryotic cell is the basic unit of animals and plants. At the microscope, it looks highly structured and subdivided in many membrane-bound compartments. Each compartment has a specific function, and its membrane is populated by specific molecules. How does the cell preserve this amazing internal order, and (in the absence of pathologies) does not degrade into a shapeless bunch of molecules? Such degradation is countered by a continuous process of molecule sorting by which similar molecules are collected and dispatched to the "right" destinations, similarly to what happens when a house is kept clean and ...
COVID-19, the disease caused by the pandemic coronavirus SARS-CoV-2, is primarily regarded as a respiratory infection. Yet the virus has also become known for affecting other parts of the body in ways not as well understood, sometimes with longer-term consequences, such as heart arrhythmia, fatigue and "brain fog."
Researchers at University of California San Diego School of Medicine are using stem cell-derived organoids -- small balls of human cells that look and act like mini-organs in a laboratory dish -- to study how the virus interacts with various organ systems and to develop therapies to block infection.
"We're finding that SARS-CoV-2 doesn't infect the entire body in the same way," said Tariq Rana, PhD, professor ...
If Affordable Care Act protections for pre-existing condition coverage are no longer available, the coronavirus pandemic would leave many Americans - a disproportionate number of whom are people of color - without health insurance, a new Oregon Health & Science University study indicates.
Published in the Journal of the American Board of Family Medicine, the study's findings reveal a third of the more than 7,500 COVID-19 patients who received care at U.S. community health centers between March and October 2020 did not have a pre-existing condition prior to contracting the novel ...
UCLA RESEARCH BRIEF
Enrique Rivero
FINDINGS
Older people correctly ascertained basic information such as dosage and duration of use for more than 70% of the medications they were prescribed, regardless of whether their physician explained it during an office visit. But when physicians failed to verbally provide information about potential side effects, people incorrectly assumed that about 55% of their prescribed medications had none. Even when physicians did discuss possible side effects, their patients incorrectly assumed there were no side effects for 22% of the medications.
BACKGROUND
There is a shortage of data about how well people understand basic information about the medications they are prescribed. This information ...
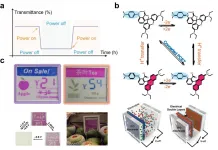
The development of low-energy-consumption and user-friendly electronic displays has become a long-term goal for future global sustainable development. Bistable electronic display, which requires very little electric drive to turn pages without consuming additional power to continuously display information/images, is one of the very good potential alternatives. Reflective display technologies with partial/complete bistable characteristics include e-ink, cholesteric liquid crystal, and electrochromic technologies, etc. They display information in light reflection mode, which can still be read under high-brightness outdoor sunlight and relatively dark indoor environments. It is also very friendly to the ...
The yellow fever mosquito (Aedes aegypti) is a main vector of deadly diseases like dengue fever, chikungunya, and the Zika virus, which result in hundreds of thousands of deaths worldwide each year. Because Ae. aegypti prefers to bite humans and there are no vaccines for many of these diseases they carry, developing methods to control these insects is imperative in the fight to control illness.
In a study recently published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, a Yale-led research team developed a new method to track how Ae. aegypti move through the environment. ...
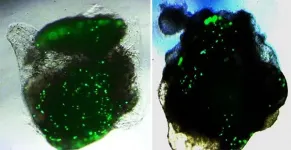
Live tracking and analyzing of the dynamics of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cells targeting cancer cells can open new avenues for the development of cancer immunotherapy. However, imaging via conventional microscopy approaches can result in cellular damage, and assessments of cell-to-cell interactions are extremely difficult and labor-intensive. When researchers applied deep learning and 3D holographic microscopy to the task, however, they not only avoided these difficultues but found that AI was better at it than humans were.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is helping researchers decipher images from a new holographic microscopy technique needed to investigate ...
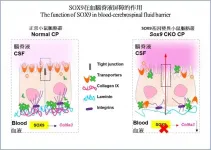
The finding, recently published in the prestigious scientific journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS), has provided the scientific community a novel understanding to the molecular regulatory mechanisms behind the function of the blood-CSF barrier and lays the groundwork for developing novel therapeutic strategies for preventing and treating neurodevelopmental disorders.
Dysfunction of blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier is common in various neurological diseases
CSF is a clear, colourless body fluid that surrounds the brain and spinal cord, providing them a cushion against injuries. It also ...
In Japan, the suppression of Christianity increased from the end of the 16th century to the beginning of the 17th century, and many missionaries and Japanese believers were martyred during this period. New research has uncovered a letter indicating that Hosokawa Tadaoki, lord of the Kokura domain from 1600 to 1620, ordered the execution of Diego Hayato Kagayama, a chief vassal of the Hosokawa family, and the banishment of Genya Ogasawara, both Christians. The punishment and martyrdom of both men was previously known only from reports by Jesuit missionaries to Rome. The discovery of primary historical documents created within the Hosokawa ...
Integrated photonics was rejuvenated as Si starting challenging the dominant position of conventional III-V compound semiconductors at onset of the new millennium. Heterogeneous Si photonics utilizes wafer bonding to transfer functioning non-Si thin film onto Si substrate to make up missing or weak optoelectronic functionalities of Si material. In the past 15 years, it has evolved into a broad technology with many branches as shown in Fig. 1. As the most mature one among them, heterogeneous III-V-on-silicon integration provides an ideal platform to marry their respective material and production advantages. Two veteran researchers in this field, Dr. Di Liang from Hewlett Packard Labs and Prof. ...